TbAGO1, an argonaute protein required for RNA interference, is involved in mitosis and chromosome segregation in Trypanosoma brucei
- PMID: 14670085
- PMCID: PMC317389
- DOI: 10.1186/1741-7007-1-2
TbAGO1, an argonaute protein required for RNA interference, is involved in mitosis and chromosome segregation in Trypanosoma brucei
Abstract
Background: RNA silencing processes are widespread in almost all eukaryotic organisms. They have various functions including genome protection, and the control of gene expression, development and heterochromatin formation. RNA interference (RNAi) is the post-transcriptional destruction of RNA, which is mediated by a ribonucleoprotein complex that contains, among several components, RNA helicases and Argonaute proteins. RNAi is functional in trypanosomes, protozoan parasites that separated very early from the main eukaryotic lineage and exhibit several intriguing features in terms of the control of gene expression. In this report, we investigated the functions of RNAi in Trypanosoma brucei.
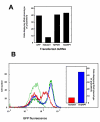
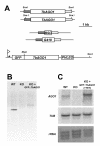
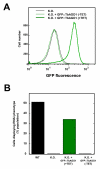
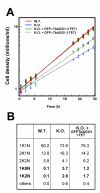
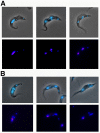
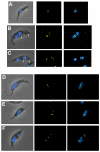
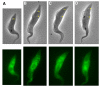
Results: By searching through genome databases, novel Argonaute-like proteins were identified in several protozoa that belong to the kinetoplastid order, a group of organisms that diverged early from the main eukaryotic lineage. T. brucei possesses two Argonaute-like genes termed TbAGO1 and TbPWI1. Dual transient transfection assays suggest that TbAGO1, but not TbPWI1, is involved in RNAi. The entire coding region of TbAGO1 was deleted by double gene knockout. TbAGO1-/- cells turned out to be completely resistant to RNAi generated either by transfected double-stranded RNA or by expression of an inverted repeat. TbAGO1-/- cells were viable but showed a dramatically reduced growth rate. This was probably due to defects in mitosis and abnormal chromosome segregation as revealed by in situ analysis. The RNAi and growth phenotypes were complemented by the inducible expression of a GFP::TbAGO1 fusion protein that revealed the cytoplasmic location of the protein.
Conclusions: The requirement of TbAGO1 for RNAi in trypanosomes demonstrates the evolutionary ancient involvement of Argonaute proteins in RNAi silencing processes. RNAi-deficient TbAGO1-/- cells showed numerous defects in chromosome segregation and mitotic spindle assembly. We propose a working hypothesis in which RNAi would be involved in heterochromatin formation at the centromere and therefore in chromosome segregation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Argonaute protein TbAGO1 contributes to large and mini-chromosome segregation and is required for control of RIME retroposons and RHS pseudogene-associated transcripts.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2007 Dec;156(2):144-53. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2007.07.016. Epub 2007 Aug 1. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2007. PMID: 17822785
-
Depletion of newly synthesized Argonaute1 impairs the RNAi response in Trypanosoma brucei.RNA. 2007 Jul;13(7):1132-9. doi: 10.1261/rna.474707. Epub 2007 May 25. RNA. 2007. PMID: 17526643 Free PMC article.
-
RNA interference as a genetic tool in trypanosomes.Methods Mol Biol. 2008;442:83-94. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-191-8_7. Methods Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18369780
-
RNA interference in protozoan parasites.Cell Microbiol. 2004 Jun;6(6):509-19. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2004.00399.x. Cell Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15104593 Review.
-
RNA interference in Trypanosoma brucei: a high-throughput engine for functional genomics in trypanosomatids?Trends Parasitol. 2007 Aug;23(8):348-51. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2007.06.008. Epub 2007 Jul 2. Trends Parasitol. 2007. PMID: 17604223 Review.
Cited by
-
The Flagellar Arginine Kinase in Trypanosoma brucei Is Important for Infection in Tsetse Flies.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 28;10(7):e0133676. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133676. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26218532 Free PMC article.
-
The centromeric retrotransposons of rice are transcribed and differentially processed by RNA interference.Genetics. 2007 Jun;176(2):749-61. doi: 10.1534/genetics.107.071902. Epub 2007 Apr 3. Genetics. 2007. PMID: 17409063 Free PMC article.
-
RNAi in Arthropods: Insight into the Machinery and Applications for Understanding the Pathogen-Vector Interface.Genes (Basel). 2012 Nov 6;3(4):702-41. doi: 10.3390/genes3040702. Genes (Basel). 2012. PMID: 24705082 Free PMC article.
-
The structure and repertoire of small interfering RNAs in Leishmania (Viannia) braziliensis reveal diversification in the trypanosomatid RNAi pathway.Mol Microbiol. 2013 Feb;87(3):580-93. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12117. Epub 2012 Dec 26. Mol Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23217017 Free PMC article.
-
Expression site silencing and life-cycle progression appear normal in Argonaute1-deficient Trypanosoma brucei.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2006 Sep;149(1):102-107. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2006.04.005. Epub 2006 May 12. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2006. PMID: 16735068 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

