Effect of laparoscopic Roux-en Y gastric bypass on type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 14530719
- PMCID: PMC1360104
- DOI: 10.1097/01.sla.0000089851.41115.1b
Effect of laparoscopic Roux-en Y gastric bypass on type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate pre- and postoperative clinical parameters associated with improvement of diabetes up to 4 years after laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (LRYGBP) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Summary background data: The surgical treatment of morbid obesity leads to dramatic improvement in the comorbidity status of most patients with T2DM. However, little is known concerning what preoperative clinical factors are associated with postoperative long-term improvement in diabetes in the morbidly obese patient with diabetes. METHODS We evaluated pre- and postoperative data, including demographics, duration of diabetes, metabolic parameters, and clinical outcomes, in all patients with impaired fasting glucose (IFG) and type T2DM undergoing LRYGBP from July 1997 to May 2002.
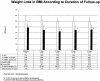
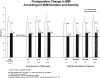
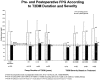
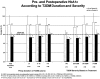
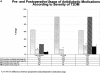
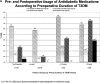
Results: During this 5-year period, 1160 patients underwent LRYGBP and 240 (21%) had IFG or T2DM. Follow up was possible in 191 of 240 patients (80%). There were 144 females (75%) with a mean preoperative age of 48 years (range, 26-67 years). After surgery, weight and body mass index decreased from 308 lbs and 50.1 kg/m2 to 211 lbs and 34 kg/m2 for a mean weight loss of 97 lbs and mean excess weight loss of 60%. Fasting plasma glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin concentrations returned to normal levels (83%) or markedly improved (17%) in all patients. A significant reduction in use of oral antidiabetic agents (80%) and insulin (79%) followed surgical treatment. Patients with the shortest duration (<5 years), the mildest form of T2DM (diet controlled), and the greatest weight loss after surgery were most likely to achieve complete resolution of T2DM.
Conclusion: LRYGBP resulted in significant weight loss (60% percent of excess body weight loss) and resolution (83%) of T2DM. Patients with the shortest duration and mildest form of T2DM had a higher rate of T2DM resolution after surgery, suggesting that early surgical intervention is warranted to increase the likelihood of rendering patients euglycemic.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long-term outcomes in gastric bypass patients with and without type 2 diabetes--Waitemata District Health Board experience.N Z Med J. 2013 Nov 22;126(1386):21-30. N Z Med J. 2013. PMID: 24316990
-
Long-term effects of laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass on diabetes mellitus, hypertension and dyslipidaemia in morbidly obese patients.Obes Surg. 2014 Nov;24(11):1835-42. doi: 10.1007/s11695-014-1310-2. Obes Surg. 2014. PMID: 25027982
-
Relationships between type 2 diabetes remission after gastric bypass and different weight loss metrics: arguments against excess weight loss in metabolic surgery.Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2016 Feb;12(2):274-82. doi: 10.1016/j.soard.2015.07.005. Epub 2015 Jul 9. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2016. PMID: 26476492
-
Impact of roux-en Y gastric bypass surgery on prognostic factors of type 2 diabetes mellitus: meta-analysis and systematic review.Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2015 Oct;31(7):653-62. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.2622. Epub 2014 Dec 17. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2015. PMID: 25387821 Review.
-
Role of bariatric-metabolic surgery in the treatment of obese type 2 diabetes with body mass index <35 kg/m2: a literature review.Diabetes Technol Ther. 2012 Apr;14(4):365-72. doi: 10.1089/dia.2011.0127. Epub 2011 Dec 16. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2012. PMID: 22176155 Review.
Cited by
-
Meta-analysis of bariatric surgery versus non-surgical treatment for type 2 diabetes mellitus.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 27;7(52):87511-87522. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11961. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27626180 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in gastrointestinal hormone responses, insulin sensitivity, and beta-cell function within 2 weeks after gastric bypass in non-diabetic subjects.Obes Surg. 2012 Jul;22(7):1084-96. doi: 10.1007/s11695-012-0621-4. Obes Surg. 2012. PMID: 22359255
-
Metabolic syndrome and the hepatorenal reflex.Surg Neurol Int. 2016 Sep 13;7:83. doi: 10.4103/2152-7806.190438. eCollection 2016. Surg Neurol Int. 2016. PMID: 27656314 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of bariatric surgery on glucose homeostasis and type 2 diabetes.Gastroenterology. 2012 Oct;143(4):897-912. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.07.114. Epub 2012 Aug 8. Gastroenterology. 2012. PMID: 22885332 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Equivalent weight loss with marked metabolic benefit observed in a matched cohort with and without type 2 diabetes 12 months following gastric bypass surgery.Obes Surg. 2012 Nov;22(11):1723-9. doi: 10.1007/s11695-012-0719-8. Obes Surg. 2012. PMID: 22895804 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Higa KD, Boone KB, Ho T. Complications of the laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: 1, 040 patients—what have we learned? Obes Surg. 2000;10:509–513. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen NT, Ho HS, Palmer LS, et al. A comparison study of laparoscopic versus open gastric bypass for morbid obesity. J Am Coll Surg. 2000;191:149–155. - PubMed
-
- Wittgrove A, Clark G. Laparoscopic gastric bypass, Roux-en-Y 500 patients: technique and results, with 3–60 month follow-up. Obes Surg. 2000;10:233–239. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

