Differential effects of P2Y1 and P2Y12 nucleotide receptors on ERK1/ERK2 and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signalling and cell proliferation in serum-deprived and nonstarved glioma C6 cells
- PMID: 14718252
- PMCID: PMC1574220
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705639
Differential effects of P2Y1 and P2Y12 nucleotide receptors on ERK1/ERK2 and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signalling and cell proliferation in serum-deprived and nonstarved glioma C6 cells
Abstract
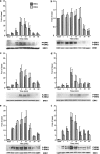
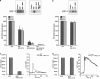
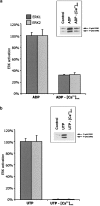
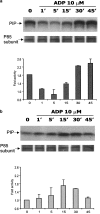
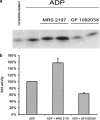
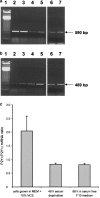
We have previously shown that, in glioma C6 cells, two nucleotide ADP-sensitive receptors coexist: P2Y1, coupled to PLC and responsible for Ca2+ release, and P2Y12, negatively coupled to adenylate cyclase. In the present study, we examined the effects of the stimulation of these two receptors on ERK1/2 and PI3-K activation, and cell proliferation in either serum-deprived or nonstarved C6 cells. In response to ADP and its analogues, in serum-starved cells, both p44 ERK1 and p42 ERK2 were activated in a time-dependent manner, as monitored by Western blot analysis using an antiphospho-p42/p44 MAPK antibody. The phosphorylation was reduced both by removal of the extracellular Ca2+ and partially or almost completely by MRS2179 or AR-C69931MX, specific antagonists of the P2Y1 and P2Y12 receptors, respectively. The inhibitory effect of antagonists was additive. These data indicate the involvement of both receptors, P2Y1 and P2Y12, in the ERK1/2 activation, but the P2Y12 receptor contribution predominates. ERK1/2 activity was positively correlated with cell proliferation of cultured glioma C6 cells. In nonstarved cells, ADP markedly decreased the PI3-K activity. In contrast, in serum-starved cells, ADP evoked an increase in the PI3-K activity. Blocking of the P2Y1 receptor by MRS2179 additionally increased this ADP response. These results suggest that the P2Y1 receptor has an inhibitory and the P2Y12 receptor a stimulatory effect on PI3-K signalling pathway. RT-PCR analysis revealed different mRNA expression of both receptors in starved and nonstarved cells. In nonstarved cells, the P2Y1 receptor mRNA predominates, whereas in serum-deprived cells the expression of P2Y12 mRNA becomes more pronounced. British Journal of Pharmacology (2004) 141, 497-507. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0705639
Figures
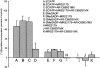
Similar articles
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
P(2Y) purinoceptor subtypes recruit different mek activators in astrocytes.Br J Pharmacol. 2000 Mar;129(5):927-36. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703138. Br J Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10696092 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidants for female subfertility.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Aug 27;8(8):CD007807. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007807.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32851663 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in Surgical and Nonsurgical Aesthetic Procedures: A 14-Year Analysis of the International Society of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery-ISAPS.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024 Oct;48(20):4217-4227. doi: 10.1007/s00266-024-04260-2. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024. PMID: 39103642 Review.
Cited by
-
Purinergic signalling and cancer.Purinergic Signal. 2013 Dec;9(4):491-540. doi: 10.1007/s11302-013-9372-5. Purinergic Signal. 2013. PMID: 23797685 Free PMC article. Review.
-
P2Y12 Purinergic Receptor and Brain Tumors: Implications on Glioma Microenvironment.Molecules. 2021 Oct 12;26(20):6146. doi: 10.3390/molecules26206146. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34684726 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplay between PIP3 and calmodulin regulation of olfactory cyclic nucleotide-gated channels.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Oct 17;103(42):15635-40. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0603344103. Epub 2006 Oct 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 17032767 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of transient receptor potential mucolipin-2 ion channels in gliomas: role in tumor growth and progression.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 12;7(28):43654-43668. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9661. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27248469 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of P2Y receptor-activated signal transduction pathways in G protein-dependent signalling networks.Purinergic Signal. 2006 Sep;2(3):451-69. doi: 10.1007/s11302-006-9008-0. Epub 2006 Jun 7. Purinergic Signal. 2006. PMID: 18404483 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ABBRACCHIO M.P., BURNSTOCK G. Purinoceptors: are there families of P2X and P2Y purinoceptors. Pharmacol. Ther. 1994;64:445–475. - PubMed
-
- BALLOU L.M., LIN H.-Y., FAN G., JIANG Y.-P., LIN R.Z. Activated Gαq inhibits p110α phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and Akt. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:23472–23479. - PubMed
-
- BARAŃSKA J., CHABAN V., CZARNY M., SABAŁA P. Changes in Ca2+ concentration in phorbol ester and thapsigargin treated glioma C6 cells. The role of protein kinase C in regulation of Ca2+ entry. Cell Calcium. 1995;17:207–215. - PubMed
-
- BARAŃSKA J., PRZYBYŁEK K., SABAŁA P. Capacitative calcium entry. Glioma C6 cells as a model of nonexcitable cells. Polish J. Pharmacol. 1999;51:153–162. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

