Pulmonary collectins modulate strain-specific influenza a virus infection and host responses
- PMID: 15280465
- PMCID: PMC479098
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.78.16.8565-8572.2004
Pulmonary collectins modulate strain-specific influenza a virus infection and host responses
Abstract
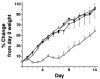
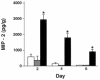
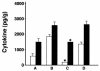
Collectins are secreted collagen-like lectins that bind, agglutinate, and neutralize influenza A virus (IAV) in vitro. Surfactant proteins A and D (SP-A and SP-D) are collectins expressed in the airway and alveolar epithelium and could have a role in the regulation of IAV infection in vivo. Previous studies have shown that binding of SP-D to IAV is dependent on the glycosylation of specific sites on the HA1 domain of hemagglutinin on the surface of IAV, while the binding of SP-A to the HA1 domain is dependent on the glycosylation of the carbohydrate recognition domain of SP-A. Here, using SP-A and SP-D gene-targeted mice on a common C57BL6 background, we report that viral replication and the host response as measured by weight loss, neutrophil influx into the lung, and local cytokine release are regulated by SP-D but not SP-A when the IAV is glycosylated at a specific site (N165) on the HA1 domain. SP-D does not protect against IAV infection with a strain lacking glycosylation at N165. With the exception of a small difference on day 2 after infection with X-79, we did not find any significant difference in viral load in SP-A(-/-) mice with either IAV strain, although small differences in the cytokine responses to IAV were detected in SP-A(-/-) mice. Mice deficient in both SP-A and SP-D responded to IAV similarly to mice deficient in SP-D alone. Since most strains of IAV currently circulating are glycosylated at N165, SP-D may play a role in protection from IAV infection.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Full-length human surfactant protein A inhibits influenza A virus infection of A549 lung epithelial cells: A recombinant form containing neck and lectin domains promotes infectivity.Immunobiology. 2019 May;224(3):408-418. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2019.02.006. Epub 2019 Feb 11. Immunobiology. 2019. PMID: 30954271
-
Porcine pulmonary collectins show distinct interactions with influenza A viruses: role of the N-linked oligosaccharides in the carbohydrate recognition domain.J Immunol. 2003 Aug 1;171(3):1431-40. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.3.1431. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12874235
-
Reduced influenza viral neutralizing activity of natural human trimers of surfactant protein D.Respir Res. 2007 Feb 5;8(1):9. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-8-9. Respir Res. 2007. PMID: 17280604 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary surfactant protein D in first-line innate defence against influenza A virus infections.J Innate Immun. 2013;5(3):197-208. doi: 10.1159/000346374. Epub 2013 Feb 5. J Innate Immun. 2013. PMID: 23391661 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Surfactant protein A and surfactant protein D variation in pulmonary disease.Immunobiology. 2007;212(4-5):381-416. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2007.01.003. Epub 2007 Feb 23. Immunobiology. 2007. PMID: 17544823 Review.
Cited by
-
Monoclonal antibody-assisted structure-function analysis of the carbohydrate recognition domain of surfactant protein D.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2010 Sep;299(3):L384-92. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00096.2010. Epub 2010 Jul 2. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20601494 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of a single N-linked glycan from the hemagglutinin of influenza virus is associated with resistance to collectins and increased virulence in mice.Respir Res. 2009 Nov 23;10(1):117. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-10-117. Respir Res. 2009. PMID: 19930664 Free PMC article.
-
Collectins and cationic antimicrobial peptides of the respiratory epithelia.Vet Pathol. 2006 Sep;43(5):595-612. doi: 10.1354/vp.43-5-595. Vet Pathol. 2006. PMID: 16966437 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Airway Surfactant Protein D Deficiency in Adults With Severe Asthma.Chest. 2016 May;149(5):1165-72. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2015.11.012. Epub 2016 Jan 13. Chest. 2016. PMID: 26836907 Free PMC article.
-
Intranasal Bifidobacterium longum protects against viral-induced lung inflammation and injury in a murine model of lethal influenza infection.EBioMedicine. 2020 Oct;60:102981. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102981. Epub 2020 Sep 11. EBioMedicine. 2020. PMID: 32927273 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beharka, A. A., C. D. Gaynor, B. K. Kang, D. R. Voelker, F. X. McCormack, and L. S. Schlesinger. 2002. Pulmonary surfactant protein A up-regulates activity of the mannose receptor, a pattern recognition receptor expressed on human macrophages. J. Immunol. 169:3565-3573. - PubMed
-
- Benne, C. A., B. Benaissa-Trouw, J. A. van Strijp, C. A. Kraaijeveld, and J. F. van Iwaarden. 1997. Surfactant protein A, but not surfactant protein D, is an opsonin for influenza A virus phagocytosis by rat alveolar macrophages. Eur. J. Immunol. 27:886-890. - PubMed
-
- Benne, C. A., C. A. Kraaijeveld, J. A. van Strijp, E. Brouwer, M. Harmsen, J. Verhoef, L. M. van Golde, and J. F. van Iwaarden. 1995. Interactions of surfactant protein A with influenza A viruses: binding and neutralization. J. Infect. Dis. 171:335-341. - PubMed
-
- Botas, C., F. Poulain, J. Akiyama, C. Brown, L. Allen, J. Goerke, J. Clements, E. Carlson, A. M. Gillespie, C. Epstein, and S. Hawgood. 1998. Altered surfactant homeostasis and alveolar type II cell morphology in mice lacking surfactant protein D. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95:11869-11874. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

