Coronavirus 229E-related pneumonia in immunocompromised patients
- PMID: 13130404
- PMCID: PMC7107892
- DOI: 10.1086/377612
Coronavirus 229E-related pneumonia in immunocompromised patients
Abstract
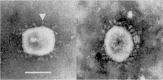
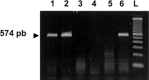
Coronaviruses strains 229E and OC43 have been associated with various respiratory illnesses ranging from the self-resolving common cold to severe pneumonia. Although chronic underlying conditions are major determinants of severe respiratory virus infections, few data about coronavirus-related pneumonia in immunocompromised patients are available. Here we report 2 well-documented cases of pneumonia related to coronavirus 229E, each with a different clinical presentation. Diagnosis was made on the basis of viral culture and electron microscopy findings that exhibited typical crown-like particles and through amplification of the viral genome by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction. On the basis of this report, coronaviruses should be considered as potential causative microorganisms of pneumonia in immunocompromised patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Development of one-step, real-time, quantitative reverse transcriptase PCR assays for absolute quantitation of human coronaviruses OC43 and 229E.J Clin Microbiol. 2005 Nov;43(11):5452-6. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.11.5452-5456.2005. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16272469 Free PMC article.
-
Direct diagnosis of human respiratory coronaviruses 229E and OC43 by the polymerase chain reaction.J Virol Methods. 2001 Sep;97(1-2):59-66. doi: 10.1016/s0166-0934(01)00343-3. J Virol Methods. 2001. PMID: 11483217 Free PMC article.
-
Coronavirus HKU1 and other coronavirus infections in Hong Kong.J Clin Microbiol. 2006 Jun;44(6):2063-71. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02614-05. J Clin Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16757599 Free PMC article.
-
[Coronaviruses as the cause of respiratory infections].Internist (Berl). 2019 Nov;60(11):1136-1145. doi: 10.1007/s00108-019-00671-5. Internist (Berl). 2019. PMID: 31455974 Free PMC article. Review. German.
-
Update on rhinovirus and coronavirus infections.Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2011 Aug;32(4):433-46. doi: 10.1055/s-0031-1283283. Epub 2011 Aug 19. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2011. PMID: 21858748 Review.
Cited by
-
Indomethacin inhibits human seasonal coronaviruses at late stages of viral replication in lung cells: Impact on virus-induced COX-2 expression.J Virus Erad. 2024 Sep 1;10(3):100387. doi: 10.1016/j.jve.2024.100387. eCollection 2024 Sep. J Virus Erad. 2024. PMID: 39399815 Free PMC article.
-
Human coronaviruses activate and hijack the host transcription factor HSF1 to enhance viral replication.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Sep 7;81(1):386. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05370-5. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39243335 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-RBD IgG antibodies from endemic coronaviruses do not protect against the acquisition of SARS-CoV-2 infection among exposed uninfected individuals.Front Immunol. 2024 May 23;15:1396603. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1396603. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38846944 Free PMC article.
-
Insights from Real-World Practice: The Dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 Infections and Vaccinations in a Large German Multiple Sclerosis Cohort.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Mar 3;12(3):265. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12030265. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38543899 Free PMC article.
-
Time to death and its predictors among adult patients with COVID-19: A retrospective cohort study in Ethiopia.Front Epidemiol. 2023 Jan 17;2:1065184. doi: 10.3389/fepid.2022.1065184. eCollection 2022. Front Epidemiol. 2023. PMID: 38455333 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Soubani AO, Miller KB, Hassoun PM. Pulmonary complications of bone marrow transplantatio. Chest. 1996;109:1066–77. - PubMed
-
- Hendley JO, Fishburne HB, Gwaltney JM., Jr Coronavirus infections in working adults. Eight-year study with 229 E and OC 4. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1972;105:805–11. - PubMed
-
- Wenzel RP, Hendley JO, Davies JA, Gwaltney JM., Jr Coronavirus infections in military recruits. Three-year study with coronavirus strains OC43 and 229. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1974;109:621–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

