Telomere-associated protein TIN2 is essential for early embryonic development through a telomerase-independent pathway
- PMID: 15254230
- PMCID: PMC444850
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.15.6631-6634.2004
Telomere-associated protein TIN2 is essential for early embryonic development through a telomerase-independent pathway
Abstract
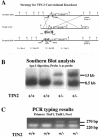
TIN2 is a negative regulator of telomere elongation that interacts with telomeric DNA repeat binding factor 1 (TRF1) and affects telomere length by a telomerase-dependent mechanism. Here we show that inactivation of the mouse TRF1-interacting protein 2 (TIN2) gene results in early embryonic lethality. We further observed that the embryonic lethality of TIN2 mutant mice was not affected by inactivation of the telomerase reverse transcriptase gene, indicating that embryonic lethality is not the result of telomerase-dependent changes in telomere length or function. Our findings suggest that TIN2 has a role independent of telomere length regulation that is essential for embryonic development and cell viability.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expression of telomeric repeat binding factor 1 and 2 and TRF1-interacting nuclear protein 2 in human gastric carcinomas.Int J Oncol. 2001 Sep;19(3):507-12. Int J Oncol. 2001. PMID: 11494028
-
TIN2 is a tankyrase 1 PARP modulator in the TRF1 telomere length control complex.Nat Genet. 2004 Jun;36(6):618-23. doi: 10.1038/ng1360. Epub 2004 May 9. Nat Genet. 2004. PMID: 15133513
-
POT1 as a terminal transducer of TRF1 telomere length control.Nature. 2003 Jun 26;423(6943):1013-8. doi: 10.1038/nature01688. Epub 2003 May 25. Nature. 2003. PMID: 12768206
-
Regulation of telomerase by telomeric proteins.Annu Rev Biochem. 2004;73:177-208. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.73.071403.160049. Annu Rev Biochem. 2004. PMID: 15189140 Review.
-
The levels of telomere-binding proteins in human tumours and therapeutic implications.Eur J Cancer. 2009 Mar;45(4):536-50. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2008.11.014. Epub 2008 Dec 27. Eur J Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19114299 Review.
Cited by
-
53BP1 deficiency combined with telomere dysfunction activates ATR-dependent DNA damage response.J Cell Biol. 2012 Apr 16;197(2):283-300. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201110124. J Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22508511 Free PMC article.
-
The role of telomere-binding modulators in pluripotent stem cells.Protein Cell. 2020 Jan;11(1):60-70. doi: 10.1007/s13238-019-0651-y. Epub 2019 Jul 27. Protein Cell. 2020. PMID: 31350723 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic p53 deficiency partially rescues the adrenocortical dysplasia phenotype at the expense of increased tumorigenesis.Cancer Cell. 2009 Jun 2;15(6):465-76. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2009.04.011. Cancer Cell. 2009. PMID: 19477426 Free PMC article.
-
TIN2 deficiency leads to ALT-associated phenotypes and differentiation defects in embryonic stem cells.Stem Cell Reports. 2022 May 10;17(5):1183-1197. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2022.03.005. Epub 2022 Apr 7. Stem Cell Reports. 2022. PMID: 35395177 Free PMC article.
-
Moderate expression of TRF2 in the hematopoietic system increases development of large cell blastic T-cell lymphomas.Aging (Albany NY). 2009 Jan;1(1):122-130. doi: 10.18632/aging.100015. Aging (Albany NY). 2009. PMID: 20046894 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baumann, P., and T. R. Cech. 2001. Pot1, the putative telomere end-binding protein in fission yeast and humans. Science 292:1171-1175. - PubMed
-
- Bonin, A., S. W. Reid, and L. Tessarollo. 2001. Gene knockouts: isolation, microinjection and transfer of mouse blastocysts. Methods Mol. Biol. 158:121-134. - PubMed
-
- Broccoli, D., L. Chong, S. Oelmann, A. A. Fernald, N. Marziliano, B. van Steensel, D. Kipling, M. M. Le Beau, and T. de Lange. 1997. Comparison of the human and mouse genes encoding the telomeric protein, TRF1: chromosomal localization, expression and conserved protein domains. Hum. Mol. Genet. 6:69-76. - PubMed
-
- Broccoli, D., A. Smogorzewska, L. Chong, and T. de Lange. 1997. Human telomeres contain two distinct Myb-related proteins, TRF1 and TRF2. Nat. Genet. 17:231-235. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
