Essential role of GATA-4 in cell survival and drug-induced cardiotoxicity
- PMID: 15100413
- PMCID: PMC406451
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0401833101
Essential role of GATA-4 in cell survival and drug-induced cardiotoxicity
Abstract
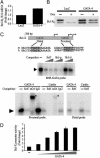
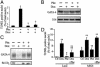
In recent years, significant progress has been made in understanding cardiomyocyte differentiation. However, little is known about the regulation of myocyte survival despite the fact that myocyte apoptosis is a leading cause of heart failure. Here we report that transcription factor GATA-4 is a survival factor for differentiated, postnatal cardiomyocytes and an upstream activator of the antiapoptotic gene Bcl-X. An early event in the cardiotoxic effect of the antitumor drug doxorubicin is GATA-4 depletion, which in turn causes cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Mouse heterozygotes for a null Gata4 allele have enhanced susceptibility to doxorubicin cardiotoxicity. Genetic or pharmacologic enhancement of GATA-4 prevents cardiomyocyte apoptosis and drug-induced cardiotoxicity. The results indicate that GATA-4 is an antiapoptotic factor required for the adaptive stress response of the adult heart. Modulation of survival/apoptosis genes by tissue-specific transcription factors may be a general paradigm that can be exploited effectively for cell-specific regulation of apoptosis in disease states.
Figures
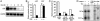



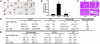
Similar articles
-
Peritoneal dialysate effluent during peritonitis induces human cardiomyocyte apoptosis by regulating the expression of GATA-4 and Bcl-2 families.J Cell Physiol. 2011 Jan;226(1):94-102. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22309. J Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 20625998
-
Regulation of cardiac myocyte apoptosis by the GATA-4 transcription factor.Life Sci. 2004 Feb 27;74(15):1829-38. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2003.10.002. Life Sci. 2004. PMID: 14761664 Review.
-
Transcription factor gata4 regulates cardiac BCL2 gene expression in vitro and in vivo.FASEB J. 2006 Apr;20(6):800-2. doi: 10.1096/fj.05-5426fje. Epub 2006 Feb 9. FASEB J. 2006. PMID: 16469847
-
MicroRNA-208a Silencing Attenuates Doxorubicin Induced Myocyte Apoptosis and Cardiac Dysfunction.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015;2015:597032. doi: 10.1155/2015/597032. Epub 2015 Jun 7. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015. PMID: 26137188 Free PMC article.
-
GATA transcription factors in the developing and adult heart.Cardiovasc Res. 2004 Aug 1;63(2):196-207. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2004.03.025. Cardiovasc Res. 2004. PMID: 15249177 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel exons in the tbx5 gene locus generate protein isoforms with distinct expression domains and function.J Biol Chem. 2015 Mar 13;290(11):6844-56. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.634451. Epub 2015 Jan 25. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25623069 Free PMC article.
-
Formation of mitochondrial-derived vesicles is an active and physiologically relevant mitochondrial quality control process in the cardiac system.J Physiol. 2016 Sep 15;594(18):5343-62. doi: 10.1113/JP272703. Epub 2016 Jul 24. J Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27311616 Free PMC article.
-
Paracrine factors released by GATA-4 overexpressed mesenchymal stem cells increase angiogenesis and cell survival.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010 Dec;299(6):H1772-81. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00557.2010. Epub 2010 Sep 24. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20870802 Free PMC article.
-
Convergence of protein kinase C and JAK-STAT signaling on transcription factor GATA-4.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Nov;25(22):9829-44. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.22.9829-9844.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16260600 Free PMC article.
-
Deacetylase-independent function of SIRT6 couples GATA4 transcription factor and epigenetic activation against cardiomyocyte apoptosis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 May 21;48(9):4992-5005. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa214. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32239217 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

