Pathogenetic mechanisms in usual interstitial pneumonia/idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 14595745
- PMCID: PMC2810622
- DOI: 10.1002/path.1446
Pathogenetic mechanisms in usual interstitial pneumonia/idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
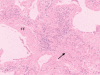
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a progressive, usually fatal, form of interstitial lung disease characterized by failure of alveolar re-epithelialization, persistence of fibroblasts/myofibroblasts, deposition of extracellular matrix, and distortion of lung architecture which ultimately results in respiratory failure. Clinical IPF is associated with a histopathological pattern of usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) on surgical lung biopsy. Therapy for this disease with glucocorticoids and other immunomodulatory agents is largely ineffective and recent trials of newer anti-fibrotic agents have been disappointing. While the inciting event(s) leading to the initiation of scar formation in UIP remain unknown, recent advances in our understanding of the mechanisms underlying both normal and aberrant wound healing have shed some light on pathogenetic mechanisms that may play significant roles in this disease. Unlike other fibrotic diseases of the lung, such as those associated with collagen vascular disease, occupational exposure, or chemotherapeutic agents, UIP is not associated with a significant inflammatory response; rather, dysregulated epithelial-mesenchymal interactions predominate. Identification of pathways crucial to fibrogenesis might offer potentially novel therapeutic targets to slow or halt the progression of IPF. This review focuses on evolving concepts of cellular and molecular mechanisms in the pathogenesis of UIP/IPF.
Copyright 2003 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis].Vnitr Lek. 2005 Dec;51(12):1375-84. Vnitr Lek. 2005. PMID: 16430105 Review. Czech.
-
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: new insights into pathogenesis.Clin Chest Med. 2004 Dec;25(4):749-58, vii. doi: 10.1016/j.ccm.2004.04.003. Clin Chest Med. 2004. PMID: 15564020 Review.
-
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis fibroblasts migrate and proliferate to CC chemokine ligand 21.Eur Respir J. 2007 Jun;29(6):1082-93. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00122806. Epub 2007 Mar 1. Eur Respir J. 2007. PMID: 17331965
-
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: pathogenesis and therapeutic approaches.Drugs. 2004;64(4):405-30. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200464040-00005. Drugs. 2004. PMID: 14969575 Review.
-
Usual interstitial pneumonia and smoking-related interstitial fibrosis display epithelial to mesenchymal transition in fibroblastic foci.Respir Med. 2014 Sep;108(9):1377-86. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2014.06.008. Epub 2014 Jul 17. Respir Med. 2014. PMID: 25066934
Cited by
-
Transformation of macrophages into myofibroblasts in fibrosis-related diseases: emerging biological concepts and potential mechanism.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 25;15:1474688. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1474688. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39386212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Geniposide ameliorates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice by inhibiting TGF-β/Smad and p38MAPK signaling pathways.PLoS One. 2024 Sep 6;19(9):e0309833. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0309833. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39240867 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of mTOR differently modulates planar and subepithelial fibrogenesis in human conjunctival fibroblasts.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2024 Jul 23. doi: 10.1007/s00417-024-06481-2. Online ahead of print. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 39042147
-
Identification and validation of mutual hub genes in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and rheumatoid arthritis-associated usual interstitial pneumonia.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 22;10(7):e28088. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28088. eCollection 2024 Apr 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38571583 Free PMC article.
-
Anoctamin-1 is induced by TGF-β and contributes to lung myofibroblast differentiation.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2024 Jan 1;326(1):L111-L123. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00155.2023. Epub 2023 Dec 12. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38084409 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Segura A, Yuste A, Cercos A, et al. Pulmonary fibrosis induced by cyclophosphamide. Ann Pharmacother. 2001;35:894–897. - PubMed
-
- Lynch JP, III, Hunninghake GW. Pulmonary complications of collagen vascular disease. Annu Rev Med. 1992;43:17–35. - PubMed
-
- De Vuyst P, Camus P. The past and present of pneumoconioses. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2000;6:151–156. - PubMed
-
- Liebow AA, Carrington CB. The interstitial pneumonias. In: Simon M, Potchen EJ, LeMay M, editors. Frontiers of Pulmonary Radiology. 1st edn Grune & Stratton; New York: 1969. pp. 102–141.
-
- Katzenstein AL, Myers JL. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: clinical relevance of pathologic classification. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998;157:1301–1315. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

