Specific Inhibition of IkappaB kinase reduces hyperalgesia in inflammatory and neuropathic pain models in rats
- PMID: 14973242
- PMCID: PMC6730471
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3118-03.2004
Specific Inhibition of IkappaB kinase reduces hyperalgesia in inflammatory and neuropathic pain models in rats
Abstract
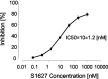
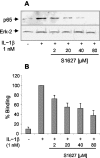
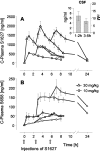
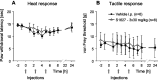
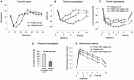
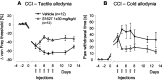
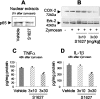
Phosphorylation of IkappaB through IkappaB kinase (IKK) is the first step in nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) activation and upregulation of NF-kappaB-responsive genes. Hence, inhibition of IKK activity may be expected to prevent injury-, infection-, or stress-induced upregulation of various proinflammatory genes and may thereby reduce hyperalgesia and inflammation. In the present study, we tested this hypothesis using a specific and potent IKK inhibitor (S1627). In an IKK assay, S1627 inhibited IKK activity with an IC50 value of 10.0 +/- 1.2 nm. In cell culture experiments, S1627 inhibited interleukin (IL)-1beta-stimulated nuclear translocation and DNA-binding of NF-kappaB. Plasma concentration time courses after intraperitoneal injection revealed a short half-life of 2.8 hr in rats. Repeated intraperitoneal injections were, therefore, chosen as the dosing regimen. S1627 reversed thermal and mechanical hyperalgesia at 3x 30 mg/kg in the zymosan-induced paw inflammation model and reduced the inflammatory paw edema at 3x 40 mg/kg. S1627 also significantly reduced tactile and cold allodynia in the chronic constriction injury model of neuropathic pain at 30 mg/kg once daily. The drug had no effect on acute inflammatory nociception in the formalin test and did not affect responses to heat and tactile stimuli in naive animals. As hypothesized, S1627 prevented the zymosan-induced nuclear translocation of NF-kappaB in the spinal cord and the upregulation of NF-kappaB-responsive genes including cyclooxygenase-2, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and IL-1beta. Our data indicate that IKK may prove an interesting novel drug target in the treatment of pathological pain and inflammation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Picroside II Attenuates CCI-Induced Neuropathic Pain in Rats by Inhibiting Spinal Reactive Astrocyte-Mediated Neuroinflammation Through the NF-κB Pathway.Neurochem Res. 2018 May;43(5):1058-1066. doi: 10.1007/s11064-018-2518-7. Epub 2018 Apr 18. Neurochem Res. 2018. PMID: 29671236
-
Conjugated polyhydroxybenzene derivatives block tumor necrosis factor-alpha-mediated nuclear factor-kappaB activation and cyclooxygenase-2 gene transcription by targeting IkappaB kinase activity.Mol Pharmacol. 2001 Dec;60(6):1439-48. doi: 10.1124/mol.60.6.1439. Mol Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11723253
-
Effect of Ceftiofur on Hyperalgesia and Allodynia in a Rat Neuropathic Pain Model: The Role of Immune Processes.Neuroimmunomodulation. 2017;24(1):21-28. doi: 10.1159/000475757. Epub 2017 Jun 15. Neuroimmunomodulation. 2017. PMID: 28614825
-
Regulation and function of IKK and IKK-related kinases.Sci STKE. 2006 Oct 17;2006(357):re13. doi: 10.1126/stke.3572006re13. Sci STKE. 2006. PMID: 17047224 Review.
-
HPLC-DAD-UV analysis, anti-inflammatory and anti-neuropathic effects of methanolic extract of Sideritis bilgeriana (lamiaceae) by NF-κB, TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 involvement.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Jan 30;265:113338. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113338. Epub 2020 Sep 10. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 32920137 Review.
Cited by
-
MAPK Pathways Are Involved in Neuropathic Pain in Rats with Chronic Compression of the Dorsal Root Ganglion.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016;2016:6153215. doi: 10.1155/2016/6153215. Epub 2016 Jul 18. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016. PMID: 27504140 Free PMC article.
-
Role of NFkappaB in an animal model of complex regional pain syndrome-type I (CRPS-I).J Pain. 2009 Nov;10(11):1161-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2009.04.012. J Pain. 2009. PMID: 19878863 Free PMC article.
-
IκB kinase β (IKKβ): Structure, transduction mechanism, biological function, and discovery of its inhibitors.Int J Biol Sci. 2023 Aug 6;19(13):4181-4203. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.85158. eCollection 2023. Int J Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37705738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Photobiomodulation reduces neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury by downregulating CXCL10 expression.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2023 Dec;29(12):3995-4017. doi: 10.1111/cns.14325. Epub 2023 Jul 20. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2023. PMID: 37475184 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of capillary dysfunction on oxygen and glucose extraction in diabetic neuropathy.Diabetologia. 2015 Apr;58(4):666-77. doi: 10.1007/s00125-014-3461-z. Epub 2014 Dec 16. Diabetologia. 2015. PMID: 25512003 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- An G, Lin TN, Liu JS, Xue JJ, He YY, Hsu CY (1993) Expression of c-fos and c-jun family genes after focal cerebral ischemia. Ann Neurol 33: 457-464. - PubMed
-
- Anest V, Hanson JL, Cogswell PC, Steinbrecher KA, Strahl BD, Baldwin AS (2003) A nucleosomal function for IkappaB kinase-alpha in NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression. Nature 423: 659-663. - PubMed
-
- Aubin N, Curet O, Deffois A, Carter C (1998) Aspirin and salicylate protect against MPTP-induced dopamine depletion in mice. J Neurochem 71: 1635-1642. - PubMed
-
- Auphan N, DiDonato JA, Rosette C, Helmberg A, Karin M (1995) Immunosuppression by glucocorticoids: inhibition of NF-kappa B activity through induction of I kappa B synthesis. Science 270: 286-290. - PubMed
-
- Bales KR, Du Y, Dodel RC, Yan GM, Hamilton-Byrd E, Paul SM (1998) The NF-kappaB/Rel family of proteins mediates Amyloid-beta-induced neurotoxicity and glial activation. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 57: 63-72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
