The multi-country evaluation of the integrated management of childhood illness strategy: lessons for the evaluation of public health interventions
- PMID: 14998804
- PMCID: PMC1448266
- DOI: 10.2105/ajph.94.3.406
The multi-country evaluation of the integrated management of childhood illness strategy: lessons for the evaluation of public health interventions
Abstract
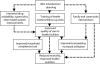
The Multi-Country Evaluation of the Integrated Management of Childhood Illness (IMCI) includes studies of the effectiveness, cost, and impact of the IMCI strategy in Bangladesh, Brazil, Peru, Tanzania, and Uganda. Seven questions were addressed when the evaluation was designed: who would be in charge, through what mechanisms IMCI could affect child health, whether the focus would be efficacy or effectiveness, what indicators would be measured, what types of inference would be made, how costs would be incorporated, and what elements would constitute the plan of analysis. We describe how these questions were answered, the challenges encountered in implementing the evaluation, and the 5 study designs. The methodological insights gained can improve future evaluations of public health programs.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Programmatic pathways to child survival: results of a multi-country evaluation of Integrated Management of Childhood Illness.Health Policy Plan. 2005 Dec;20 Suppl 1:i5-i17. doi: 10.1093/heapol/czi055. Health Policy Plan. 2005. PMID: 16306070
-
Are health interventions implemented where they are most needed? District uptake of the integrated management of childhood illness strategy in Brazil, Peru and the United Republic of Tanzania.Bull World Health Organ. 2006 Oct;84(10):792-801. doi: 10.2471/blt.06.030502. Bull World Health Organ. 2006. PMID: 17128359 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of Integrated Management of Childhood Illness on observed quality of care of under-fives in rural Tanzania.Health Policy Plan. 2004 Jan;19(1):1-10. doi: 10.1093/heapol/czh001. Health Policy Plan. 2004. PMID: 14679280
-
Integrated Management of Childhood Illness (IMCI): a robust strategy.Indian J Pediatr. 2002 Jan;69(1):41-8. doi: 10.1007/BF02723776. Indian J Pediatr. 2002. PMID: 11876120 Review.
-
National implementation of Integrated Management of Childhood Illness (IMCI): policy constraints and strategies.Health Policy. 2010 Jul;96(2):128-33. doi: 10.1016/j.healthpol.2010.01.013. Epub 2010 Feb 21. Health Policy. 2010. PMID: 20176407 Review.
Cited by
-
The grand challenges of the Gates Foundation: what impact on global child health?J R Soc Med. 2006 Apr;99(4):171-4. doi: 10.1177/014107680609900412. J R Soc Med. 2006. PMID: 16574966 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Rethinking the scale up of Integrated Management of Childhood Illness.BMJ. 2018 Jul 30;362:k2993. doi: 10.1136/bmj.k2993. BMJ. 2018. PMID: 30061095 Free PMC article.
-
Does integrated management of childhood illness (IMCI) training improve the skills of health workers? A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 12;8(6):e66030. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066030. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23776599 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Implementation of UNICEF and WHO's care for child development package: Lessons from a global review and key informant interviews.Front Public Health. 2023 Feb 16;11:1140843. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1140843. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36875409 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating delivery systems: complex evaluations and plausibility inference.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2010 Apr;82(4):672-7. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.2010.09-0473. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2010. PMID: 20348517 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Child and adolescent health and development. Available at: http://www.who.int/child-adolescent-health. Accessed December 11, 2003.
-
- Tulloch J. Integrated approach to child health in developing countries. Lancet. 1999;354(suppl 2):SII16–SII20. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization Multi-Country Evaluation. Available at: http://www.who.int/imci-mce. Accessed December 11, 2003.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical