Expression cloning of functional receptor used by SARS coronavirus
- PMID: 14766227
- PMCID: PMC7111169
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.01.076
Expression cloning of functional receptor used by SARS coronavirus
Abstract
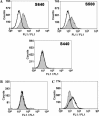
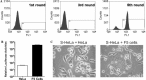
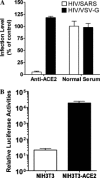
We have expressed a series of truncated spike (S) glycoproteins of SARS-CoV and found that the N-terminus 14-502 residuals were sufficient to bind to SARS-CoV susceptible Vero E6 cells. With this soluble S protein fragment as an affinity ligand, we screened HeLa cells transduced with retroviral cDNA library from Vero E6 cells and obtained a HeLa cell clone which could bind with the S protein. This cell clone was susceptible to HIV/SARS pseudovirus infection and the presence of a functional receptor for S protein in this cell clone was confirmed by the cell-cell fusion assay. Further studies showed the susceptibility of this cell was due to the expression of endogenous angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) which was activated by inserted LTR from retroviral vector used for expression cloning. When human ACE2 cDNA was transduced into NIH3T3 cells, the ACE2 expressing NIH3T3 cells could be infected with HIV/SARS pseudovirus. These data clearly demonstrated that ACE2 was the functional receptor for SARS-CoV.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A study on antigenicity and receptor-binding ability of fragment 450-650 of the spike protein of SARS coronavirus.Virology. 2007 Mar 15;359(2):362-70. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2006.09.022. Epub 2006 Oct 20. Virology. 2007. PMID: 17055551 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is a functional receptor for the SARS coronavirus.Nature. 2003 Nov 27;426(6965):450-4. doi: 10.1038/nature02145. Nature. 2003. PMID: 14647384 Free PMC article.
-
Importance of cholesterol-rich membrane microdomains in the interaction of the S protein of SARS-coronavirus with the cellular receptor angiotensin-converting enzyme 2.Virology. 2008 Nov 25;381(2):215-21. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2008.08.026. Epub 2008 Sep 23. Virology. 2008. PMID: 18814896 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: a functional receptor for SARS coronavirus.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2004 Nov;61(21):2738-43. doi: 10.1007/s00018-004-4242-5. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2004. PMID: 15549175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights from the association of SARS-CoV S-protein with its receptor, ACE2.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2006;581:209-18. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-33012-9_36. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2006. PMID: 17037532 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
The Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS) in COVID-19 Disease: Where We Are 3 Years after the Beginning of the Pandemic.Microorganisms. 2024 Mar 14;12(3):583. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12030583. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38543635 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2-mediated thromboinflammation by CLEC2.Fc.EMBO Mol Med. 2023 Jul 10;15(7):e16351. doi: 10.15252/emmm.202216351. Epub 2023 May 22. EMBO Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37211986 Free PMC article.
-
Subversion of autophagy machinery and organelle-specific autophagy by SARS-CoV-2 and coronaviruses.Autophagy. 2023 Apr;19(4):1055-1069. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2022.2116677. Epub 2022 Aug 31. Autophagy. 2023. PMID: 36005882 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective neutralizing epitopes in SARS-CoV-2.Immunol Rev. 2022 Sep;310(1):76-92. doi: 10.1111/imr.13084. Epub 2022 May 22. Immunol Rev. 2022. PMID: 35599305 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Known Cellular and Receptor Interactions of Animal and Human Coronaviruses: A Review.Viruses. 2022 Feb 8;14(2):351. doi: 10.3390/v14020351. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35215937 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Deng H.K., Unutmaz D., KewalRamani V.N., Littman D.R. Expression cloning of new receptors used by simian and human immunodeficiency viruses. Nature. 1997;388:296–300. - PubMed
-
- Chan S.Y., Empig C.J., Welte F.J., Speck R.F., Schmaljohn A., Kreisberg J.F., Goldsmith M.A. Folate receptor-alpha is a cofactor for cellular entry by Marburg and Ebola viruses. Cell. 2001;106:117–126. - PubMed
-
- Pileri P., Uematsu Y., Campagnoli S., Galli G., Falugi F., Petracca R., Weiner A.J., Houghton M., Rosa D., Grandi G., Abrignani S. Binding of hepatitis C virus to CD81. Science. 1998;282:938–941. - PubMed
-
- Ksiazek T.G., Erdman D., Goldsmith C.S., Zaki S.R., Peret T., Emery S., Tong S., Urbani C., Comer J.A., Lim W., Rollin P.E., Dowell S.F., Ling A.E., Humphrey C.D., Shieh W.J., Guarner J., Paddock C.D., Rota P., Fields B., DeRisi J., Yang J.Y., Cox N., Hughes J.M., LeDuc J.W., Bellini W.J., Anderson L.J. A novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003;348:1953–1966. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

