Direct interaction between nucleosome assembly protein 1 and the papillomavirus E2 proteins involved in activation of transcription
- PMID: 14966293
- PMCID: PMC350572
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.5.2153-2168.2004
Direct interaction between nucleosome assembly protein 1 and the papillomavirus E2 proteins involved in activation of transcription
Abstract
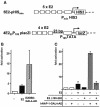
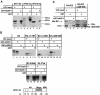
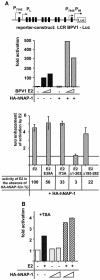
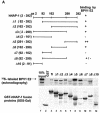
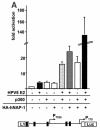
Using a yeast two-hybrid screen, we identified human nucleosome assembly protein 1 (hNAP-1) as a protein interacting with the activation domain of the transcriptional activator encoded by papillomaviruses (PVs), the E2 protein. We show that the interaction between E2 and hNAP-1 is direct and not merely mediated by the transcriptional coactivator p300, which is bound by both proteins. Coexpression of hNAP-1 strongly enhances activation by E2, indicating a functional interaction as well. E2 binds to at least two separate domains within hNAP-1, one within the C terminus and an internal domain. The binding of E2 to hNAP-1 is necessary for cooperativity between the factors. Moreover, the N-terminal 91 amino acids are crucial for the transcriptional activity of hNAP-1, since deletion mutants lacking this N-terminal portion fail to cooperate with E2. We provide evidence that hNAP-1, E2, and p300 can form a ternary complex efficient in the activation of transcription. We also show that p53 directly interacts with hNAP-1, indicating that transcriptional activators in addition to PV E2 interact with hNAP-1. These results suggest that the binding of sequence-specific DNA binding proteins to hNAP-1 may be an important step contributing to the activation of transcription.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The histone chaperone protein Nucleosome Assembly Protein-1 (hNAP-1) binds HIV-1 Tat and promotes viral transcription.Retrovirology. 2008 Jan 28;5:8. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-5-8. Retrovirology. 2008. PMID: 18226242 Free PMC article.
-
The amino-terminal C/H1 domain of CREB binding protein mediates zta transcriptional activation of latent Epstein-Barr virus.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Mar;19(3):1617-26. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.3.1617. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10022850 Free PMC article.
-
Coactivators p300 and PCAF physically and functionally interact with the foamy viral trans-activator.BMC Mol Biol. 2004 Sep 6;5:16. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-5-16. BMC Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 15350211 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein 2 interacts with p300, CBP, and PCAF histone acetyltransferases in activation of the LMP1 promoter.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Jan 4;97(1):430-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.1.430. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 10618435 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional activators and activation mechanisms.Protein Cell. 2011 Nov;2(11):879-88. doi: 10.1007/s13238-011-1101-7. Epub 2011 Dec 17. Protein Cell. 2011. PMID: 22180087 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association of bovine papillomavirus E2 protein with nuclear structures in vivo.J Virol. 2005 Aug;79(16):10528-39. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.16.10528-10539.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16051845 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis C Virus NS5A Targets Nucleosome Assembly Protein NAP1L1 To Control the Innate Cellular Response.J Virol. 2017 Aug 24;91(18):e00880-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00880-17. Print 2017 Sep 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28659470 Free PMC article.
-
Brd4-independent transcriptional repression function of the papillomavirus e2 proteins.J Virol. 2007 Sep;81(18):9612-22. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00447-07. Epub 2007 Jul 11. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17626100 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of papillomavirus E2 protein with the Brm chromatin remodeling complex leads to enhanced transcriptional activation.J Virol. 2007 Mar;81(5):2213-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01746-06. Epub 2006 Dec 6. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17151122 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of the papillomavirus E8--E2C protein with the cellular CHD6 protein contributes to transcriptional repression.J Virol. 2010 Sep;84(18):9505-15. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00678-10. Epub 2010 Jul 14. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20631145 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Armstrong, J. A., J. J. Bieker, and B. M. Emerson. 1998. A SWI/SNF-related chromatin remodeling complex, E-RC1 is required for tissue specific transcriptional regulation by EKLF in vitro. Cell 95:93-104. - PubMed
-
- Avantaggiati, M. L., V. V. Ogryzko, K. Gardner, A. Giordano, S. A. Levine, and K. Kelly. 1997. Recruitment of p300/CBP in p53 dependent signal pathways. Cell 89:1175-1184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
