4-1BB and OX40 stimulation enhance CD8 and CD4 T-cell responses to a DNA prime, poxvirus boost vaccine
- PMID: 15270726
- PMCID: PMC1782516
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2004.01917.x
4-1BB and OX40 stimulation enhance CD8 and CD4 T-cell responses to a DNA prime, poxvirus boost vaccine
Abstract
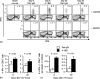
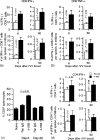
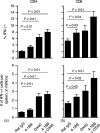
4-1BB (CD137) is a tumour necrosis factor receptor (TNFR) family member, expressed primarily on CD8 T cells after activation. Signalling through 4-1BB has been reported to enhance CD8 T-cell expansion and to protect activated CD8 T cells from death, resulting in an enlarged memory population. Although stimulating 4-1BB has been shown to significantly improve the immune response to weak immunogens such as tumours, little is known about its effect on the CD8 T-cell response to a powerful viral vector such as vaccinia. To test 4-1BB's ability to improve the murine CD8 T cell response to a DNA prime, poxvirus boost vaccine, similar to those used for human immunodeficiency virus and simian immunodeficiency virus vaccines, we administered 4-1BB agonist antibody at the time of the poxvirus boost. 4-1BB stimulation increased the number of functional memory CD8 T cells by two- to fourfold. However, we saw a similar enhancement at the peak of the response and in the memory phase, thus we found no evidence in the context of virus infection that 4-1BB stimulation could increase the percentage of CD8 T cells that survive the acute activation phase to become memory cells. OX40 (CD134) is an analogous TNFR family member expressed primarily on activated CD4 T cells. OX40 stimulation increased the number of antigen-specific CD4 T cells approximately threefold. Stimulating both 4-1BB and OX40 enhanced the CD8 T-cell response more than 4-1BB alone. Thus stimulating these receptors can improve the response to a powerful virus vector, and may be useful in vaccine development.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expression and costimulatory effects of the TNF receptor superfamily members CD134 (OX40) and CD137 (4-1BB), and their role in the generation of anti-tumor immune responses.Eur J Immunol. 2002 Dec;32(12):3617-27. doi: 10.1002/1521-4141(200212)32:12<3617::AID-IMMU3617>3.0.CO;2-M. Eur J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12516549
-
Anti-4-1BB monoclonal antibody enhances rejection of large tumor burden by promoting survival but not clonal expansion of tumor-specific CD8+ T cells.Cancer Res. 2002 Jun 15;62(12):3459-65. Cancer Res. 2002. PMID: 12067989
-
Anti-OX40 stimulation in vivo enhances CD8+ memory T cell survival and significantly increases recall responses.Eur J Immunol. 2007 Jan;37(1):157-66. doi: 10.1002/eji.200636428. Eur J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17183611
-
Co-stimulatory members of the TNFR family: keys to effective T-cell immunity?Nat Rev Immunol. 2003 Aug;3(8):609-20. doi: 10.1038/nri1148. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12974476 Review.
-
Role of 4-1BB in immune responses.Semin Immunol. 1998 Dec;10(6):481-9. doi: 10.1006/smim.1998.0157. Semin Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9826581 Review.
Cited by
-
Betting on improved cancer immunotherapy by doubling down on CD134 and CD137 co-stimulation.Oncoimmunology. 2013 Jan 1;2(1):e22837. doi: 10.4161/onci.22837. Oncoimmunology. 2013. PMID: 23482891 Free PMC article.
-
Manipulation of acute inflammatory lung disease.Mucosal Immunol. 2008 Jul;1(4):265-78. doi: 10.1038/mi.2008.16. Epub 2008 May 7. Mucosal Immunol. 2008. PMID: 19079188 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD137 costimulation enhances the antiviral activity of Vγ9Vδ2-T cells against influenza virus.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020 Jun 3;5(1):74. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-0174-2. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020. PMID: 32488072 Free PMC article.
-
Boosting Antitumor Response by Costimulatory Strategies Driven to 4-1BB and OX40 T-cell Receptors.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jun 30;9:692982. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.692982. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34277638 Free PMC article. Review.
-
OX40:OX40L axis: emerging targets for improving poxvirus-based CD8(+) T-cell vaccines against respiratory viruses.Immunol Rev. 2011 Nov;244(1):149-68. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2011.01062.x. Immunol Rev. 2011. PMID: 22017437 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hanke T, McMichael AJ, Mwau M, et al. Development of a DNA-MVA/HIVA vaccine for Kenya. Vaccine. 2002;20::1995–8. - PubMed
-
- Ahlers JD, Belyakov IM, Berzofsky JA. Cytokine, chemokine, and costimulatory molecule modulation to enhance efficacy of HIV vaccines. Curr Mol Med. 2003;3:285. - PubMed
-
- Hurtado JC, Kim YJ, Kwon BS. Signals through 4–1BB are costimulatory to previously activated splenic T cells and inhibit activation-induced cell death. J Immunol. 1997;158:2600. - PubMed
-
- Cannons JL, Lau P, Ghumman B, DeBenedette MA, Yagita H, Okumura K, Watts TH. 4-1BB ligand induces cell division, sustains survival, and enhances effector function of CD4 and CD8 T cells with similar efficacy. J Immunol. 2001;167:1313. - PubMed
-
- Gramaglia I, Weinberg AD, Lemon M, Croft M. Ox-40 ligand: a potent costimulatory molecule for sustaining primary CD4 T cell responses. J Immunol. 1998;161:6510. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
