Human cytomegalovirus stimulates cellular IKK2 activity and requires the enzyme for productive replication
- PMID: 14990741
- PMCID: PMC353729
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.78.6.3190-3195.2004
Human cytomegalovirus stimulates cellular IKK2 activity and requires the enzyme for productive replication
Abstract
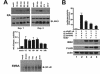
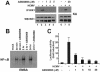
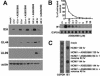
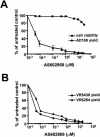
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) exploits the host transcription factor NF-kappaB to enhance its own replication, dissemination, and reactivation from latency. Here we report that HCMV infection activates the upstream IkappaB kinase (IKK) complex and that its catalytic IKK2 subunit is required for HCMV-induced NF-kappaB activation, as well as the replication of different HCMV strains. These results indicate that IKK2 is essential for HCMV replication and emphasize the feasibility of blocking NF-kappaB activation as a way of inhibiting infection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting the NF-kappaB pathway through pharmacological inhibition of IKK2 prevents human cytomegalovirus replication and virus-induced inflammatory response in infected endothelial cells.Antiviral Res. 2007 Mar;73(3):175-84. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2006.10.001. Epub 2006 Oct 23. Antiviral Res. 2007. PMID: 17070604
-
Activation of the NF-kappaB pathway in human cytomegalovirus-infected cells is necessary for efficient transactivation of the major immediate-early promoter.J Virol. 2004 May;78(9):4498-507. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.9.4498-4507.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15078930 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the virus-induced IKK/NF-kappaB signalling axis is critical for the replication of human cytomegalovirus in quiescent cells.Cell Microbiol. 2007 Aug;9(8):2040-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2007.00936.x. Epub 2007 Apr 5. Cell Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17419715
-
Regulation and function of IKK and IKK-related kinases.Sci STKE. 2006 Oct 17;2006(357):re13. doi: 10.1126/stke.3572006re13. Sci STKE. 2006. PMID: 17047224 Review.
-
Phosphorylation meets ubiquitination: the control of NF-[kappa]B activity.Annu Rev Immunol. 2000;18:621-63. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.18.1.621. Annu Rev Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10837071 Review.
Cited by
-
The Elk-1 and serum response factor binding sites in the major immediate-early promoter of human cytomegalovirus are required for efficient viral replication in quiescent cells and compensate for inactivation of the NF-kappaB sites in proliferating cells.J Virol. 2010 May;84(9):4481-93. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02141-09. Epub 2010 Feb 10. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20147408 Free PMC article.
-
An Attenuated Strain of Human Cytomegalovirus for the Establishment of a Subviral Particle Vaccine.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Aug 16;10(8):1326. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10081326. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36016214 Free PMC article.
-
Virus-host protein interactions as footprints of human cytomegalovirus replication.Curr Opin Virol. 2022 Feb;52:135-147. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2021.11.016. Epub 2021 Dec 16. Curr Opin Virol. 2022. PMID: 34923282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of the NF-kappaB pathway by varicella-zoster virus in vitro and in human epidermal cells in vivo.J Virol. 2006 Jun;80(11):5113-24. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01956-05. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16698992 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of the NFκb Signalling Pathway by Human Cytomegalovirus.Virology (Hyderabad). 2017 Aug;1(1):104. Epub 2017 Jul 31. Virology (Hyderabad). 2017. PMID: 29082387 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bhagwat, S., I. B. Brydon, I. Satoh, E. C. O′Leary, J. Leisten, G. S. Firestein, D. L. Boyle, M. Dreano, D. W. Anderson, and C. E. Grimshaw. 2001. The small molecule IKK2 inhibitor SPC839 is efficacious in an animal model of arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 44:S213.
-
- Dixit, V., and T. W. Mak. 2002. NF-κB signaling: many roads lead to Madrid. Cell 111:615-619. - PubMed
-
- Fortunato, E. A., and D. H. Spector. 1999. Regulation of human cytomegalovirus gene expression. Adv. Virus Res. 54:1-128. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

