The Arabidopsis double-stranded RNA-binding protein HYL1 plays a role in microRNA-mediated gene regulation
- PMID: 14722360
- PMCID: PMC327156
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0307969100
The Arabidopsis double-stranded RNA-binding protein HYL1 plays a role in microRNA-mediated gene regulation
Abstract
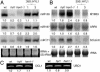
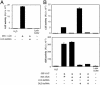
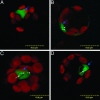
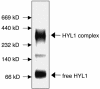
The Arabidopsis HYL1 gene encodes a nuclear double-stranded RNA-binding protein. A knockout mutation of the hyl1 gene is recessive and pleiotropic, causing developmental abnormalities, increasing sensitivity to abscisic acid, and reducing sensitivity to auxin and cytokinin. We report that levels of several microRNAs (miRNAs; miR159, -167, and -171) are reduced in homozygous mutant plants, and levels of two of three tested target mRNAs are elevated. Conversely, the miRNA levels are elevated in plants expressing a HYL1 cDNA from a strong promoter, and the corresponding target RNAs are reduced. These changes result from alterations in the stability of the target RNAs. However, double-stranded RNA-induced posttranscriptional gene silencing is unaffected by the hyl1 mutation. One-third to one-half of the cellular HYL1 protein is in a macromolecular complex, and a GFP-HYL1 fusion protein is found predominantly in the nucleus, although it is observed in both nucleus and cytoplasm in some cells. Within nuclei, HYL1 is associated with subnuclear bodies and ring-like structures. These observations provide evidence that the HYL1 protein is part of a nuclear macromolecular complex that is involved in miRNA-mediated gene regulation. Because hyl1 mutants show marked abnormalities in hormone responses, these results further suggest that miRNA-mediated changes in mRNA stability play a vital role in plant hormone signaling.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The N-terminal double-stranded RNA binding domains of Arabidopsis HYPONASTIC LEAVES1 are sufficient for pre-microRNA processing.Plant Cell. 2007 Mar;19(3):914-25. doi: 10.1105/tpc.106.048637. Epub 2007 Mar 2. Plant Cell. 2007. PMID: 17337628 Free PMC article.
-
The nuclear dsRNA binding protein HYL1 is required for microRNA accumulation and plant development, but not posttranscriptional transgene silencing.Curr Biol. 2004 Feb 17;14(4):346-51. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2004.01.035. Curr Biol. 2004. PMID: 14972688
-
Abscisic acid does not influence the subcellular distribution of the HYL1 protein from Arabidopsis thaliana.Acta Biochim Pol. 2008;55(3):517-24. Epub 2008 Aug 20. Acta Biochim Pol. 2008. PMID: 18714403
-
HYL1's multiverse: A journey through miRNA biogenesis and beyond canonical and non-canonical functions of HYL1.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2024 Aug;80:102546. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2024.102546. Epub 2024 May 7. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 38718678 Review.
-
Post-Translational Regulation of miRNA Pathway Components, AGO1 and HYL1, in Plants.Mol Cells. 2016 Aug 31;39(8):581-6. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2016.0085. Epub 2016 Jul 20. Mol Cells. 2016. PMID: 27440184 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nuclear processing and export of microRNAs in Arabidopsis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Mar 8;102(10):3691-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0405570102. Epub 2005 Feb 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15738428 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of function of OsDCL1 affects microRNA accumulation and causes developmental defects in rice.Plant Physiol. 2005 Sep;139(1):296-305. doi: 10.1104/pp.105.063420. Epub 2005 Aug 26. Plant Physiol. 2005. PMID: 16126864 Free PMC article.
-
RNAi-Based Antiviral Innate Immunity in Plants.Viruses. 2022 Feb 20;14(2):432. doi: 10.3390/v14020432. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35216025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Insights into Plant miRNA Biogenesis: Multiple Layers of miRNA Level Regulation.Plants (Basel). 2023 Jan 11;12(2):342. doi: 10.3390/plants12020342. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36679055 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A pathogen-inducible endogenous siRNA in plant immunity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Nov 21;103(47):18002-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0608258103. Epub 2006 Oct 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 17071740 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

