The transcriptional response to Raf activation is almost completely dependent on Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase Kinase activity and shows a major autocrine component
- PMID: 15090615
- PMCID: PMC452596
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e03-11-0807
The transcriptional response to Raf activation is almost completely dependent on Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase Kinase activity and shows a major autocrine component
Abstract
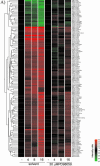
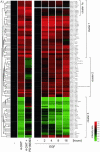
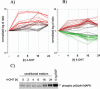
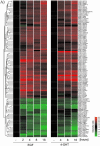
The Raf protein kinases are major effectors of Ras GTPases and key components of the transcriptional response to serum factors, acting at least in part through the extracellular signal-regulated kinase/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. It has recently been suggested that Raf also may trigger other as yet uncharacterized signaling pathways. Here, we have used cDNA microarrays to dissect changes in gene expression induced by activation of inducible c-Raf-1 constructs in human mammary epithelial and ovarian epithelial cells. The majority of Raf-induced transcriptional responses are shown to be blocked by pharmacological inhibition of the Raf substrate mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase, indicating that potential mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase-independent Raf signaling pathways have no significant influence on gene expression. In addition, we used epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitory drugs to address the contribution of autocrine signaling by Raf-induced EGF family proteins to the Raf transcriptional response. At least one-half of the transcription induced by Raf activation requires epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor function The EGF receptor-independent component of the Raf transcriptional response is entirely up-regulation of gene expression, whereas the EGF receptor-dependent component is an equal mixture of up- and down-regulation. The use of transcriptional profiling in this way allows detailed analysis of the architecture of signaling pathways to be undertaken.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Induction of beta3-integrin gene expression by sustained activation of the Ras-regulated Raf-MEK-extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathway.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 May;21(9):3192-205. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.9.3192-3205.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11287623 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the transcriptional program induced by Raf in epithelial cells.Genes Dev. 2001 Apr 15;15(8):981-94. doi: 10.1101/gad.191101. Genes Dev. 2001. PMID: 11316792 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor activates the ETS1 transcription factor by a RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK signaling pathway.Oncogene. 2002 Apr 4;21(15):2309-19. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205297. Oncogene. 2002. PMID: 11948414
-
Differential dose-dependent effects of epidermal growth factor on gene expression in A431 cells: evidence for a signal transduction pathway that can bypass Raf-1 activation.Endocrinology. 1998 May;139(5):2382-91. doi: 10.1210/endo.139.5.5981. Endocrinology. 1998. PMID: 9564849
-
Second nature: biological functions of the Raf-1 "kinase".FEBS Lett. 2005 Jun 13;579(15):3271-7. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2005.03.024. Epub 2005 Mar 23. FEBS Lett. 2005. PMID: 15943972 Review.
Cited by
-
Ultrasonic bioreactor as a platform for studying cellular response.Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2013 Mar;19(3):244-55. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEC.2012.0199. Epub 2012 Sep 24. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2013. PMID: 22873765 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic control and resistance of the EGFR-driven signaling network in glioblastoma.Cell Commun Signal. 2015 Mar 31;13:23. doi: 10.1186/s12964-015-0098-6. Cell Commun Signal. 2015. PMID: 25885672 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mapping the molecular determinants of BRAF oncogene dependence in human lung cancer.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Feb 18;111(7):E748-57. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1320956111. Epub 2014 Feb 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24550319 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling in cell differentiation and morphogenesis.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2012 Jun 1;4(6):a008151. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a008151. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2012. PMID: 22570373 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases.Cell. 2010 Jun 25;141(7):1117-34. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.06.011. Cell. 2010. PMID: 20602996 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alessi, D.R., Cuenda, A., Cohen, P., Dudley, D.T., and Saltiel, A.R. (1995). PD 098059 is a specific inhibitor of the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase in vitro and in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 27489-27494. - PubMed
-
- Bonni, A., Brunet, A., West, A.E., Datta, S.R., Takasu, M.A., and Greenberg, M.E. (1999). Cell survival promoted by the Ras-MAPK signaling pathway by transcription-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Science 286, 1358-1362. - PubMed
-
- Bos, J.L. (1989). ras oncogenes in human cancer: a review. Cancer Res. 49, 4682-4689. - PubMed
-
- Bosch, E., Cherwinski, H., Peterson, D., and McMahon, M. (1997). Mutations of critical amino acids affect the biological and biochemical properties of oncogenic A-Raf and Raf-1. Oncogene 15, 1021-1033. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

