Cluster analysis of mass spectrometry data reveals a novel component of SAGA
- PMID: 15282323
- PMCID: PMC479721
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.16.7249-7259.2004
Cluster analysis of mass spectrometry data reveals a novel component of SAGA
Abstract
The SAGA histone acetyltransferase and TFIID complexes play key roles in eukaryotic transcription. Using hierarchical cluster analysis of mass spectrometry data to identify proteins that copurify with components of the budding yeast TFIID transcription complex, we discovered that an uncharacterized protein corresponding to the YPL047W open reading frame significantly associated with shared components of the TFIID and SAGA complexes. Using mass spectrometry and biochemical assays, we show that YPL047W (SGF11, 11-kDa SAGA-associated factor) is an integral subunit of SAGA. However, SGF11 does not appear to play a role in SAGA-mediated histone acetylation. DNA microarray analysis showed that SGF11 mediates transcription of a subset of SAGA-dependent genes, as well as SAGA-independent genes. SAGA purified from a sgf11 Delta deletion strain has reduced amounts of Ubp8p, and a ubp8 Delta deletion strain shows changes in transcription similar to those seen with the sgf11 Delta deletion strain. Together, these data show that Sgf11p is a novel component of the yeast SAGA complex and that SGF11 regulates transcription of a subset of SAGA-regulated genes. Our data suggest that the role of SGF11 in transcription is independent of SAGA's histone acetyltransferase activity but may involve Ubp8p recruitment to or stabilization in SAGA.
Figures

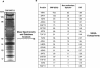



Similar articles
-
In-depth profiling of post-translational modifications on the related transcription factor complexes TFIID and SAGA.J Proteome Res. 2009 Nov;8(11):5020-30. doi: 10.1021/pr900449e. J Proteome Res. 2009. PMID: 19731963
-
Differential requirement of SAGA subunits for Mot1p and Taf1p recruitment in gene activation.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Jun;25(12):4863-72. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.12.4863-4872.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15923605 Free PMC article.
-
Adenovirus E1A requires the yeast SAGA histone acetyltransferase complex and associates with SAGA components Gcn5 and Tra1.Oncogene. 2002 Feb 21;21(9):1411-22. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205201. Oncogene. 2002. PMID: 11857084
-
SAGA and TFIID: Friends of TBP drifting apart.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2021 Feb;1864(2):194604. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2020.194604. Epub 2020 Jul 14. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2021. PMID: 32673655 Review.
-
SAGA unveiled.Trends Biochem Sci. 2005 Jan;30(1):7-10. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2004.11.007. Trends Biochem Sci. 2005. PMID: 15653319 Review.
Cited by
-
Activation of the ADE genes requires the chromatin remodeling complexes SAGA and SWI/SNF.Eukaryot Cell. 2007 Aug;6(8):1474-85. doi: 10.1128/EC.00068-07. Epub 2007 Jun 15. Eukaryot Cell. 2007. PMID: 17573544 Free PMC article.
-
Glaucomatous tissue stress and the regulation of immune response through glial Toll-like receptor signaling.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010 Nov;51(11):5697-707. doi: 10.1167/iovs.10-5407. Epub 2010 Jun 10. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010. PMID: 20538986 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial effect of microvesicles released from human neutrophilic granulocytes.Blood. 2013 Jan 17;121(3):510-8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-05-431114. Epub 2012 Nov 8. Blood. 2013. PMID: 23144171 Free PMC article.
-
The SAGA continues: expanding the cellular role of a transcriptional co-activator complex.Oncogene. 2007 Aug 13;26(37):5329-40. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210603. Oncogene. 2007. PMID: 17694076 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relative Abundance of Proteins in Blood Plasma Samples from Patients with Chronic Cerebral Ischemia.J Mol Neurosci. 2018 Mar;64(3):440-448. doi: 10.1007/s12031-018-1040-3. Epub 2018 Mar 5. J Mol Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29508191
References
-
- Balasubramanian, R., M. G. Pray-Grant, W. Selleck, P. A. Grant, and S. Tan. 2002. Role of the Ada2 and Ada3 transcriptional coactivators in histone acetylation. J. Biol. Chem. 277:7989-7995. - PubMed
-
- Chiang, Y. C., P. Komarnitsky, D. Chase, and C. L. Denis. 1996. ADR1 activation domains contact the histone acetyltransferase GCN5 and the core transcriptional factor TFIIB. J. Biol. Chem. 271:32359-32365. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CA098131/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 GM052461/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 1 P50 CA90949/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL068744/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA098131/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM052461/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA090949/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32-HL69765/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- GM64779/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL069765/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM064779/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM068900/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- ES11993/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS043952/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS43952/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- GM52461/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HL68744/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES011993/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
