An Alu transposition model for the origin and expansion of human segmental duplications
- PMID: 14505274
- PMCID: PMC1180605
- DOI: 10.1086/378594
An Alu transposition model for the origin and expansion of human segmental duplications
Abstract
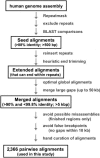
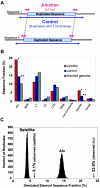
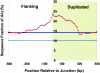
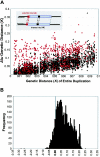
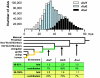
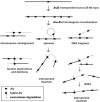
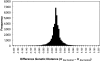
Relative to genomes of other sequenced organisms, the human genome appears particularly enriched for large, highly homologous segmental duplications (> or =90% sequence identity and > or =10 kbp in length). The molecular basis for this enrichment is unknown. We sought to gain insight into the mechanism of origin, by systematically examining sequence features at the junctions of duplications. We analyzed 9,464 junctions within regions of high-quality finished sequence from a genomewide set of 2,366 duplication alignments. We observed a highly significant (P<.0001) enrichment of Alu short interspersed element (SINE) sequences near or within the junction. Twenty-seven percent of all segmental duplications terminated within an Alu repeat. The Alu junction enrichment was most pronounced for interspersed segmental duplications separated by > or =1 Mb of intervening sequence. Alu elements at the junctions showed higher levels of divergence, consistent with Alu-Alu-mediated recombination events. When we classified Alu elements into major subfamilies, younger elements (AluY and AluS) accounted for the enrichment, whereas the oldest primate family (AluJ) showed no enrichment. We propose that the primate-specific burst of Alu retroposition activity (which occurred 35-40 million years ago) sensitized the ancestral human genome for Alu-Alu-mediated recombination events, which, in turn, initiated the expansion of gene-rich segmental duplications and their subsequent role in nonallelic homologous recombination.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Shuffling of genes within low-copy repeats on 22q11 (LCR22) by Alu-mediated recombination events during evolution.Genome Res. 2003 Dec;13(12):2519-32. doi: 10.1101/gr.1549503. Genome Res. 2003. PMID: 14656960 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the human Alu Ye lineage.BMC Evol Biol. 2005 Feb 22;5:18. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-5-18. BMC Evol Biol. 2005. PMID: 15725352 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-genome analysis of Alu repeat elements reveals complex evolutionary history.Genome Res. 2004 Nov;14(11):2245-52. doi: 10.1101/gr.2693004. Genome Res. 2004. PMID: 15520288 Free PMC article.
-
Alu elements and the human genome.Genetica. 2000;108(1):57-72. doi: 10.1023/a:1004099605261. Genetica. 2000. PMID: 11145422 Review.
-
Alu repeats and human genomic diversity.Nat Rev Genet. 2002 May;3(5):370-9. doi: 10.1038/nrg798. Nat Rev Genet. 2002. PMID: 11988762 Review.
Cited by
-
The contribution of alu elements to mutagenic DNA double-strand break repair.PLoS Genet. 2015 Mar 11;11(3):e1005016. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005016. eCollection 2015 Mar. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 25761216 Free PMC article.
-
Duplicative and conservative transpositions of larval serum protein 1 genes in the genus Drosophila.Genetics. 2004 Sep;168(1):253-64. doi: 10.1534/genetics.103.025916. Genetics. 2004. PMID: 15454541 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of uncommon recurrent Potocki-Lupski syndrome-associated duplications and the distribution of rearrangement types and mechanisms in PTLS.Am J Hum Genet. 2010 Mar 12;86(3):462-70. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2010.02.001. Epub 2010 Feb 25. Am J Hum Genet. 2010. PMID: 20188345 Free PMC article.
-
Copy number variation in human health, disease, and evolution.Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2009;10:451-81. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genom.9.081307.164217. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2009. PMID: 19715442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Duplication processes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae haploid strains.Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Nov 3;33(19):6319-26. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki941. Print 2005. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 16269823 Free PMC article.
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- NCBI Genome Assembly, ftp://ftp.ncbi.nih.gov/genomes/H_sapiens/ (for the build 30 genome assembly)
-
- RepeatMasker Server Home Page, http://repeatmasker.genome.washington.edu/
-
- UCSC Genome Bioinformatics Home Page, http://genome.ucsc.edu/ (for build 30 genome assembly and annotation)
References
-
- Bailey JA, Gu Z, Clark RA, Reinert K, Samonte RV, Schwartz S, Adams MD, Myers EW, Li PW, Eichler EE (2002) Recent segmental duplications in the human genome. Science 297:1003–1007 - PubMed
-
- Batzer MA, Deininger PL (2002) Alu repeats and human genomic diversity. Nat Rev Genet 3:370–379 - PubMed
-
- Calabretta B, Robberson DL, Barrera-Saldana HA, Lambrou TP, Saunders GF (1982) Genome instability in a region of human DNA enriched in Alu repeat sequences. Nature 296:219–225 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

