Severe acute respiratory syndrome: temporal stability and geographic variation in case-fatality rates and doubling times
- PMID: 12967499
- PMCID: PMC3020622
- DOI: 10.3201/eid0908.030334
Severe acute respiratory syndrome: temporal stability and geographic variation in case-fatality rates and doubling times
Abstract
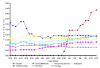
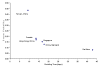
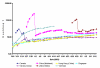
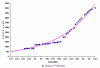
We analyzed temporal stability and geographic trends in cumulative case-fatality rates and average doubling times of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS). In part, we account for correlations between case-fatality rates and doubling times through differences in control measures. Factors that may alter future estimates of case-fatality rates, reasons for heterogeneity in doubling times among countries, and implications for the control of SARS are discussed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Relationship between the severity, course, fatality of severe acute respiratory syndrome patients and the timing of hospitalization].Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2004 Apr;25(4):308-11. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2004. PMID: 15231197 Chinese.
-
[SARS--two months later. Development in China during the immediate future will probably determine the situation in the world].Lakartidningen. 2003 May 28;100(22):1970-3. Lakartidningen. 2003. PMID: 12833728 Swedish. No abstract available.
-
[Epidemiological features of severe acute respiratory syndrome in Beijing].Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2003 Dec;24(12):1096-9. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2003. PMID: 14761623 Chinese.
-
[Severe acute respiratory syndrome: a global overview of the epidemic].Salud Publica Mex. 2003 May-Jun;45(3):211-20. Salud Publica Mex. 2003. PMID: 12870423 Review. Spanish.
-
Clinical brief: severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS).AAOHN J. 2003 Jul;51(7):303-5. AAOHN J. 2003. PMID: 12880233 Review.
Cited by
-
Early epidemiological assessment of the virulence of emerging infectious diseases: a case study of an influenza pandemic.PLoS One. 2009 Aug 31;4(8):e6852. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006852. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19718434 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 antibody seroprevalence in India, August-September, 2020: findings from the second nationwide household serosurvey.Lancet Glob Health. 2021 Mar;9(3):e257-e266. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(20)30544-1. Epub 2021 Jan 27. Lancet Glob Health. 2021. PMID: 33515512 Free PMC article.
-
Geographical variation in case fatality rate and doubling time during the COVID-19 pandemic.Epidemiol Infect. 2020 Jul 27;148:e163. doi: 10.1017/S0950268820001685. Epidemiol Infect. 2020. PMID: 32713371 Free PMC article.
-
The determinants of the changing speed of spread of COVID-19 across Italy.Epidemiol Infect. 2022 May 6;150:1-26. doi: 10.1017/S095026882200084X. Online ahead of print. Epidemiol Infect. 2022. PMID: 35514091 Free PMC article.
-
A comparative epidemiologic analysis of SARS in Hong Kong, Beijing and Taiwan.BMC Infect Dis. 2010 Mar 6;10:50. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-10-50. BMC Infect Dis. 2010. PMID: 20205928 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cumulative number of reported cases of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS). Geneva: World Health Organization, 2003. Cited May 12, 2003. Available from: URL: http://www.who.int/csr/sarscountry/en/
-
- Donnelly CA, Ghani AC, Leung GM, Hedley AJ, Fraser C, Riley S, et al. Epidemiological determinants of spread of causal agent of severe acute respiratory syndrome in Hong Kong. Lancet online May 7, 2003. Available from: URL: http://image.thelancet.com/extras/03art4453web.pdf - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cleveland WS. Robust locally weighted regression and smoothing scatterplots. J Am Stat Assoc. 1979;74:829–36. 10.2307/2286407 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
