Nuclear receptor corepressor RIP140 regulates fat accumulation
- PMID: 15155905
- PMCID: PMC420412
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0401013101
Nuclear receptor corepressor RIP140 regulates fat accumulation
Abstract
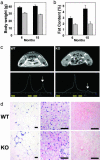
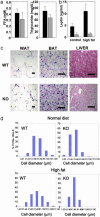
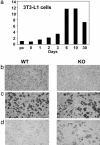
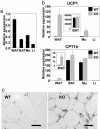
Nuclear receptors and their coactivators have been shown to function as key regulators of adipose tissue biology. Here we show that a ligand-dependent transcriptional repressor for nuclear receptors plays a crucial role in regulating the balance between energy storage and energy expenditure. Mice devoid of the corepressor protein RIP140 are lean, show resistance to high-fat diet-induced obesity and hepatic steatosis, and have increased oxygen consumption. Although the process of adipogenesis is unaffected, expression of certain lipogenic enzymes is reduced. In contrast, genes involved in energy dissipation and mitochondrial uncoupling, including uncoupling protein 1, are markedly increased. Therefore, the maintenance of energy homeostasis requires the action of a transcriptional repressor in white adipose tissue, and ligand-dependent recruitment of RIP140 to nuclear receptors may provide a therapeutic target in the treatment of obesity and related disorders.
Figures
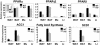
Similar articles
-
Metabolic regulation by the nuclear receptor corepressor RIP140.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2006 Aug;17(6):243-50. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2006.06.008. Epub 2006 Jul 11. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2006. PMID: 16815031 Review.
-
RIP140-targeted repression of gene expression in adipocytes.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Nov;25(21):9383-91. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.21.9383-9391.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16227589 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of oxidative metabolism and mitochondrial biogenesis by the transcriptional corepressor RIP140 in mouse adipocytes.J Clin Invest. 2006 Jan;116(1):125-36. doi: 10.1172/JCI26040. Epub 2005 Dec 22. J Clin Invest. 2006. PMID: 16374519 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the RIP140 corepressor in ovulation and adipose biology.J Endocrinol. 2005 Apr;185(1):1-9. doi: 10.1677/joe.1.05896. J Endocrinol. 2005. PMID: 15817822 Review.
-
RIP140 represses the "brown-in-white" adipocyte program including a futile cycle of triacylglycerol breakdown and synthesis.Mol Endocrinol. 2014 Mar;28(3):344-56. doi: 10.1210/me.2013-1254. Epub 2014 Jan 30. Mol Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 24479876 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Transcriptional and epigenetic control of brown and beige adipose cell fate and function.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016 Aug;17(8):480-95. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2016.62. Epub 2016 Jun 2. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27251423 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cold-inducible Zfp516 activates UCP1 transcription to promote browning of white fat and development of brown fat.Mol Cell. 2015 Jan 22;57(2):235-46. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.12.005. Epub 2015 Jan 8. Mol Cell. 2015. PMID: 25578880 Free PMC article.
-
PPARγ agonists induce a white-to-brown fat conversion through stabilization of PRDM16 protein.Cell Metab. 2012 Mar 7;15(3):395-404. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2012.01.019. Cell Metab. 2012. PMID: 22405074 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of strong candidate genes for backfat and intramuscular fatty acid composition in three crosses based on the Iberian pig.Sci Rep. 2020 Aug 18;10(1):13962. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-70894-2. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32811870 Free PMC article.
-
Ectopic brown adipose tissue in muscle provides a mechanism for differences in risk of metabolic syndrome in mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Feb 13;104(7):2366-71. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0610416104. Epub 2007 Feb 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17283342 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Spiegelman, B. M. & Flier, J. S. (2001) Cell 104, 531-543. - PubMed
-
- Ahima, R. S. & Flier, J. S. (2000) Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 11, 327-332. - PubMed
-
- Rajala, M. W. & Scherer, P. E. (2003) Endocrinology 144, 3765-3773. - PubMed
-
- Lowell, B. B. & Spiegelman, B. M. (2000) Nature 404, 652-660. - PubMed
-
- Francis, G. A., Fayard, E., Picard, F. & Auwerx, J. (2003) Annu. Rev. Physiol. 65, 261-311. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

