A20, a regulator of NFkappaB, maps to an atherosclerosis locus and differs between parental sensitive C57BL/6J and resistant FVB/N strains
- PMID: 14614151
- PMCID: PMC283575
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1835672100
A20, a regulator of NFkappaB, maps to an atherosclerosis locus and differs between parental sensitive C57BL/6J and resistant FVB/N strains
Abstract
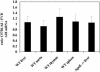
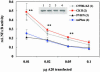
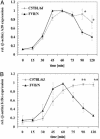
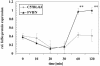
An intercross between atherosclerosis susceptible (C57BL/6J ApoE0) and resistant (FVB/N ApoE0) mice revealed a susceptibility locus on chromosome 10 (11 cM, logarithm of odds 7.8). Surprisingly, the genotypic means for this locus revealed that heterozygosity or homozygosity for the C57BL/6J allele was associated with decreased atherosclerosis. A candidate gene in this region is A20, which is involved in the feedback suppression of NFkappaB activation induced by tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha). We sequenced the A20 gene coding region from the parental strains and found a single-nucleotide polymorphism resulting in a single amino acid exchange, Glu627Ala (C57BL/6J vs. FVB/N). This mutation introduces a putative casein kinase 2 phosphorylation site in C57BL/6J-A20 not present in FVB/N-A20. NFkappaB reporter gene assays showed that this amino acid change results in less effective termination of TNFalpha-stimulated NFkappaB activation by C57BL/6J-A20. In accordance, the TNFalpha-induced expression of NFkappaB target genes (A20, IkappaBalpha) in vascular smooth muscle cells was prolonged in cells isolated from C57BL/6J compared with FVB/N mice. In light of the genotypic means for atherosclerosis at the chromosome 10 locus in F2 mice from this intercross, the observations now reported suggest that prolonged expression of genes induced by NFkappaB might be antirather than proatherogenic.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The protective effect of A20 on atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice is associated with reduced expression of NF-kappaB target genes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Nov 20;104(47):18601-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0709011104. Epub 2007 Nov 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 18006655 Free PMC article.
-
Aggravation of post-ischemic liver injury by overexpression of A20, an NF-κB suppressor.J Hepatol. 2011 Aug;55(2):328-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2010.11.029. Epub 2010 Dec 15. J Hepatol. 2011. PMID: 21167234
-
A20 is dynamically regulated in the heart and inhibits the hypertrophic response.Circulation. 2003 Aug 12;108(6):664-7. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000086978.95976.41. Epub 2003 Aug 4. Circulation. 2003. PMID: 12900338
-
Combined expression of A1 and A20 achieves optimal protection of renal proximal tubular epithelial cells.Kidney Int. 2005 Oct;68(4):1520-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1755.2005.00564.x. Kidney Int. 2005. PMID: 16164629
-
Frequent inactivation of A20 through gene mutation in B-cell lymphomas.Rinsho Ketsueki. 2011 Jun;52(6):313-9. Rinsho Ketsueki. 2011. PMID: 21737982 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
A20/TNFAIP3 Increases ENOS Expression in an ERK5/KLF2-Dependent Manner to Support Endothelial Cell Health in the Face of Inflammation.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 May 7;8:651230. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.651230. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34026871 Free PMC article.
-
Bcl10 is an essential regulator for A20 gene expression.J Physiol Biochem. 2013 Dec;69(4):821-34. doi: 10.1007/s13105-013-0259-2. Epub 2013 May 16. J Physiol Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23677497
-
TNFalpha induces ABCA1 through NF-kappaB in macrophages and in phagocytes ingesting apoptotic cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Feb 28;103(9):3112-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0510345103. Epub 2006 Feb 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16492740 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association scan yields new insights into the immunopathogenesis of psoriasis.Genes Immun. 2009 Apr;10(3):201-9. doi: 10.1038/gene.2009.11. Epub 2009 Mar 5. Genes Immun. 2009. PMID: 19262574 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A20: central gatekeeper in inflammation and immunity.J Biol Chem. 2009 Mar 27;284(13):8217-21. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R800032200. Epub 2008 Nov 13. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19008218 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Glass, C. K. & Witztum, J. L. (2001) Cell 104, 503–516. - PubMed
-
- Fox, C. S., Polak, J. F., Chazaro, I., Cupples, A., Wolf, P. A., D'Agostino, R. A. & O'Donnell, C. J. (2003) Stroke 34, 397–401. - PubMed
-
- Smith, J. D. (1998) Lab. Anim. Sci. 48, 573–579. - PubMed
-
- Plump, A. S., Smith, J. D., Hayek, T., Aalto-Setala, K., Walsh, A., Verstuyft, J. G., Rubin, E. M. & Breslow, J. L. (1992) Cell 71, 343–353. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

