Enhanced osteoclast development in collagen-induced arthritis in interferon-gamma receptor knock-out mice as related to increased splenic CD11b+ myelopoiesis
- PMID: 15142268
- PMCID: PMC416444
- DOI: 10.1186/ar1167
Enhanced osteoclast development in collagen-induced arthritis in interferon-gamma receptor knock-out mice as related to increased splenic CD11b+ myelopoiesis
Abstract
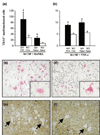
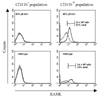
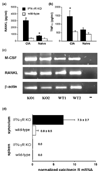
Collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) in mice is accompanied by splenomegaly due to the selective expansion of immature CD11b+ myeloblasts. Both disease manifestations are more pronounced in interferon-gamma receptor knock-out (IFN-gammaR KO) mice. We have taken advantage of this difference to test the hypothesis that the expanding CD11b+ splenic cell population constitutes a source from which osteoclast precursors are recruited to the joint synovia. We found larger numbers of osteoclasts and more severe bone destruction in joints of IFN-gammaR KO mice than in joints of wild-type mice. Osteoclast-like multinucleated cells appeared in splenocyte cultures established in the presence of macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) and stimulated with the osteoclast-differentiating factor receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand (RANKL) or with tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha). Significantly larger numbers of such cells could be generated from splenocytes of IFN-gammaR KO mice than from those of wild-type mice. This was not accompanied, as might have been expected, by increased concentrations of the intracellular adaptor protein TRAF6, known to be involved in signalling of RANKL- and TNF-alpha-induced osteoclast formation. Splenocyte cultures of IFN-gammaR KO mice also produced more TNF-alpha and more RANKL than those of wild-type mice. Finally, splenocytes isolated from immunised IFN-gammaR KO mice contained comparatively low levels of pro-interleukin-1beta (pro-IL-1beta) and pro-caspase-1, indicating more extensive conversion of pro-IL-1beta into secreted active IL-1beta. These observations provide evidence that all conditions are fulfilled for the expanding CD11b+ splenocytes to act as a source of osteoclasts and to be indirectly responsible for bone destruction in CIA. They also provide a plausible explanation for the higher susceptibility of IFN-gammaR KO mice to CIA.
Figures
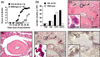

Similar articles
-
Freund's complete adjuvant induces arthritis in mice lacking a functional interferon-gamma receptor by triggering tumor necrosis factor alpha-driven osteoclastogenesis.Arthritis Rheum. 2007 Aug;56(8):2595-607. doi: 10.1002/art.22791. Arthritis Rheum. 2007. PMID: 17665444
-
Interleukin (IL) 18 stimulates osteoclast formation through synovial T cells in rheumatoid arthritis: comparison with IL1 beta and tumour necrosis factor alpha.Ann Rheum Dis. 2004 Nov;63(11):1379-86. doi: 10.1136/ard.2003.018481. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004. PMID: 15479886 Free PMC article.
-
RANK signaling is not required for TNFalpha-mediated increase in CD11(hi) osteoclast precursors but is essential for mature osteoclast formation in TNFalpha-mediated inflammatory arthritis.J Bone Miner Res. 2004 Feb;19(2):207-13. doi: 10.1359/JBMR.0301233. J Bone Miner Res. 2004. PMID: 14969390
-
[Bone and bone related biochemical examinations. Bone and collagen related metabolites. Regulatory mechanisms of osteoclast differentiation and function].Clin Calcium. 2006 Jun;16(6):940-47. Clin Calcium. 2006. PMID: 16751689 Review. Japanese.
-
A new member of tumor necrosis factor ligand family, ODF/OPGL/TRANCE/RANKL, regulates osteoclast differentiation and function.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999 Mar 24;256(3):449-55. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1999.0252. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999. PMID: 10080918 Review.
Cited by
-
Effector mechanisms of interleukin-17 in collagen-induced arthritis in the absence of interferon-gamma and counteraction by interferon-gamma.Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11(4):R122. doi: 10.1186/ar2787. Epub 2009 Aug 17. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009. PMID: 19686583 Free PMC article.
-
Parasitic helminths: new weapons against immunological disorders.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010;2010:743758. doi: 10.1155/2010/743758. Epub 2010 Feb 10. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20169100 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interferon-gamma targets cancer cells and osteoclasts to prevent tumor-associated bone loss and bone metastases.J Biol Chem. 2009 Feb 13;284(7):4658-66. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M804812200. Epub 2008 Dec 5. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19059914 Free PMC article.
-
Parasitic infection as a potential therapeutic tool against rheumatoid arthritis.Exp Ther Med. 2016 Oct;12(4):2359-2366. doi: 10.3892/etm.2016.3660. Epub 2016 Sep 5. Exp Ther Med. 2016. PMID: 27698735 Free PMC article.
-
Defective CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cell functioning in collagen-induced arthritis: an important factor in pathogenesis, counter-regulated by endogenous IFN-gamma.Arthritis Res Ther. 2005;7(2):R402-15. doi: 10.1186/ar1500. Epub 2005 Jan 28. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005. PMID: 15743488 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Manoury-Schwartz B, Chiocchia G, Bessis N, Abehsira-Amar O, Batteux F, Muller S, Huang S, Boissier M-C, Fournier C. High susceptibility to collagen-induced arthritis in mice lacking IFN-γ receptors. J Immunol. 1997;158:5501–5506. - PubMed
-
- Vermeire K, Heremans H, Vandeputte M, Huang J, Billiau A, Matthys P. Accelerated collagen-induced arthritis in interferon-γ receptor-deficient mice. J Immunol. 1997;158:5507–5513. - PubMed
-
- Matthys P, Vermeire K, Mitera T, Heremans H, Huang J, Schols D, Dewolf-Peeters C, Billiau A. Enhanced autoimmune arthritis in IFN-γ receptor-deficient mice is conditioned by mycobacteria in Freund's adjuvant and by increased expansion of Mac-1+ myeloid cells. J Immunol. 1999;163:3503–3510. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

