Angiotensin II-induced ERK1/ERK2 activation and protein synthesis are redox-dependent in glomerular mesangial cells
- PMID: 15027896
- PMCID: PMC1133781
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20031614
Angiotensin II-induced ERK1/ERK2 activation and protein synthesis are redox-dependent in glomerular mesangial cells
Abstract
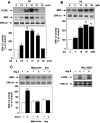
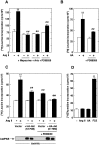
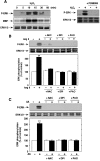
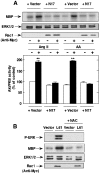
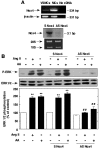
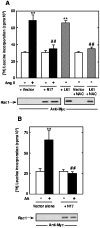
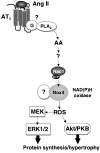
Angiotensin II (Ang II) stimulates hypertrophy of glomerular mesangial cells. The signalling mechanism by which Ang II exerts this effect is not precisely known. Downstream potential targets of Ang II are the extracellular-signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 (ERK1/ERK2). We demonstrate that Ang II activates ERK1/ERK2 via the AT1 receptor. Arachidonic acid (AA) mimics the action of Ang II on ERK1/ERK2 and phospholipase A2 inhibitors blocked Ang II-induced ERK1/ERK2 activation. The antioxidant N-acetylcysteine as well as the NAD(P)H oxidase inhibitors diphenylene iodonium and phenylarsine oxide abolished both Ang II- and AA-induced ERK1/ERK2 activation. Moreover, dominant-negative Rac1 (N17Rac1) blocks activation of ERK1/ERK2 in response to Ang II and AA, whereas constitutively active Rac1 resulted in an increase in ERK1/ERK2 activity. Antisense oligonucleotides for Nox4 NAD(P)H oxidase significantly reduce activation of ERK1/ERK2 by Ang II and AA. We also show that protein synthesis in response to Ang II and AA is inhibited by N17Rac1 or MEK (mitogen-activated protein kinase/ERK kinase) inhibitor. These results demonstrate that Ang II stimulates ERK1/ERK2 by AA and Nox4-derived reactive oxygen species, suggesting that these molecules act as downstream signal transducers of Ang II in the signalling pathway linking the Ang II receptor AT1 to ERK1/ERK2 activation. This pathway involving AA, Rac1, Nox4, reactive oxygen species and ERK1/ERK2 may play an important role in Ang II-induced mesangial cell hypertrophy.
Figures
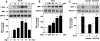
Similar articles
-
Nox4 mediates angiotensin II-induced activation of Akt/protein kinase B in mesangial cells.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2003 Aug;285(2):F219-29. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00414.2002. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12842860
-
Redox-dependent MAP kinase signaling by Ang II in vascular smooth muscle cells: role of receptor tyrosine kinase transactivation.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2003 Feb;81(2):159-67. doi: 10.1139/y02-164. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12710530
-
Angiotensin II activates Akt/protein kinase B by an arachidonic acid/redox-dependent pathway and independent of phosphoinositide 3-kinase.FASEB J. 2001 Sep;15(11):1909-20. doi: 10.1096/fj..01-0165com. FASEB J. 2001. PMID: 11532971
-
Recent advances in angiotensin II signaling.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2002 Sep;35(9):1001-15. doi: 10.1590/s0100-879x2002000900001. Epub 2002 Aug 30. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2002. PMID: 12219172 Review.
-
Angiotensin II, NADPH oxidase, and redox signaling in the vasculature.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013 Oct 1;19(10):1110-20. doi: 10.1089/ars.2012.4641. Epub 2012 Jun 11. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013. PMID: 22530599 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cell signaling through protein kinase C oxidation and activation.Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(9):10697-10721. doi: 10.3390/ijms130910697. Epub 2012 Aug 24. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 23109817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NADPH oxidase 4 mediates flow-induced superoxide production in thick ascending limbs.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012 Oct 15;303(8):F1151-6. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00181.2012. Epub 2012 Aug 15. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22896039 Free PMC article.
-
Prevention of Oxidative Stress-Induced Pancreatic Beta Cell Damage by Broussonetia Kazinoki Siebold Fruit Extract Via the ERK-Nox4 Pathway.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 May 10;9(5):406. doi: 10.3390/antiox9050406. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32397640 Free PMC article.
-
Redox control of renal function and hypertension.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2008 Dec;10(12):2047-89. doi: 10.1089/ars.2008.2034. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2008. PMID: 18821850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker attenuates the activation of ERK and NADPH oxidase by mechanical strain in mesangial cells in the absence of angiotensin II.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2009 May;296(5):F1052-60. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00580.2007. Epub 2009 Mar 4. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19261744 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ardaillou R., Chansel D., Chatziantoniou C., Dussaule J. C. Mesangial AT1 receptors: expression, signaling, and regulation. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1999;10:S40–S46. - PubMed
-
- Gorin Y., Kim N.-H., Feliers D., Bhandari B., Ghosh Choudhury G., Abboud H. E. Angiotensin II activates Akt/protein kinase B by an arachidonic acid/redox-dependent pathway and independent of phosphoinositide 3-kinase. FASEB J. 2001;15:1909–1920. - PubMed
-
- Schlondorff D., DeCandido S., Satriano J. A. Angiotensin II stimulates phospholipases C and A2 in cultured rat mesangial cells. Am. J. Physiol. 1987;253:C113–C120. - PubMed
-
- Alexander L. D., Cui X. L., Falck J. R., Douglas J. G. Arachidonic acid directly activates members of the mitogen-activated protein kinase superfamily in rabbit proximal tubule cells. Kidney Int. 2001;59:2039–2053. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

