Increased expression of the natural killer cell inhibitory receptor CD85j/ILT2 on antigen-specific effector CD8 T cells and its impact on CD8 T-cell function
- PMID: 15270723
- PMCID: PMC1782522
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2004.01907.x
Increased expression of the natural killer cell inhibitory receptor CD85j/ILT2 on antigen-specific effector CD8 T cells and its impact on CD8 T-cell function
Abstract
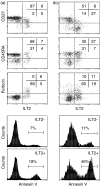
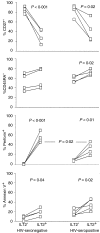
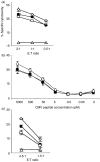
We investigated whether inhibitory natural killer cell receptor (iNKR) expression contributes to impaired antigen-specific cytotoxicity and interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) production by CD8 T cells during chronic infection. iNKR immunoglobulin-like transcript-2 (ILT2/CD85j) is expressed on 40-55% of cytomegalovirus (CMV)-, Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)- and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-specific CD8 T cells in both healthy and HIV-infected donors. Other iNKRs (CD158a, b1, e1/e2, k, CD94/NKG2A) are expressed on only a small minority of CD8 T cells and are not preferentially expressed on tetramer-staining virus-specific cells. In normal donors, ILT2 is expressed largely on perforin(+) CD27(-) effector cells. However, in HIV-infected donors, only a third of ILT2(+) cells are also perforin(+). In both normal and HIV-infected donors, ILT2(+) cells are prone to spontaneous apoptosis. Therefore, ILT2 is normally expressed during effector cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) differentiation, but can also be expressed when effector maturation is incomplete, as in HIV infection. The effect of ILT2 on CD8 cell function was assessed by preincubating effector cells with ILT2 antibody. While blocking ILT2 engagement has no appreciable effect on cytotoxicity, it increases antiviral IFN-gamma production by approximately threefold in both normal and HIV-infected donors. Thus, ILT2 expression, increased on antiviral CD8 cells in chronic infection, may interfere with protective CD8 T-cell function by suppressing IFN-gamma production.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
2B4 expression on natural killer cells increases in HIV-1 infected patients followed prospectively during highly active antiretroviral therapy.Clin Exp Immunol. 2005 Sep;141(3):526-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2005.02869.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16045743 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Specific CD8+ T Cell Responses with TIGIT Blockade Involves Trogocytosis.Pathogens. 2024 Dec 23;13(12):1137. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13121137. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 39770396 Free PMC article.
-
Far Posterior Approach for Rib Fracture Fixation: Surgical Technique and Tips.JBJS Essent Surg Tech. 2024 Dec 6;14(4):e23.00094. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.ST.23.00094. eCollection 2024 Oct-Dec. JBJS Essent Surg Tech. 2024. PMID: 39650795 Free PMC article.
-
Conservative, physical and surgical interventions for managing faecal incontinence and constipation in adults with central neurological diseases.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Oct 29;10(10):CD002115. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002115.pub6. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39470206
Cited by
-
LILRB1 polymorphisms influence posttransplant HCMV susceptibility and ligand interactions.J Clin Invest. 2018 Apr 2;128(4):1523-1537. doi: 10.1172/JCI96174. Epub 2018 Mar 12. J Clin Invest. 2018. PMID: 29528338 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor subfamily B: therapeutic targets in cancer.Antib Ther. 2021 Feb 9;4(1):16-33. doi: 10.1093/abt/tbab002. eCollection 2021 Jan. Antib Ther. 2021. PMID: 33928233 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of the inhibitory receptor leukocyte Ig-like receptor 1 on human natural killer cells.Front Immunol. 2011 Sep 20;2:46. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2011.00046. eCollection 2011. Front Immunol. 2011. PMID: 22566836 Free PMC article.
-
Human papillomavirus immunization is associated with increased expression of different innate immune regulatory receptors.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2012 Jul;19(7):1005-11. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00043-12. Epub 2012 May 9. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22573736 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic human infection with Trypanosoma cruzi drives CD4+ T cells to immune senescence.J Immunol. 2009 Sep 15;183(6):4103-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0900852. Epub 2009 Aug 19. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19692645 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lieberman J, Shankar P, Manjunath N, Andersson J. Dressed to kill? A review of why antiviral CD8 T lymphocytes fail to prevent progressive immunodeficiency in HIV-1 infection. Blood. 2001;98:1667–77. - PubMed
-
- McMichael AJ, Rowland-Jones SL. Cellular immune responses to HIV. Nature. 2001;410:980–7. - PubMed
-
- Lieberman J, Manjunath N, Shankar P. Avoiding the kiss of death: how HIV and other chronic viruses survive. Curr Opin Immunol. 2002;14:478–86. - PubMed
-
- Shankar P, Russo M, Harnisch B, Patterson M, Skolnik P, Lieberman J. Impaired function of circulating HIV-specific CD8(+) T cells in chronic human immunodeficiency virus infection. Blood. 2000;96:3094–101. - PubMed
-
- Gea-Banacloche JC, Migueles SA, Martino L, et al. Maintenance of large numbers of virus-specific CD8+ T cells in HIV-infected progressors and long-term nonprogressors. J Immunol. 2000;165:1082–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
