Herpes simplex virus type-1 induces IFN-alpha production via Toll-like receptor 9-dependent and -independent pathways
- PMID: 15272082
- PMCID: PMC509215
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0403555101
Herpes simplex virus type-1 induces IFN-alpha production via Toll-like receptor 9-dependent and -independent pathways
Abstract
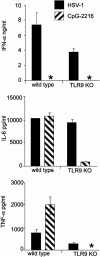
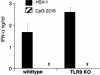
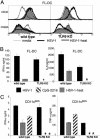
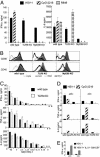
Type I IFN production in response to the DNA virus herpes simplex virus type-1 (HSV-1) is essential in controlling viral replication. We investigated whether plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDC) were the major tissue source of IFN-alpha, and whether the production of IFN-alpha in response to HSV-1 depended on Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9). Total spleen cells or bone marrow (BM) cells, or fractions thereof, including highly purified pDC, from WT, TLR9, and MyD88 knockout mice were stimulated with known ligands for TLR9 or active HSV-1. pDC freshly isolated from both spleen and BM were the major source of IFN-alpha in response to oligodeoxynucleotides containing CpG motifs, but in response to HSV-1 the majority of IFN-alpha was produced by other cell types. Moreover, IFN-alpha production by non-pDC was independent of TLR9. The tissue source determined whether pDC responded to HSV-1 in a strictly TLR9-dependent fashion. Freshly isolated BM pDC or pDC derived from culture of BM precursors with FMS-like tyrosine kinase-3 ligand, produced IFN-alpha in the absence of functional TLR9, whereas spleen pDC did not. Heat treatment of HSV-1 abolished maturation and IFN-alpha production from all TLR9-deficient DC but not WT DC. Thus pDC and non-pDC produce IFN-alpha in response to HSV-1 via both TLR9-independent and -dependent pathways.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Toll-like receptor 9-mediated recognition of Herpes simplex virus-2 by plasmacytoid dendritic cells.J Exp Med. 2003 Aug 4;198(3):513-20. doi: 10.1084/jem.20030162. J Exp Med. 2003. PMID: 12900525 Free PMC article.
-
IRF-7 is the master regulator of type-I interferon-dependent immune responses.Nature. 2005 Apr 7;434(7034):772-7. doi: 10.1038/nature03464. Epub 2005 Mar 30. Nature. 2005. PMID: 15800576
-
Spatiotemporal regulation of MyD88-IRF-7 signalling for robust type-I interferon induction.Nature. 2005 Apr 21;434(7036):1035-40. doi: 10.1038/nature03547. Epub 2005 Apr 6. Nature. 2005. PMID: 15815647
-
Plasmacytoid dendritic cell precursors/type I interferon-producing cells sense viral infection by Toll-like receptor (TLR) 7 and TLR9.Springer Semin Immunopathol. 2005 Jan;26(3):221-9. doi: 10.1007/s00281-004-0180-4. Epub 2004 Nov 13. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 2005. PMID: 15592841 Review.
-
Impact of Toll-Like Receptors (TLRs) and TLR Signaling Proteins in Trigeminal Ganglia Impairing Herpes Simplex Virus 1 (HSV-1) Progression to Encephalitis: Insights from Mouse Models.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2024 Mar 14;29(3):102. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2903102. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2024. PMID: 38538263 Review.
Cited by
-
A proteomics perspective on viral DNA sensors in host defense and viral immune evasion mechanisms.J Mol Biol. 2015 Jun 5;427(11):1995-2012. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2015.02.016. Epub 2015 Feb 26. J Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25728651 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human plasmacytoid dentritic cells elicit a Type I Interferon response by sensing DNA via the cGAS-STING signaling pathway.Eur J Immunol. 2016 Jul;46(7):1615-21. doi: 10.1002/eji.201546113. Epub 2016 May 27. Eur J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27125983 Free PMC article.
-
Innate immune response of human plasmacytoid dendritic cells to poxvirus infection is subverted by vaccinia E3 via its Z-DNA/RNA binding domain.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e36823. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036823. Epub 2012 May 14. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22606294 Free PMC article.
-
Mammalian DNA is an endogenous danger signal that stimulates local synthesis and release of complement factor B.Mol Med. 2012 Jul 18;18(1):851-60. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2012.00011. Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22526919 Free PMC article.
-
HSV-1/TLR9-Mediated IFNβ and TNFα Induction Is Mal-Dependent in Macrophages.J Innate Immun. 2020;12(5):387-398. doi: 10.1159/000504542. Epub 2019 Dec 18. J Innate Immun. 2020. PMID: 31851971 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wagner, H. (2001) Immunity 14, 499–502. - PubMed
-
- Akira, S. & Hemmi, H. (2003) Immunol. Lett. 85, 85–95. - PubMed
-
- Diebold, S. S., Kaisho, T., Hemmi, H., Akira, S. & Reis, E. S. C. (2004) Science 303, 1529–1531. - PubMed
-
- Heil, F., Hemmi, H., Hochrein, H., Ampenberger, F., Kirschning, C., Akira, S., Lipford, G., Wagner, H. & Bauer, S. (2004) Science 303, 1526–1529. - PubMed
-
- O'Neill, L. A., Fitzgerald, K. A. & Bowie, A. G. (2003) Trends Immunol. 24, 286–290. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

