ERK and p38 MAPK-activated protein kinases: a family of protein kinases with diverse biological functions
- PMID: 15187187
- PMCID: PMC419926
- DOI: 10.1128/MMBR.68.2.320-344.2004
ERK and p38 MAPK-activated protein kinases: a family of protein kinases with diverse biological functions
Abstract
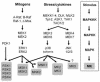
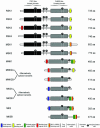
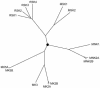
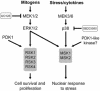
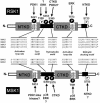
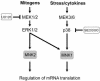
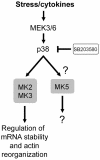
Conserved signaling pathways that activate the mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) are involved in relaying extracellular stimulations to intracellular responses. The MAPKs coordinately regulate cell proliferation, differentiation, motility, and survival, which are functions also known to be mediated by members of a growing family of MAPK-activated protein kinases (MKs; formerly known as MAPKAP kinases). The MKs are related serine/threonine kinases that respond to mitogenic and stress stimuli through proline-directed phosphorylation and activation of the kinase domain by extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 and p38 MAPKs. There are currently 11 vertebrate MKs in five subfamilies based on primary sequence homology: the ribosomal S6 kinases, the mitogen- and stress-activated kinases, the MAPK-interacting kinases, MAPK-activated protein kinases 2 and 3, and MK5. In the last 5 years, several MK substrates have been identified, which has helped tremendously to identify the biological role of the members of this family. Together with data from the study of MK-knockout mice, the identities of the MK substrates indicate that they play important roles in diverse biological processes, including mRNA translation, cell proliferation and survival, and the nuclear genomic response to mitogens and cellular stresses. In this article, we review the existing data on the MKs and discuss their physiological functions based on recent discoveries.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Activation and function of the MAPKs and their substrates, the MAPK-activated protein kinases.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2011 Mar;75(1):50-83. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00031-10. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21372320 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of RSK by UV-light: phosphorylation dynamics and involvement of the MAPK pathway.Oncogene. 2000 Aug 31;19(37):4221-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203712. Oncogene. 2000. PMID: 10980595
-
Identification of a docking groove on ERK and p38 MAP kinases that regulates the specificity of docking interactions.EMBO J. 2001 Feb 1;20(3):466-79. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.3.466. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11157753 Free PMC article.
-
Ribotoxic stress response to the trichothecene deoxynivalenol in the macrophage involves the SRC family kinase Hck.Toxicol Sci. 2005 Jun;85(2):916-26. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfi146. Epub 2005 Mar 16. Toxicol Sci. 2005. PMID: 15772366
-
In the cellular garden of forking paths: how p38 MAPKs signal for downstream assistance.Biol Chem. 2002 Oct;383(10):1519-36. doi: 10.1515/BC.2002.173. Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12452429 Review.
Cited by
-
Gemfibrozil pretreatment resulted in a sexually dimorphic outcome in the rat models of global cerebral ischemia-reperfusion via modulation of mitochondrial pro-survival and apoptotic cell death factors as well as MAPKs.J Mol Neurosci. 2013 Jul;50(3):379-93. doi: 10.1007/s12031-012-9932-0. Epub 2013 Jan 5. J Mol Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23288702
-
Identification of a receptor for extracellular renalase.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 23;10(4):e0122932. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0122932. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25906147 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleus-localized 21.5-kDa myelin basic protein promotes oligodendrocyte proliferation and enhances neurite outgrowth in coculture, unlike the plasma membrane-associated 18.5-kDa isoform.J Neurosci Res. 2013 Mar;91(3):349-62. doi: 10.1002/jnr.23166. Epub 2012 Nov 27. J Neurosci Res. 2013. PMID: 23184356 Free PMC article.
-
Presence of terminal EPIYA phosphorylation motifs in Helicobacter pylori CagA contributes to IL-8 secretion, irrespective of the number of repeats.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e56291. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056291. Epub 2013 Feb 7. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23409168 Free PMC article.
-
Acupuncture Activates ERK-CREB Pathway in Rats Exposed to Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:469765. doi: 10.1155/2013/469765. Epub 2013 Jun 17. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013. PMID: 23843874 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arthur, J. S., and P. Cohen. 2000. MSK1 is required for CREB phosphorylation in response to mitogens in mouse embryonic stem cells. FEBS Lett. 482:44-48. - PubMed
-
- Ballif, B. A., and J. Blenis. 2001. Molecular mechanisms mediating mammalian mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinase (MEK)-MAPK cell survival signals. Cell Growth Differ. 12:397-408. - PubMed
-
- Behn-Krappa, A., and A. C. Newton. 1999. The hydrophobic phosphorylation motif of conventional protein kinase C is regulated by autophosphorylation. Curr. Biol. 9:728-737. - PubMed
-
- Bellacosa, A., T. O. Chan, N. N. Ahmed, K. Datta, S. Malstrom, D. Stokoe, F. McCormick, J. Feng, and P. Tsichlis. 1998. Akt activation by growth factors is a multiple-step process: the role of the PH domain. Oncogene 17:313-325. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

