Toll-like receptor 4-dependent activation of dendritic cells by a retrovirus
- PMID: 14694089
- PMCID: PMC368791
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.78.2.576-584.2004
Toll-like receptor 4-dependent activation of dendritic cells by a retrovirus
Abstract
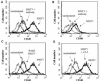
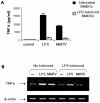
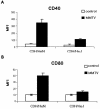
Mouse mammary tumor virus (MMTV) is a milk-borne retrovirus that exploits the adaptive immune system. It has recently been shown that MMTV activates B cells via Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), a molecule involved in innate immune responses. Here, we show that direct virus binding to TLR4 induced maturation of bone marrow-derived dendritic cells and up-regulated expression of the MMTV entry receptor (CD71) on these cells. In vivo, MMTV increased the number of dendritic cells in neonatal Peyer's patches and their expression of CD71; both these effects were dependent on TLR4. Thus, retroviral signaling through TLRs plays a critical role in dendritic-cell participation during infection.
Figures
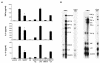


Similar articles
-
Murine retroviruses activate B cells via interaction with toll-like receptor 4.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Feb 19;99(4):2281-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.042355399. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 11854525 Free PMC article.
-
Increases in IgA(+) B cells in Peyer's patches during milk-borne mouse mammary tumor virus infection are influenced by Toll-like receptor 4 and are completely dependent on the superantigen response.J Gen Virol. 2010 Nov;91(Pt 11):2814-20. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.023358-0. Epub 2010 Aug 4. J Gen Virol. 2010. PMID: 20685932
-
Exogenous mouse mammary tumor virus (MMTV) infection induces endogenous MMTV sag expression.Virology. 1996 Jan 15;215(2):113-23. doi: 10.1006/viro.1996.0014. Virology. 1996. PMID: 8560758
-
Intestinal Immune System and Amplification of Mouse Mammary Tumor Virus.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Jan 13;11:807462. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.807462. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35096654 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mouse mammary tumor virus and the immune system.Immunol Res. 2003;27(2-3):469-80. doi: 10.1385/IR:27:2-3:469. Immunol Res. 2003. PMID: 12857990 Review.
Cited by
-
Sensing of RNA viruses: a review of innate immune receptors involved in recognizing RNA virus invasion.J Virol. 2012 Mar;86(6):2900-10. doi: 10.1128/JVI.05738-11. Epub 2012 Jan 18. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22258243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytosolic Sensors for Pathogenic Viral and Bacterial Nucleic Acids in Fish.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 2;21(19):7289. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197289. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33023222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatitis C virus induces toll-like receptor 4 expression, leading to enhanced production of beta interferon and interleukin-6.J Virol. 2006 Jan;80(2):866-74. doi: 10.1128/JVI.80.2.866-874.2006. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16378988 Free PMC article.
-
TLR2/MyD88 pathway-dependent regulation of dendritic cells by dengue virus promotes antibody-dependent enhancement via Th2-biased immunity.Oncotarget. 2017 Nov 20;8(62):106050-106070. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22525. eCollection 2017 Dec 1. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29285314 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between Ebola virus glycoprotein and host toll-like receptor 4 leads to induction of proinflammatory cytokines and SOCS1.J Virol. 2010 Jan;84(1):27-33. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01462-09. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 19846529 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Banchereau, J., and R. Steinman. 1998. Dendritic cells and the control of immunity. Nature 392:245-252. - PubMed
-
- Banchereau, J., F. Briere, C. Caux, J. Davoust, S. Lebecque, Y. J. Liu, B. Pulendran, and K. Palucka. 2000. Immunobiology of dendritic cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 18:767-811. - PubMed
-
- Barton, G. M., and R. Medzhitov. 2002. Control of adaptive immune responses by Toll-like receptors. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 14:380-383. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

