A human-mouse chimera of the alpha3alpha4alpha5(IV) collagen protomer rescues the renal phenotype in Col4a3-/- Alport mice
- PMID: 14507670
- PMCID: PMC1868284
- DOI: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)63520-1
A human-mouse chimera of the alpha3alpha4alpha5(IV) collagen protomer rescues the renal phenotype in Col4a3-/- Alport mice
Abstract
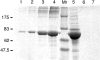
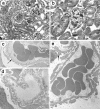
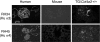
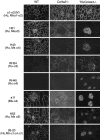
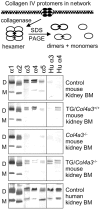
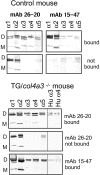
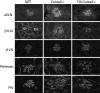
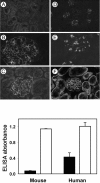
Collagen IV is a major structural component of basement membranes. In the glomerular basement membrane (GBM) of the kidney, the alpha3, alpha4, and alpha5(IV) collagen chains form a distinct network that is essential for the long-term stability of the glomerular filtration barrier, and is absent in most patients affected with Alport syndrome, a progressive inherited nephropathy associated with mutation in COL4A3, COL4A4, or COL4A5 genes. To investigate, in vivo, the regulation of the expression, assembly, and function of the alpha3alpha4alpha5(IV) protomer, we have generated a yeast artificial chromosome transgenic line of mice carrying the human COL4A3-COL4A4 locus. Transgenic mice expressed the human alpha3 and alpha4(IV) chains in a tissue-specific manner. In the kidney, when expressed onto a Col4a3(-/-) background, the human alpha3(IV) chain restored the expression of and co-assembled with the mouse alpha4 and alpha5(IV) chains specifically at sites where the human alpha3(IV) was expressed, demonstrating that the expression of all three chains is required for network assembly. The co-assembly of the human and mouse chains into a hybrid network in the GBM restores a functional GBM and rescues the Alport phenotype, providing further evidence that defective assembly of the alpha3-alpha4-alpha5(IV) protomer, caused by mutations in any of the three chains, is the pathogenic mechanism responsible for the disease. This line of mice, humanized for the alpha3(IV) collagen chain, will also provide a valuable model for studying the pathogenesis of Goodpasture syndrome, an autoimmune disease caused by antibodies against this chain.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Endothelial cell-specific collagen type IV-α3 expression does not rescue Alport syndrome in Col4a3-/- mice.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019 May 1;316(5):F830-F837. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00556.2018. Epub 2019 Feb 6. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30724107 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of alpha3/alpha4(IV) collagen from the glomerular basement membrane induces a strain-dependent isoform switch to alpha5alpha6(IV) collagen associated with longer renal survival in Col4a3-/- Alport mice.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006 Jul;17(7):1962-9. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2006020165. Epub 2006 Jun 12. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006. PMID: 16769745
-
Collagen IV diseases: A focus on the glomerular basement membrane in Alport syndrome.Matrix Biol. 2017 Jan;57-58:45-54. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2016.08.005. Epub 2016 Aug 27. Matrix Biol. 2017. PMID: 27576055 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Laminin-1 reexpression in Alport mouse glomerular basement membranes.Kidney Int. 2003 Mar;63(3):826-34. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2003.00800.x. Kidney Int. 2003. PMID: 12631063
-
Organization and expression of basement membrane collagen IV genes and their roles in human disorders.J Biochem. 1998 May;123(5):767-76. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a022003. J Biochem. 1998. PMID: 9562604 Review.
Cited by
-
Deletion of CD151 results in a strain-dependent glomerular disease due to severe alterations of the glomerular basement membrane.Am J Pathol. 2008 Oct;173(4):927-37. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2008.071149. Epub 2008 Sep 11. Am J Pathol. 2008. PMID: 18787104 Free PMC article.
-
Murine membranous nephropathy: immunization with α3(IV) collagen fragment induces subepithelial immune complexes and FcγR-independent nephrotic syndrome.J Immunol. 2012 Apr 1;188(7):3268-77. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1103368. Epub 2012 Feb 27. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22371398 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoscale protein architecture of the kidney glomerular basement membrane.Elife. 2013 Oct 8;2:e01149. doi: 10.7554/eLife.01149. Elife. 2013. PMID: 24137544 Free PMC article.
-
Human podocytes adhere to the KRGDS motif of the alpha3alpha4alpha5 collagen IV network.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008 Apr;19(4):677-84. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2007070793. Epub 2008 Jan 30. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008. PMID: 18235087 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the NC1 domain of {alpha}3 chain as critical for {alpha}3{alpha}4{alpha}5 type IV collagen network assembly.J Biol Chem. 2010 Dec 31;285(53):41874-85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.149534. Epub 2010 Sep 16. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20847057 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boutaud A, Borza DB, Bondar O, Gunwar S, Netzer KO, Singh N, Ninomiya Y, Sado Y, Noelken ME, Hudson BG: Type IV collagen of the glomerular basement membrane. Evidence that the chain specificity of network assembly is encoded by the noncollagenous NC1 domains. J Biol Chem 2000, 275:30716-30724 - PubMed
-
- Borza DB, Bondar O, Todd P, Sundaramoorthy M, Sado Y, Ninomiya Y, Hudson BG: Quaternary organization of the Goodpasture autoantigen, the alpha 3(IV) collagen chain: sequestration of two cryptic autoepitopes by intra-protomer interactions with the alpha 4 and alpha 5 NC1 domains. J Biol Chem 2002, 277:40075-40083 - PubMed
-
- Timpl R, Wiedemann H, van Delden V, Furthmayr H, Kuhn KA: Network model for the organization of type IV collagen molecules in basement membranes. Eur J Biochem 1981, 120:203-211 - PubMed
-
- Yurchenco PD, Furthmayr H: Self-assembly of basement membrane collagen. Biochemistry 1984, 23:1839-1850 - PubMed
-
- Gunwar S, Ballester F, Noelken ME, Sado Y, Ninomiya Y, Hudson BG: Glomerular basement membrane. Identification of a novel disulfide-cross-linked network of alpha3, alpha4, and alpha5 chains of type IV collagen and its implications for the pathogenesis of Alport syndrome. J Biol Chem 1998, 273:8767-8775 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

