D-beta-hydroxybutyrate rescues mitochondrial respiration and mitigates features of Parkinson disease
- PMID: 12975474
- PMCID: PMC193668
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI18797
D-beta-hydroxybutyrate rescues mitochondrial respiration and mitigates features of Parkinson disease
Abstract
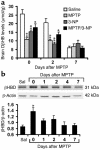
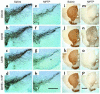
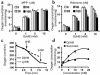
Parkinson disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by a loss of the nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurons accompanied by a deficit in mitochondrial respiration. 1-Methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) is a neurotoxin that causes dopaminergic neurodegeneration and a mitochondrial deficit reminiscent of PD. Here we show that the infusion of the ketone body d-beta-hydroxybutyrate (DbetaHB) in mice confers partial protection against dopaminergic neurodegeneration and motor deficits induced by MPTP. These effects appear to be mediated by a complex II-dependent mechanism that leads to improved mitochondrial respiration and ATP production. Because of the safety record of ketone bodies in the treatment of epilepsy and their ability to penetrate the blood-brain barrier, DbetaHB may be a novel neuroprotective therapy for PD.
Figures
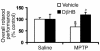
Similar articles
-
Protective role of SIRT5 against motor deficit and dopaminergic degeneration in MPTP-induced mice model of Parkinson's disease.Behav Brain Res. 2015 Mar 15;281:215-21. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2014.12.035. Epub 2014 Dec 23. Behav Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25541039
-
L-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase II protects in a model of Parkinson's disease.Ann Neurol. 2004 Jul;56(1):51-60. doi: 10.1002/ana.20133. Ann Neurol. 2004. PMID: 15236401
-
Systemically administered neuregulin-1β1 rescues nigral dopaminergic neurons via the ErbB4 receptor tyrosine kinase in MPTP mouse models of Parkinson's disease.J Neurochem. 2015 May;133(4):590-7. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13026. Epub 2015 Jan 26. J Neurochem. 2015. PMID: 25581060
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson's disease.Biochem Soc Symp. 1999;66:85-97. doi: 10.1042/bss0660085. Biochem Soc Symp. 1999. PMID: 10989660 Review.
-
KTX 0101: a potential metabolic approach to cytoprotection in major surgery and neurological disorders.CNS Drug Rev. 2005 Summer;11(2):113-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1527-3458.2005.tb00265.x. CNS Drug Rev. 2005. PMID: 16007235 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Low-Carbohydrate High-Fat Diet: A SWOC Analysis.Metabolites. 2022 Nov 17;12(11):1126. doi: 10.3390/metabo12111126. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 36422267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Time-dependent modulation of rat serum paraoxonase 1 activity by fasting.Pflugers Arch. 2007 Mar;453(6):831-7. doi: 10.1007/s00424-006-0174-2. Epub 2006 Dec 5. Pflugers Arch. 2007. PMID: 17146679
-
Non-invasive assessment of disease progression and neuroprotective effects of dietary coconut oil supplementation in the ALS SOD1G93A mouse model: A 1H-magnetic resonance spectroscopic study.Neuroimage Clin. 2018;20:1092-1105. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2018.09.011. Epub 2018 Sep 19. Neuroimage Clin. 2018. PMID: 30368196 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Ketogenic Diets in Neurodegenerative Diseases (Alzheimer's Disease and Parkinson's Disease).Nutrients. 2019 Jan 15;11(1):169. doi: 10.3390/nu11010169. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 30650523 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Combined Influences of Exercise, Diet and Sleep on Neuroplasticity.Front Psychol. 2022 Apr 26;13:831819. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.831819. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 35558719 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fahn, S., and Przedborski, S. 2000. Parkinsonism. In Merritt’s neurology. L.P. Rowland, editor. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. New York, New York, USA. 679–693.
-
- Przedborski, S., Kostic, V., Giladi, N., and Eidelberg, D. 2003. Dopaminergic system in Parkinson’s disease. In Dopamine receptors and transporters. A. Sidhu, M. Laruelle, and P. Vernier, editors. Marcel Dekker Inc. New York, New York, USA. 363–402.
-
- Nicklas WJ, Yougster SK, Kindt MV, Heikkila RE. MPTP, MPP+ and mitochondrial function. Life Sci. 1987;40:721–729. - PubMed
-
- Langston JW, Ballard P, Irwin I. Chronic parkinsonism in humans due to a product of meperidine-analog synthesis. Science. 1983;219:979–980. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

