Extracellular alpha 6 integrin cleavage by urokinase-type plasminogen activator in human prostate cancer
- PMID: 15023541
- PMCID: PMC2715336
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2003.11.023
Extracellular alpha 6 integrin cleavage by urokinase-type plasminogen activator in human prostate cancer
Abstract
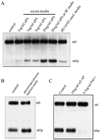
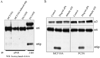
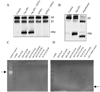
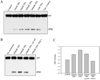
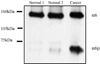
During human prostate cancer progression, the integrin alpha6beta1 (laminin receptor) is expressed on the cancer cell surface during invasion and in lymph node metastases. We previously identified a novel structural variant of the alpha6 integrin called alpha6p. This variant was produced on the cell surface and was missing the beta-barrel extracellular domain. Using several different concentrations of amiloride, aminobenzamidine and PAI-1 and the urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) function-blocking antibody (3689), we showed that uPA, acting as a protease, is responsible for production of alpha6p. We also showed that addition of uPA in the culture media of cells that do not produce alpha6p, resulted in a dose-dependent alpha6p production. In contrast, the addition of uPA did not result in the cleavage of other integrins. Using alpha2-antiplasmin and plasmin depleted media, we observed that uPA cleaves the alpha6 integrin directly. Further, 12-o-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate (TPA) induced the production of alpha6p, and this induction was abolished by PAI-1 but not alpha2-antiplasmin. Finally, the alpha6p integrin variant was detected in invasive human prostate carcinoma tissue indicating that this is not a tissue culture phenomenon. These data, taken together, suggest that this is a novel function of uPA, that is, to remove the beta-barrel ligand-binding domain of the integrin while preserving its heterodimer association.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Integrin alpha6 cleavage: a novel modification to modulate cell migration.Exp Cell Res. 2007 Apr 1;313(6):1080-9. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2007.01.006. Epub 2007 Jan 17. Exp Cell Res. 2007. PMID: 17303120 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin clipping: a novel adhesion switch?J Cell Biochem. 2004 Jan 1;91(1):26-35. doi: 10.1002/jcb.10675. J Cell Biochem. 2004. PMID: 14689578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasminogen activator system modulates invasive capacity and proliferation in prostatic tumor cells.Clin Exp Metastasis. 1998 Aug;16(6):513-28. doi: 10.1023/a:1006590217724. Clin Exp Metastasis. 1998. PMID: 9872599
-
Macrophage-dependent cleavage of the laminin receptor α6β1 in prostate cancer.Mol Cancer Res. 2011 Oct;9(10):1319-28. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-11-0080. Epub 2011 Aug 8. Mol Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21824975 Free PMC article.
-
Structure, function and expression on blood and bone marrow cells of the urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor, uPAR.Stem Cells. 1997;15(6):398-408. doi: 10.1002/stem.150398. Stem Cells. 1997. PMID: 9402652 Review.
Cited by
-
A high level of integrin α6 expression in human intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cells is associated with a migratory and invasive phenotype.Dig Dis Sci. 2013 Jun;58(6):1627-35. doi: 10.1007/s10620-012-2524-6. Epub 2013 Jan 11. Dig Dis Sci. 2013. PMID: 23306848
-
The laminin binding integrin alpha6beta1 in prostate cancer perineural invasion.J Cell Physiol. 2010 Aug;224(2):283-8. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22149. J Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20432448 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biophysical phenotype mixtures reveal advantages for tumor muscle invasion in vivo.Biophys J. 2023 Nov 7;122(21):4194-4206. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2023.09.016. Epub 2023 Sep 26. Biophys J. 2023. PMID: 37766428 Free PMC article.
-
Androgen receptor-induced integrin α6β1 and Bnip3 promote survival and resistance to PI3K inhibitors in castration-resistant prostate cancer.Oncogene. 2020 Jul;39(31):5390-5404. doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-1370-9. Epub 2020 Jun 21. Oncogene. 2020. PMID: 32565538 Free PMC article.
-
The host microenvironment influences prostate cancer invasion, systemic spread, bone colonization, and osteoblastic metastasis.Front Oncol. 2014 Dec 15;4:364. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2014.00364. eCollection 2014. Front Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25566502 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Giancotti FG, Ruoslahti E. Integrin signaling. Science. 1999;285:1028–1032. - PubMed
-
- Miranti CK, Brugge JS. Sensing the environment: a historical perspective on integrin signal transduction. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002;4:E83–E90. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz MA, Schaller MD, Ginsberg MH. Integrins: emerging paradigms of signal transduction. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1995;11:549–599. - PubMed
-
- Green LJ, Mould AP, Humphries MJ. The integrin beta subunit. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1998;30:179–184. - PubMed
-
- Xiong JP, Stehle T, Zhang R, Joachimiak A, Frech M, Goodman SL, Arnaout MA. Crystal structure of the extracellular segment of integrin alpha Vbeta3 in complex with an Arg –Gly –Asp ligand. Science. 2002;296:151–155. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

