A gateway cloning vector set for high-throughput functional analysis of genes in planta
- PMID: 14555774
- PMCID: PMC523872
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.103.027979
A gateway cloning vector set for high-throughput functional analysis of genes in planta
Abstract
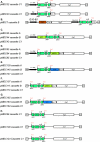
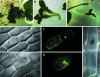
The current challenge, now that two plant genomes have been sequenced, is to assign a function to the increasing number of predicted genes. In Arabidopsis, approximately 55% of genes can be assigned a putative function, however, less than 8% of these have been assigned a function by direct experimental evidence. To identify these functions, many genes will have to undergo comprehensive analyses, which will include the production of chimeric transgenes for constitutive or inducible ectopic expression, for antisense or dominant negative expression, for subcellular localization studies, for promoter analysis, and for gene complementation studies. The production of such transgenes is often hampered by laborious conventional cloning technology that relies on restriction digestion and ligation. With the aim of providing tools for high throughput gene analysis, we have produced a Gateway-compatible Agrobacterium sp. binary vector system that facilitates fast and reliable DNA cloning. This collection of vectors is freely available, for noncommercial purposes, and can be used for the ectopic expression of genes either constitutively or inducibly. The vectors can be used for the expression of protein fusions to the Aequorea victoria green fluorescent protein and to the beta-glucuronidase protein so that the subcellular localization of a protein can be identified. They can also be used to generate promoter-reporter constructs and to facilitate efficient cloning of genomic DNA fragments for complementation experiments. All vectors were derived from pCambia T-DNA cloning vectors, with the exception of a chemically inducible vector, for Agrobacterium sp.-mediated transformation of a wide range of plant species.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Homologous recombination-mediated cloning and manipulation of genomic DNA regions using Gateway and recombineering systems.BMC Biotechnol. 2008 Nov 17;8:88. doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-8-88. BMC Biotechnol. 2008. PMID: 19014699 Free PMC article.
-
A dual-site gateway cloning system for simultaneous cloning of two genes for plant transformation.Plasmid. 2017 Jul;92:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.plasmid.2017.05.001. Epub 2017 May 9. Plasmid. 2017. PMID: 28499723
-
A novel gateway-compatible binary vector series (PC-GW) for flexible cloning of multiple genes for genetic transformation of plants.Plasmid. 2015 Sep;81:55-62. doi: 10.1016/j.plasmid.2015.06.003. Epub 2015 Jul 15. Plasmid. 2015. PMID: 26188330
-
Higher plant transformation: principles and molecular tools.Int J Dev Biol. 2013;57(6-8):483-94. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.130232mv. Int J Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 24166431 Review.
-
Modular cloning in plant cells.Trends Plant Sci. 2005 Mar;10(3):103-5. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2005.01.008. Trends Plant Sci. 2005. PMID: 15749466 Review.
Cited by
-
Shared and distinct functions of the pseudokinase CORYNE (CRN) in shoot and root stem cell maintenance of Arabidopsis.J Exp Bot. 2016 Aug;67(16):4901-15. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erw207. Epub 2016 May 26. J Exp Bot. 2016. PMID: 27229734 Free PMC article.
-
Powerful regulatory systems and post-transcriptional gene silencing resist increases in cellulose content in cell walls of barley.BMC Plant Biol. 2015 Feb 21;15:62. doi: 10.1186/s12870-015-0448-y. BMC Plant Biol. 2015. PMID: 25850007 Free PMC article.
-
The MYB36 transcription factor orchestrates Casparian strip formation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Aug 18;112(33):10533-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1507691112. Epub 2015 Jun 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26124109 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the Nrt2.6 gene in Arabidopsis thaliana: a link with plant response to biotic and abiotic stress.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e42491. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042491. Epub 2012 Aug 7. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22880003 Free PMC article.
-
The Ralstonia solanacearum type III effector RipAY targets plant redox regulators to suppress immune responses.Mol Plant Pathol. 2018 Jan;19(1):129-142. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12504. Epub 2016 Dec 27. Mol Plant Pathol. 2018. PMID: 27768829 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arabidopsis Genome Initiative (2000) Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 408: 796-815 - PubMed
-
- Batni S, Scalzetti L, Moody SA, Knox BE (1996) Characterization of the Xenopus rhodopsin gene. J Biol Chem 271: 3179-3186 - PubMed
-
- Bechtold N, Ellis J, Pelletier G (1993) In planta Agrobacterium mediated gene transfer by infiltration of adult Arabidopsis thaliana plants. C R Acad Sci Paris Life Sci 316: 1194-1199
-
- Böhner S, Lenk I, Rieping M, Herold M, Gatz C (1999) Transcriptional activator TGV mediates dexamethasone-inducible and tatracycline-inactivatable gene expression. Plant J 19: 87-95 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

