Hypoxia-mediated down-regulation of Bid and Bax in tumors occurs via hypoxia-inducible factor 1-dependent and -independent mechanisms and contributes to drug resistance
- PMID: 15024076
- PMCID: PMC371100
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.7.2875-2889.2004
Hypoxia-mediated down-regulation of Bid and Bax in tumors occurs via hypoxia-inducible factor 1-dependent and -independent mechanisms and contributes to drug resistance
Abstract
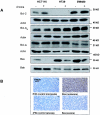
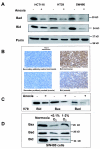
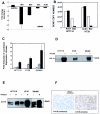
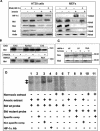
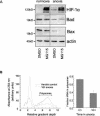
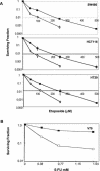
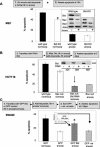
Solid tumors with disorganized, insufficient blood supply contain hypoxic cells that are resistant to radiotherapy and chemotherapy. Drug resistance, an obstacle to curative treatment of solid tumors, can occur via suppression of apoptosis, a process controlled by pro- and antiapoptotic members of the Bcl-2 protein family. Oxygen deprivation of human colon cancer cells in vitro provoked decreased mRNA and protein levels of proapoptotic Bid and Bad. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) was dispensable for the down-regulation of Bad but required for that of Bid, consistent with the binding of HIF-1alpha to a hypoxia-responsive element (positions -8484 to -8475) in the bid promoter. Oxygen deprivation resulted in proteosome-independent decreased expression of Bax in vitro, consistent with a reduction in global translation efficiency. The physiological relevance of Bid and Bax down-regulation was confirmed in tumors in vivo. Oxygen deprivation resulted in decreased drug-induced apoptosis and clonogenic resistance to agents with different mechanisms of action. The contribution of Bid and/or Bax down-regulation to drug responsiveness was demonstrated by the relative resistance of normoxic cells that had no or reduced expression of Bid and/or Bax and by the finding that forced expression of Bid in hypoxic cells resulted in increased sensitivity to the topoisomerase II inhibitor etoposide.
Figures

Similar articles
-
BID: a novel BH3 domain-only death agonist.Genes Dev. 1996 Nov 15;10(22):2859-69. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.22.2859. Genes Dev. 1996. PMID: 8918887
-
Tax contributes apoptosis resistance to HTLV-1-infected T cells via suppression of Bid and Bim expression.Cell Death Dis. 2014 Dec 18;5(12):e1575. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.536. Cell Death Dis. 2014. PMID: 25522269 Free PMC article.
-
The role of hypoxia inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) in hypoxia induced apoptosis.J Clin Pathol. 2004 Oct;57(10):1009-14. doi: 10.1136/jcp.2003.015032. J Clin Pathol. 2004. PMID: 15452150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxic human cancer cells are sensitized to BH-3 mimetic–induced apoptosis via downregulation of the Bcl-2 protein Mcl-1.J Clin Invest. 2011 Mar;121(3):1075-87. doi: 10.1172/JCI43505. J Clin Invest. 2011. PMID: 21393866 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia in tumors: molecular targets for anti-cancer therapeutics.Adv Enzyme Regul. 2004;44:93-108. doi: 10.1016/j.advenzreg.2003.11.019. Adv Enzyme Regul. 2004. PMID: 15581485 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Signaling Pathways That Control Apoptosis in Prostate Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Feb 24;13(5):937. doi: 10.3390/cancers13050937. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33668112 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sublethal cytochrome c release generates drug-tolerant persister cells.Cell. 2022 Sep 1;185(18):3356-3374.e22. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.07.025. Cell. 2022. PMID: 36055199 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-induced modulation of apoptosis and BCL-2 family proteins in different cancer cell types.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e47519. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047519. Epub 2012 Nov 5. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23139748 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of key regulatory proteins in androgen dependent prostate tumor cells by oncolytic reovirus.Virology. 2015 Nov;485:153-61. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2015.07.007. Epub 2015 Aug 8. Virology. 2015. PMID: 26264969 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of the proapoptotic protein Bid is an adverse prognostic factor for radiotherapy outcome in carcinoma of the cervix.Br J Cancer. 2005 Feb 14;92(3):449-58. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602344. Br J Cancer. 2005. PMID: 15685241 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams, J. M., and S. Cory. 1998. The Bcl-2 protein family: arbiters of cell survival. Science 281:1322-1326. - PubMed
-
- Akakura, N., M. Kobayashi, I. Horiuchi, A. Suzuki, J. Wang, J. Chen, H. Niizeki, K. Kawamura, M. Hosokawa, and M. Asaka. 2001. Constitutive expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α renders pancreatic cancer cells resistant to apoptosis induced by hypoxia and nutrient deprivation. Cancer Res. 61:6548-6554. - PubMed
-
- Baek, J. H., J. E. Jang, C. M. Kang, H. Y. Chung, N. D. Kim, and K. W. Kim. 2000. Hypoxia-induced VEGF enhances tumor survivability via suppression of serum deprivation-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 19:4621-4631. - PubMed
-
- Birner, P., M. Schindl, A. Obermair, G. Breitenecker, and G. Oberhuber. 2001. Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α in epithelial ovarian tumors: its impact on prognosis and response to chemotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 7:1661-1668. - PubMed
-
- Bos, R., H. Zhong, C. F. Hanrahan, E. C. Mommers, G. L. Semenza, H. M. Pinedo, M. D. Abeloff, J. W. Simons, P. J. van Diest, and E. van der Wall. 2001. Levels of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha during breast carcinogenesis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 93:309-314. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
