TLP, a novel modulator of TGF-beta signaling, has opposite effects on Smad2- and Smad3-dependent signaling
- PMID: 12941698
- PMCID: PMC202370
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg428
TLP, a novel modulator of TGF-beta signaling, has opposite effects on Smad2- and Smad3-dependent signaling
Abstract
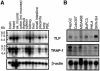
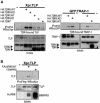
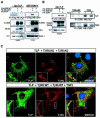
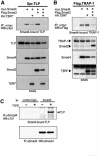
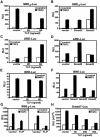
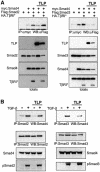
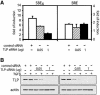
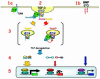
Transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) is a multifunctional cytokine signaling to the nucleus through cell surface transmembrane receptor serine/threonine kinases and cytoplasmic effectors, including Smad proteins. We describe a novel modulator of this pathway, TLP (TRAP-1-like protein), which is 25% identical to the previously described Smad4 chaperone, TRAP-1, and shows identical expression patterns in human tissues. Endogenous TLP associates with both active and kinase-deficient TGF-beta and activin type II receptors, but interacts with the common-mediator Smad4 only in the presence of TGF-beta/activin signaling. Overexpression of TLP represses the ability of TGF-beta to induce transcription from SBE-Luc, a Smad3/4-specific reporter, while it potentiates transcription from ARE-Luc, a Smad2/4-specific reporter. Consistent with this, TLP inhibits the formation of Smad3/4 complexes in the absence of effects on phosphorylation of Smad3, while it affects neither Smad2 phosphorylation nor hetero-oligomerization. We propose that TLP might regulate the balance of Smad2 and Smad3 signaling by localizing Smad4 intracellularly, thus contributing to cellular specificity of TGF-beta transcriptional responses in both normal and pathophysiology.
Figures


Similar articles
-
TGF-beta receptor-mediated signalling through Smad2, Smad3 and Smad4.EMBO J. 1997 Sep 1;16(17):5353-62. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.17.5353. EMBO J. 1997. PMID: 9311995 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between Smad anchor for receptor activation and Smad3 is not essential for TGF-beta/Smad3-mediated signaling.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001 Mar;281(5):1100-5. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2001.4489. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001. PMID: 11243848
-
Targeting endogenous transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling in SMAD4-deficient human pancreatic carcinoma cells inhibits their invasive phenotype1.Cancer Res. 2004 Aug 1;64(15):5200-11. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0018. Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15289325
-
Receptor-regulated Smads in TGF-beta signaling.Front Biosci. 2003 Sep 1;8:s1280-303. doi: 10.2741/1149. Front Biosci. 2003. PMID: 12957874 Review.
-
Intracellular signaling of the TGF-beta superfamily by Smad proteins.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999;886:73-82. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1999.tb09402.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999. PMID: 10667205 Review.
Cited by
-
In vivo Functional Genomics for Undiagnosed Patients: The Impact of Small GTPases Signaling Dysregulation at Pan-Embryo Developmental Scale.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 May 25;9:642235. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.642235. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34124035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Requirement of a dynein light chain in TGFbeta/Smad3 signaling.J Cell Physiol. 2009 Dec;221(3):707-15. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21910. J Cell Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19711352 Free PMC article.
-
Smad3 as a mediator of the fibrotic response.Int J Exp Pathol. 2004 Apr;85(2):47-64. doi: 10.1111/j.0959-9673.2004.00377.x. Int J Exp Pathol. 2004. PMID: 15154911 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bone morphogenetic protein-7 inhibits proximal tubular epithelial cell Smad3 signaling via increased SnoN expression.Am J Pathol. 2010 Mar;176(3):1139-47. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.090459. Epub 2010 Jan 21. Am J Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20093492 Free PMC article.
-
Cell contact-dependent regulation of epithelial-myofibroblast transition via the rho-rho kinase-phospho-myosin pathway.Mol Biol Cell. 2007 Mar;18(3):1083-97. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e06-07-0602. Epub 2007 Jan 10. Mol Biol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17215519 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Charng M.J., Zhang,D., Kinnunen,P. and Schneider,M.D. (1998) A novel protein distinguishes between quiescent and activated forms of the type I transforming growth factor beta receptor. J. Biol. Chem., 273, 9365–9368. - PubMed
-
- Chen R.H., Miettinen,P.J., Maruoka,E.M., Choy,L. and Derynck,R. (1995) A WD-domain protein that is associated with and phos phorylated by the type II TGF-beta receptor. Nature, 377, 548–552. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

