Aligning multiple genomic sequences with the threaded blockset aligner
- PMID: 15060014
- PMCID: PMC383317
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.1933104
Aligning multiple genomic sequences with the threaded blockset aligner
Abstract
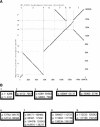
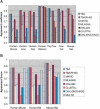
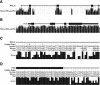
We define a "threaded blockset," which is a novel generalization of the classic notion of a multiple alignment. A new computer program called TBA (for "threaded blockset aligner") builds a threaded blockset under the assumption that all matching segments occur in the same order and orientation in the given sequences; inversions and duplications are not addressed. TBA is designed to be appropriate for aligning many, but by no means all, megabase-sized regions of multiple mammalian genomes. The output of TBA can be projected onto any genome chosen as a reference, thus guaranteeing that different projections present consistent predictions of which genomic positions are orthologous. This capability is illustrated using a new visualization tool to view TBA-generated alignments of vertebrate Hox clusters from both the mammalian and fish perspectives. Experimental evaluation of alignment quality, using a program that simulates evolutionary change in genomic sequences, indicates that TBA is more accurate than earlier programs. To perform the dynamic-programming alignment step, TBA runs a stand-alone program called MULTIZ, which can be used to align highly rearranged or incompletely sequenced genomes. We describe our use of MULTIZ to produce the whole-genome multiple alignments at the Santa Cruz Genome Browser.
Figures



Similar articles
-
MAVID: constrained ancestral alignment of multiple sequences.Genome Res. 2004 Apr;14(4):693-9. doi: 10.1101/gr.1960404. Genome Res. 2004. PMID: 15060012 Free PMC article.
-
How accurately is ncRNA aligned within whole-genome multiple alignments?BMC Bioinformatics. 2007 Oct 26;8:417. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-417. BMC Bioinformatics. 2007. PMID: 17963514 Free PMC article.
-
GS-Aligner: a novel tool for aligning genomic sequences using bit-level operations.Mol Biol Evol. 2003 Aug;20(8):1299-309. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msg139. Epub 2003 May 30. Mol Biol Evol. 2003. PMID: 12777500
-
Computation and analysis of genomic multi-sequence alignments.Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2007;8:193-213. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genom.8.080706.092300. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2007. PMID: 17489682 Review.
-
Recent developments and future directions in computational genomics.FEBS Lett. 2000 Aug 25;480(1):42-8. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(00)01776-2. FEBS Lett. 2000. PMID: 10967327 Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery of novel microRNA mimic repressors of ribosome biogenesis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Feb 28;52(4):1988-2011. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad1235. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38197221 Free PMC article.
-
RhesusBase: a knowledgebase for the monkey research community.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Jan;41(Database issue):D892-905. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks835. Epub 2012 Sep 10. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 22965133 Free PMC article.
-
Overcoming NS1-mediated immune antagonism involves both interferon-dependent and independent mechanisms.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2013 Nov;33(11):700-8. doi: 10.1089/jir.2012.0113. Epub 2013 Jun 17. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2013. PMID: 23772952 Free PMC article.
-
YOC, A new strategy for pairwise alignment of collinear genomes.BMC Bioinformatics. 2015 Apr 2;16(1):111. doi: 10.1186/s12859-015-0530-3. BMC Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 25885358 Free PMC article.
-
Elephant Genomes Reveal Accelerated Evolution in Mechanisms Underlying Disease Defenses.Mol Biol Evol. 2021 Aug 23;38(9):3606-3620. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msab127. Mol Biol Evol. 2021. PMID: 33944920 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aparicio, S., Chapman, J., Stupka, E., Putnam, N., Chia, J.M., Dehal, P., Christoffels, A., Rash, S., Hoon, S., Smit, A., et al. 2002. Whole-genome shotgun assembly and analysis of the genome of Fugu rubripes. Science 297: 1301-1310. - PubMed
-
- Brudno, M. and Morgenstern, B. 2002. Fast and sensitive alignment of large genomic sequences. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Bioinformatics Conference, pp. 138-150. IEEE Press. - PubMed
-
- Collins, F.S., Green, E.D., Guttmacher, A.E., and Guyer, M.S. 2003. A vision for the future of genomics research. Nature 422: 835-847. - PubMed
WEB SITE REFERENCES
-
- http://bio.cse.psu.edu/; TBA, simulated test data, and the Gmaj visualization tool.
-
- http://genome.ucsc.edu; MULTIZ and HUMOR alignments.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
