Mapping Drosophila mutations with molecularly defined P element insertions
- PMID: 12960394
- PMCID: PMC196893
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1832753100
Mapping Drosophila mutations with molecularly defined P element insertions
Abstract
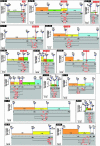
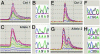
The isolation of chemically induced mutations in forward genetic screens is one of the hallmarks of Drosophila genetics. However, mapping the corresponding loci and identifying the molecular lesions associated with these mutations are often difficult and labor-intensive. Two mapping methods are most often used in flies: meiotic recombination mapping with marked chromosomes and deficiency mapping. The availability of the fly genome sequence allows the establishment and usage of molecular markers. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms have therefore recently been used to map several genes. Here we show that thousands of molecularly mapped P element insertions in fly strains that are publicly available provide a powerful alternative method to single-nucleotide polymorphism mapping. We present a strategy that allows mapping of lethal mutations, as well as viable mutations with visible phenotypes, with minimal resources. The most important unknown in using recombination rates to map at high resolution is how accurately recombination data correlate with molecular maps in small intervals. We therefore surveyed distortions of recombination rates in intervals <500 kb. We document the extent of distortions between the recombination and molecular maps and describe the required steps to map with an accuracy of <50 kb. Finally, we describe a recently developed method to determine molecular lesions in 50-kb intervals by using a heteroduplex DNA mutation detection system. Our data show that this mapping approach is inexpensive, efficient, and precise, and that it significantly broadens the application of P elements in Drosophila.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genetic mapping with SNP markers in Drosophila.Nat Genet. 2001 Dec;29(4):475-81. doi: 10.1038/ng773. Nat Genet. 2001. PMID: 11726933
-
Recovery of DNA sequences flanking P-element insertions in Drosophila: inverse PCR and plasmid rescue.Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2009 Apr;2009(4):pdb.prot5199. doi: 10.1101/pdb.prot5199. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2009. PMID: 20147142
-
Mapping of Drosophila mutations using site-specific male recombination.Genetics. 1998 May;149(1):157-63. doi: 10.1093/genetics/149.1.157. Genetics. 1998. PMID: 9584093 Free PMC article.
-
Genetics of genetics in Drosophila: P elements serving the study of homologous recombination, gene conversion and targeting.Chromosoma. 1995 Jul;103(10):659-68. doi: 10.1007/BF00344226. Chromosoma. 1995. PMID: 7664612 Review.
-
Drosophila Genetic Resource and Stock Center; The National BioResource Project.Exp Anim. 2010;59(2):125-38. doi: 10.1538/expanim.59.125. Exp Anim. 2010. PMID: 20484846 Review.
Cited by
-
Ero1L, a thiol oxidase, is required for Notch signaling through cysteine bridge formation of the Lin12-Notch repeats in Drosophila melanogaster.J Cell Biol. 2008 Sep 22;182(6):1113-25. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200805001. J Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18809725 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical mutagens, transposons, and transgenes to interrogate gene function in Drosophila melanogaster.Methods. 2014 Jun 15;68(1):15-28. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2014.02.025. Epub 2014 Feb 28. Methods. 2014. PMID: 24583113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A screen for X-linked mutations affecting Drosophila photoreceptor differentiation identifies Casein kinase 1α as an essential negative regulator of wingless signaling.Genetics. 2012 Feb;190(2):601-16. doi: 10.1534/genetics.111.133827. Epub 2011 Nov 17. Genetics. 2012. PMID: 22095083 Free PMC article.
-
The dominant cold-sensitive Out-cold mutants of Drosophila melanogaster have novel missense mutations in the voltage-gated sodium channel gene paralytic.Genetics. 2008 Oct;180(2):873-84. doi: 10.1534/genetics.108.090951. Epub 2008 Aug 24. Genetics. 2008. PMID: 18723887 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant lysosomal carbohydrate storage accompanies endocytic defects and neurodegeneration in Drosophila benchwarmer.J Cell Biol. 2005 Jul 4;170(1):127-39. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200412001. J Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15998804 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lindsley, D. L. & Zimm, G. G. (1992) The Genome of Drosophila melanogaster (Academic, San Diego).
-
- Adams, M. D., Celniker, S. E., Holt, R. A., Evans, C. A., Gocayne, J. D., Amanatides, P. G., Scherer, S. E., Li, P. W., Hoskins, R. A., Galle, R. F., et al. (2000) Science 287, 2185–2195. - PubMed
-
- Berger, J., Suzuki, T., Senti, K. A., Stubbs, J., Schaffner, G. & Dickson, B. J. (2001) Nat. Genet. 29, 475–481. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

