Two Dictyostelium orthologs of the prokaryotic cell division protein FtsZ localize to mitochondria and are required for the maintenance of normal mitochondrial morphology
- PMID: 14665465
- PMCID: PMC326642
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.2.6.1315-1326.2003
Two Dictyostelium orthologs of the prokaryotic cell division protein FtsZ localize to mitochondria and are required for the maintenance of normal mitochondrial morphology
Abstract
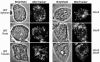
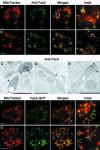
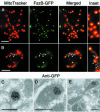
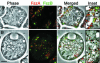
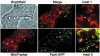
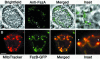
In bacteria, the protein FtsZ is the principal component of a ring that constricts the cell at division. Though all mitochondria probably arose through a single, ancient bacterial endosymbiosis, the mitochondria of only certain protists appear to have retained FtsZ, and the protein is absent from the mitochondria of fungi, animals, and higher plants. We have investigated the role that FtsZ plays in mitochondrial division in the genetically tractable protist Dictyostelium discoideum, which has two nuclearly encoded FtsZs, FszA and FszB, that are targeted to the inside of mitochondria. In most wild-type amoebae, the mitochondria are spherical or rod-shaped, but in fsz-null mutants they become elongated into tubules, indicating that a decrease in mitochondrial division has occurred. In support of this role in organelle division, antibodies to FszA and FszA-green fluorescent protein (GFP) show belts and puncta at multiple places along the mitochondria, which may define future or recent sites of division. FszB-GFP, in contrast, locates to an electron-dense, submitochondrial body usually located at one end of the organelle, but how it functions during division is unclear. This is the first demonstration of two differentially localized FtsZs within the one organelle, and it points to a divergence in the roles of these two proteins.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Defining the optimum strategy for identifying adults and children with coeliac disease: systematic review and economic modelling.Health Technol Assess. 2022 Oct;26(44):1-310. doi: 10.3310/ZUCE8371. Health Technol Assess. 2022. PMID: 36321689 Free PMC article.
-
Using Experience Sampling Methodology to Capture Disclosure Opportunities for Autistic Adults.Autism Adulthood. 2023 Dec 1;5(4):389-400. doi: 10.1089/aut.2022.0090. Epub 2023 Dec 12. Autism Adulthood. 2023. PMID: 38116059 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a novel toxicophore in anti-cancer chemotherapeutics that targets mitochondrial respiratory complex I.Elife. 2020 May 20;9:e55845. doi: 10.7554/eLife.55845. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32432547 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in Surgical and Nonsurgical Aesthetic Procedures: A 14-Year Analysis of the International Society of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery-ISAPS.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024 Oct;48(20):4217-4227. doi: 10.1007/s00266-024-04260-2. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024. PMID: 39103642 Review.
Cited by
-
Microtubules Are Essential for Mitochondrial Dynamics-Fission, Fusion, and Motility-in Dictyostelium discoideum.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2016 Mar 22;4:19. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2016.00019. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 27047941 Free PMC article.
-
Dictyostelium dynamin B modulates cytoskeletal structures and membranous organelles.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011 Aug;68(16):2751-67. doi: 10.1007/s00018-010-0590-5. Epub 2010 Nov 18. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011. PMID: 21086149 Free PMC article.
-
ARC3 Activation by PARC6 Promotes FtsZ-Ring Remodeling at the Chloroplast Division Site.Plant Cell. 2019 Apr;31(4):862-885. doi: 10.1105/tpc.18.00948. Epub 2019 Mar 1. Plant Cell. 2019. PMID: 30824505 Free PMC article.
-
A Conserved Role for LRRK2 and Roco Proteins in the Regulation of Mitochondrial Activity.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Sep 8;9:734554. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.734554. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34568343 Free PMC article.
-
An ancestral bacterial division system is widespread in eukaryotic mitochondria.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Aug 18;112(33):10239-46. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1421392112. Epub 2015 Mar 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25831547 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Addinall, S., and B. Holland. 2002. The tubulin ancester, FtsZ, draughtsman, designer and driving force for bacterial cytokinesis. J. Mol. Biol. 318:219-236. - PubMed
-
- Addinall, S., and J. Lutkenhaus. 1996. FtsZ-spirals and -arcs determine the shape of the invaginating septa in some mutants of Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 22:231-237. - PubMed
-
- Andersson, S. G. E., A. Zomorodipour, J. O. Andersson, T. Sicheritz-Pontén, U. C. M. Alsmark, R. M. Podowski, A. K. Näslund, A.-S. Eriksson, H. H. Winkler, and C. G. Kurland. 1998. The genome sequence of Rickettsia prowazekii and the origin of mitochondria. Nature 396:133-143. - PubMed
-
- Beech, P. L., and P. R. Gilson. 2000. FtsZ and organelle division in protists. Protist 151:11-16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

