Immunophilins and parvulins. Superfamily of peptidyl prolyl isomerases in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 15047905
- PMCID: PMC419802
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.103.031005
Immunophilins and parvulins. Superfamily of peptidyl prolyl isomerases in Arabidopsis
Abstract
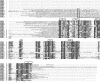
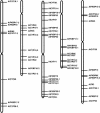
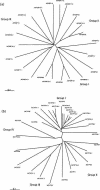
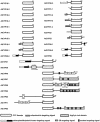
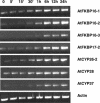
Immunophilins are defined as receptors for immunosuppressive drugs including cyclosporin A, FK506, and rapamycin. The cyclosporin A receptors are referred to as cyclophilins (CYPs) and FK506- and rapamycin-binding proteins are abbreviated as FKBPs. These two groups of proteins (collectively called immunophilins) share little sequence homology, but both have peptidyl prolyl cis/trans isomerase (PPIase) activity that is involved in protein folding processes. Studies have identified immunophilins in all organisms examined including bacteria, fungi, animals, and plants. Nevertheless, the physiological function of immunophilins is poorly understood in any organism. In this study, we have surveyed the genes encoding immunophilins in Arabidopsis genome. A total of 52 genes have been found to encode putative immunophilins, among which 23 are putative FKBPs and 29 are putative CYPs. This is by far the largest immunophilin family identified in any organism. Both FKBPs and CYPs can be classified into single domain and multiple domain members. The single domain members contain a basic catalytic domain and some of them have signal sequences for targeting to a specific organelle. The multiple domain members contain not only the catalytic domain but also defined modules that are involved in protein-protein interaction or other functions. A striking feature of immunophilins in Arabidopsis is that a large fraction of FKBPs and CYPs are localized in the chloroplast, a possible explanation for why plants have a larger immunophilin family than animals. Parvulins represent another family of PPIases that are unrelated to immunophilins in protein sequences and drug binding properties. Three parvulin genes were found in Arabidopsis genome. The expression of many immunophilin and parvulin genes is ubiquitous except for those encoding chloroplast members that are often detected only in the green tissues. The large number of genes and diversity of structure domains and cellular localization make PPIases a versatile superfamily of proteins that clearly function in many cellular processes in plants.
Figures




Comment in
-
Introducing immunophilins. From organ transplantation to plant biology.Plant Physiol. 2004 Apr;134(4):1241-3. doi: 10.1104/pp.103.900108. Plant Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15084722 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Immunophilin AtFKBP13 sustains all peptidyl-prolyl isomerase activity in the thylakoid lumen from Arabidopsis thaliana deficient in AtCYP20-2.Biochemistry. 2007 Aug 21;46(33):9432-42. doi: 10.1021/bi700426q. Epub 2007 Jul 27. Biochemistry. 2007. PMID: 17655280
-
Peptidylprolyl cis/trans isomerases (immunophilins): biological diversity--targets--functions.Curr Top Med Chem. 2003;3(12):1315-47. doi: 10.2174/1568026033451862. Curr Top Med Chem. 2003. PMID: 12871165 Review.
-
Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerases, a superfamily of ubiquitous folding catalysts.Cell Mol Life Sci. 1999 Mar;55(3):423-36. doi: 10.1007/s000180050299. Cell Mol Life Sci. 1999. PMID: 10228556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Classification of rice (Oryza sativa L. Japonica nipponbare) immunophilins (FKBPs, CYPs) and expression patterns under water stress.BMC Plant Biol. 2010 Nov 18;10:253. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-10-253. BMC Plant Biol. 2010. PMID: 21087465 Free PMC article.
-
Peptidyl-prolyl isomerase activity in chloroplast thylakoid lumen is a dispensable function of immunophilins in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant Cell Physiol. 2009 Oct;50(10):1801-14. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcp122. Epub 2009 Aug 28. Plant Cell Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19717822
Cited by
-
A redox-active FKBP-type immunophilin functions in accumulation of the photosystem II supercomplex in Arabidopsis thaliana.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Aug 15;103(33):12631-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0605452103. Epub 2006 Aug 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16894144 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclophilin nomenclature problems, or, 'a visit from the sequence police'.Hum Genomics. 2004 Aug;1(5):381-8. doi: 10.1186/1479-7364-1-5-381. Hum Genomics. 2004. PMID: 15588499 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AtFKBP16-1, a chloroplast lumenal immunophilin, mediates response to photosynthetic stress by regulating PsaL stability.Physiol Plant. 2014 Apr;150(4):620-31. doi: 10.1111/ppl.12116. Epub 2013 Oct 30. Physiol Plant. 2014. PMID: 24124981 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association analysis reveals a novel pathway mediated by a dual-TIR domain protein for pathogen resistance in cotton.Genome Biol. 2023 May 10;24(1):111. doi: 10.1186/s13059-023-02950-9. Genome Biol. 2023. PMID: 37165460 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of PvPin1, a Bamboo Homolog of PIN1-Type Parvulin 1, Delays Flowering Time in Transgenic Arabidopsis and Rice.Front Plant Sci. 2017 Sep 8;8:1526. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01526. eCollection 2017. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 28951734 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abraham RT (1998) Mammalian target of rapamycin: immunosuppressive drugs uncover a novel pathway of cytokine receptor signaling. Curr Opin Immunol 10: 330–336 - PubMed
-
- Aldape RA, Futer O, DeCenzo MT, Jarrett BP, Murcko MA, Livingston DJ (1992) Charged surface residues of FKBP12 participate in formation of the FKBP12-FK506-calcineurin complex. J Biol Chem 267: 16029–16032 - PubMed
-
- Arpagaus S, Rawyler A, Braendle R (2002) Occurrence and characteristics of the mitochondrial permeability transition in plants. J Biol Chem 277: 1780–1787 - PubMed
-
- Azevedo C, Santos-Rosa MJ, Shirasu K (2001) The U-box protein family in plants. Trends Plant Sci 6: 354–358 - PubMed
-
- Bang H, Pecht A, Raddatz G, Scior T, Solbach W, Brune K, Pahl A (2000) Prolyl isomerases in a minimal cell. Catalysis of protein folding by trigger factor from Mycoplasma genitalium. Eur J Biochem 267: 3270–3280 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

