A structural approach to the role of CCN (CYR61/CTGF/NOV) proteins in tumourigenesis
- PMID: 12969515
- PMCID: PMC194616
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2867-3-15
A structural approach to the role of CCN (CYR61/CTGF/NOV) proteins in tumourigenesis
Abstract
The CCN (CYR61 [Cystein-rich61]/CTGF [connective tissue growth factor]/NOV [Nephroblastoma overexpressed]) proteins constitute a family of regulatory factors involved in many aspects of cell proliferation and differentiation. An increasing body of evidence indicates that abnormal expression of the CCN proteins is associated to tumourgenesis. The multimodular architecture of the CCN proteins, and the production of truncated isoforms in tumours, raise interesting questions regarding the participation of each individual module to the various biological properties of these proteins. In this article, we review the current data regarding the involvement of CCN proteins in tumourigenesis. We also attempt to provide structural basis for the stimulatory and inhibitory functions of the full length and truncated CCN proteins that are expressed in various tumour tissues.
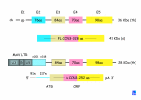
Figures




Similar articles
-
Differential expression of the CCN family members Cyr61, CTGF and Nov in human breast cancer.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2004 Dec;11(4):781-91. doi: 10.1677/erc.1.00825. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2004. PMID: 15613452
-
NOV (nephroblastoma overexpressed) and the CCN family of genes: structural and functional issues.Mol Pathol. 2001 Apr;54(2):57-79. doi: 10.1136/mp.54.2.57. Mol Pathol. 2001. PMID: 11322167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential expression of CCN family members CYR611, CTGF and NOV in gastric cancer and their association with disease progression.Oncol Rep. 2016 Nov;36(5):2517-2525. doi: 10.3892/or.2016.5074. Epub 2016 Sep 8. Oncol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27633176 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of angiogenesis and endothelial cell function by connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) and cysteine-rich 61 (CYR61).Angiogenesis. 2002;5(3):153-65. doi: 10.1023/a:1023823803510. Angiogenesis. 2002. PMID: 12831056
-
CCN proteins: multifunctional signalling regulators.Lancet. 2004 Jan 3;363(9402):62-4. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)15172-0. Lancet. 2004. PMID: 14723997 Review.
Cited by
-
Cysteine-rich protein 61 (CCN1) domain-specific stimulation of matrix metalloproteinase-1 expression through αVβ3 integrin in human skin fibroblasts.J Biol Chem. 2013 Apr 26;288(17):12386-94. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.424358. Epub 2013 Mar 15. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23504324 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Alternative splicing of CCN mRNAs .... it has been upon us.J Cell Commun Signal. 2009 Jun;3(2):153-7. doi: 10.1007/s12079-009-0051-9. Epub 2009 Apr 28. J Cell Commun Signal. 2009. PMID: 19399643 Free PMC article.
-
CCN3 and calcium signaling.Cell Commun Signal. 2003 Aug 15;1(1):1. doi: 10.1186/1478-811X-1-1. Cell Commun Signal. 2003. PMID: 14606958 Free PMC article.
-
CCN1 promotes vascular endothelial growth factor secretion through αvβ 3 integrin receptors in breast cancer.J Cell Commun Signal. 2014 Mar;8(1):23-7. doi: 10.1007/s12079-013-0214-6. Epub 2013 Dec 12. J Cell Commun Signal. 2014. PMID: 24338441 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Expression of CCN family of genes in human skin in vivo and alterations by solar-simulated ultraviolet irradiation.J Cell Commun Signal. 2009 Mar;3(1):19-23. doi: 10.1007/s12079-009-0044-8. Epub 2009 Mar 25. J Cell Commun Signal. 2009. PMID: 19319669 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

