Transporter-mediated uptake of 2-chloro- and 2-hydroxybenzoate by Pseudomonas huttiensis strain D1
- PMID: 14660391
- PMCID: PMC309881
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.69.12.7401-7408.2003
Transporter-mediated uptake of 2-chloro- and 2-hydroxybenzoate by Pseudomonas huttiensis strain D1
Abstract
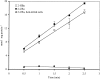
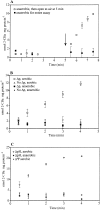
We investigated the mechanisms of uptake of 2-chlorobenzoate (2-CBa) and 2-hydroxybenzoate (2-HBa) by Pseudomonas huttiensis strain D1. Uptake was monitored by assaying intracellular accumulation of 2-[UL-ring-14C]CBa and 2-[UL-ring-14C]HBa. Uptake of 2-CBa showed substrate saturation kinetics with an apparent Km of 12.7 +/- 2.6 micromoles and a maximum velocity (Vmax) of 9.76 +/- 0.78 nmol min-1 mg of protein-1. Enhanced rates of uptake were induced by growth on 2-CBa and 2-HBa, but not by growth on benzoate or 2,5-di-CBa. Intracellular accumulations of 2-CBa and 2-HBa were 109- and 42-fold greater, respectively, than the extracellular concentrations of these substrates and were indicative of uptake mediated by a transporter rather than driven by substrate catabolism ("metabolic drag"). Results of competitor screening tests indicated that the substrate range of the transporter did not include other o-halobenzoates that serve as growth substrates for strain D1 and for which the metabolism was initiated by the same dioxygenase as 2-CBa and 2-HBa. This suggested that multiple mechanisms for substrate uptake were coupled to the same catabolic enzyme. The preponderance of evidence from tests with metabolic inhibitors and artificial electrochemical gradients suggested that 2-CBa uptake was driven by ATP hydrolysis. If so, the 2-CBa transporter would be the first of the ATP binding cassette type implicated in uptake of haloaromatic acids.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cloning of Pseudomonas sp. strain CBS3 genes specifying dehalogenation of 4-chlorobenzoate.J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):81-5. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.81-85.1986. J Bacteriol. 1986. PMID: 3759912 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning, nucleotide sequencing, and functional analysis of a novel, mobile cluster of biodegradation genes from Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain JB2.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2001 Oct;67(10):4603-9. doi: 10.1128/AEM.67.10.4603-4609.2001. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11571162 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of chlorobenzoates on the utilisation of chlorobiphenyls and chlorobenzoate mixtures by chlorobiphenyl/chlorobenzoate-mineralising hybrid bacterial strains.Arch Microbiol. 1996 Mar;165(3):213-8. doi: 10.1007/BF01692864. Arch Microbiol. 1996. PMID: 8599540
-
4-Chlorobenzoate uptake in Comamonas sp. strain DJ-12 is mediated by a tripartite ATP-independent periplasmic transporter.J Bacteriol. 2006 Dec;188(24):8407-12. doi: 10.1128/JB.00880-06. Epub 2006 Oct 13. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 17041053 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry and molecular cloning for the identification and functional characterization of mobile ortho-halobenzoate oxygenase genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain JB2.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2001 Dec;67(12):5648-55. doi: 10.1128/AEM.67.12.5648-5655.2001. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11722919 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Trans-membrane transport of n-octadecane by Pseudomonas sp. DG17.J Microbiol. 2013 Dec;51(6):791-9. doi: 10.1007/s12275-013-3259-6. Epub 2013 Dec 19. J Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 24385357
-
Garlic essential oil in water nanoemulsion prepared by high-power ultrasound: Properties, stability and its antibacterial mechanism against MRSA isolated from pork.Ultrason Sonochem. 2022 Nov;90:106201. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2022.106201. Epub 2022 Oct 12. Ultrason Sonochem. 2022. PMID: 36244094 Free PMC article.
-
Disentangling the microbial genomic traits associated with aromatic hydrocarbon degradation in a jet fuel-contaminated aquifer.Biodegradation. 2024 Nov 18;36(1):7. doi: 10.1007/s10532-024-10100-6. Biodegradation. 2024. PMID: 39557683
-
Thinned-Young Apple Polyphenols Inhibit Halitosis-Related Bacteria Through Damage to the Cell Membrane.Front Microbiol. 2022 Feb 23;12:745100. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.745100. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35281303 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome Analysis of the Global Response of Pseudomonas fragi NMC25 to Modified Atmosphere Packaging Stress.Front Microbiol. 2018 Jun 11;9:1277. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01277. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29942299 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexeyev, M. F., I. N. Shokolenko, and T. P. Croughan. 1995. New mini-Tn5 derivatives for insertion mutagenesis and genetic engineering in Gram-negative bacteria. Can. J. Microbiol. 41:1053-1055. - PubMed
-
- Allende, J. L., A. Gibello, A. Fortun, G. Mengs, E. Ferrer, and M. Martin. 2000. 4-Hydroxybenzoate uptake in an isolated soil Acinetobacter sp. Curr. Microbiol. 40:34-39. - PubMed
-
- Allende, J. L., A. Gibello, A. Fortun, M. Sanchez, and M. Martin. 2002. 4-Hydroxybenzoate uptake in Klebsiella planticola DSZ1 is driven by delta pH. Curr. Microbiol. 44:31-37. - PubMed
-
- Allende, J. L., A. Gibello, M. Martin, and A. Garrido-Pertierra. 1992. Transport of 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 292:583-588. - PubMed
-
- Allende, J. L., M. Suarez, M. Gallego, and A. Garrido-Pertierra. 1993. 4-Hydroxybenzoate uptake in Klebsiella pneumoniae is driven by electrical potential. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 300:142-147. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

