A chromosomal memory triggered by Xist regulates histone methylation in X inactivation
- PMID: 15252442
- PMCID: PMC449785
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0020171
A chromosomal memory triggered by Xist regulates histone methylation in X inactivation
Abstract
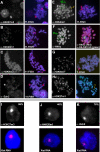
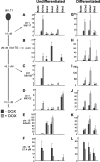
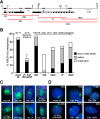
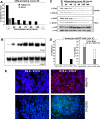
We have elucidated the kinetics of histone methylation during X inactivation using an inducible Xist expression system in mouse embryonic stem (ES) cells. Previous reports showed that the ability of Xist to trigger silencing is restricted to an early window in ES cell differentiation. Here we show that this window is also important for establishing methylation patterns on the potential inactive X chromosome. By immunofluorescence and chromatin immunoprecipitation experiments we show that histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27m3) and H4 lysine 20 monomethylation (H4K20m1) are associated with Xist expression in undifferentiated ES cells and mark the initiation of X inactivation. Both marks depend on Xist RNA localisation but are independent of silencing. Induction of Xist expression after the initiation window leads to a markedly reduced ability to induce H3K27m3, whereas expression before the restrictive time point allows efficient H3K27m3 establishment. Our data show that Xist expression early in ES cell differentiation establishes a chromosomal memory, which is maintained in the absence of silencing. One consequence of this memory is the ability to introduce H3K27m3 efficiently after the restrictive time point on the chromosome that has expressed Xist early. Our results suggest that this silencing-independent chromosomal memory has important implications for the maintenance of X inactivation, where previously self-perpetuating heterochromatin structures were viewed as the principal form of memory.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no conflicts of interest exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Methylation of histone H3 at Lys-9 is an early mark on the X chromosome during X inactivation.Cell. 2001 Dec 14;107(6):727-38. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00598-0. Cell. 2001. PMID: 11747809
-
Recruitment of PRC1 function at the initiation of X inactivation independent of PRC2 and silencing.EMBO J. 2006 Jul 12;25(13):3110-22. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601187. Epub 2006 Jun 8. EMBO J. 2006. PMID: 16763550 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin reprogramming of male somatic cell-derived XIST and TSIX in ES hybrid cells.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2002;99(1-4):106-14. doi: 10.1159/000071581. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2002. PMID: 12900552
-
X inactivation in mouse ES cells: histone modifications and FISH.Methods Enzymol. 2004;376:419-28. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(03)76028-5. Methods Enzymol. 2004. PMID: 14975322 Review. No abstract available.
-
X-chromosome inactivation and the search for chromosome-wide silencers.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2002 Apr;12(2):219-24. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(02)00289-7. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2002. PMID: 11893496 Review.
Cited by
-
trans-Acting Factors and cis Elements Involved in the Human Inactive X Chromosome Organization and Compaction.Genet Res (Camb). 2021 May 7;2021:6683460. doi: 10.1155/2021/6683460. eCollection 2021. Genet Res (Camb). 2021. PMID: 34035662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review of Rett syndrome (RTT) with induced pluripotent stem cells.Stem Cell Investig. 2016 Sep 28;3:52. doi: 10.21037/sci.2016.09.05. eCollection 2016. Stem Cell Investig. 2016. PMID: 27777941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Guided by RNAs: X-inactivation as a model for lncRNA function.J Mol Biol. 2013 Oct 9;425(19):3698-706. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2013.06.031. Epub 2013 Jun 28. J Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23816838 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Finding a balance: how diverse dosage compensation strategies modify histone h4 to regulate transcription.Genet Res Int. 2012;2012:795069. doi: 10.1155/2012/795069. Epub 2011 Oct 19. Genet Res Int. 2012. PMID: 22567401 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of sex determination and X-chromosome dosage compensation.Genetics. 2022 Feb 4;220(2):iyab197. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyab197. Genetics. 2022. PMID: 35100381 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Borsani G, Tonlorenzi R, Simmler MC, Dandolo L, Arnaud D, et al. Characterization of a murine gene expressed from the inactive X chromosome. Nature. 1991;351:325–329. - PubMed
-
- Brockdorff N. X-chromosome inactivation: Closing in on proteins that bind Xist RNA. Trends Genet. 2002;18:352–358. - PubMed
-
- Brockdorff N, Ashworth A, Kay GF, Cooper P, Smith S, et al. Conservation of position and exclusive expression of mouse Xist from the inactive X chromosome. Nature. 1991;351:329–331. - PubMed
-
- Brown CJ, Ballabio A, Rupert JL, Lafreniere RG, Grompe M, et al. A gene from the region of the human X inactivation centre is expressed exclusively from the inactive X chromosome. Nature. 1991;349:38–44. - PubMed
-
- Cao R, Wang L, Wang H, Xia L, Erdjument-Bromage H, et al. Role of histone H3 lysine 27 methylation in Polycomb-group silencing. Science. 2002;298:1039–1043. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

