Genetic contributions to generalized arousal of brain and behavior
- PMID: 12930901
- PMCID: PMC196919
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1633773100
Genetic contributions to generalized arousal of brain and behavior
Abstract
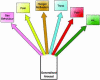
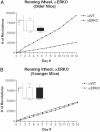
We have identified a generalized arousal component in the behavior of mice. Analyzed by mathematical/statistical approaches across experiments, investigators, and mouse populations, it accounts for about 1/3 of the variance in arousal-related measures. Knockout of the gene coding for the classical estrogen receptor (ER-alpha), a ligand-activated transcription factor, greatly reduced arousal responses. In contrast, disrupting the gene for a likely gene duplication product, ER-beta, did not have these effects. A combination of mathematical and genetic approaches to arousal in an experimentally tractable mammal opens up analysis of a CNS function of considerable theoretical and practical significance.
Figures
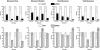
Similar articles
-
How generalized CNS arousal strengthens sexual arousal (and vice versa).Horm Behav. 2011 May;59(5):689-95. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2010.10.005. Epub 2010 Oct 13. Horm Behav. 2011. PMID: 20950622 Review.
-
Estrogen response element-independent estrogen receptor (ER)-alpha signaling does not rescue sexual behavior but restores normal testosterone secretion in male ERalpha knockout mice.Endocrinology. 2007 Nov;148(11):5288-94. doi: 10.1210/en.2007-0673. Epub 2007 Aug 2. Endocrinology. 2007. PMID: 17673514
-
Roles of estrogen receptor-alpha gene expression in reproduction-related behaviors in female mice.Endocrinology. 1998 Dec;139(12):5070-81. doi: 10.1210/endo.139.12.6357. Endocrinology. 1998. PMID: 9832446
-
Estrogen receptor-beta gene disruption potentiates estrogen-inducible aggression but not sexual behaviour in male mice.Eur J Neurosci. 2006 Apr;23(7):1860-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2006.04703.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16623843
-
Development of a sexually differentiated behavior and its underlying CNS arousal functions.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2007;79:37-59. doi: 10.1016/S0070-2153(06)79002-0. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2007. PMID: 17498546 Review.
Cited by
-
siRNA silencing of estrogen receptor-α expression specifically in medial preoptic area neurons abolishes maternal care in female mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Oct 2;109(40):16324-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1214094109. Epub 2012 Sep 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22988120 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive enhancement with central thalamic electrical stimulation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Nov 7;103(45):17007-12. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0604811103. Epub 2006 Oct 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 17065322 Free PMC article.
-
The Arousal-motor Hypothesis of Dopamine Function: Evidence that Dopamine Facilitates Reward Seeking in Part by Maintaining Arousal.Neuroscience. 2022 Sep 1;499:64-103. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2022.07.008. Epub 2022 Jul 16. Neuroscience. 2022. PMID: 35853563 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms underlying sexual and affiliative behaviors of mice: relation to generalized CNS arousal.Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2006 Dec;1(3):260-70. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsl032. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 18985112 Free PMC article.
-
Motivated state control in larval zebrafish: behavioral paradigms and anatomical substrates.J Neurogenet. 2016 Jun;30(2):122-32. doi: 10.1080/01677063.2016.1177048. Epub 2016 Jun 13. J Neurogenet. 2016. PMID: 27293113 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Magoun, H. W. (1958) The Waking Brain (Thomas, Springfield, IL), 2nd Ed.
-
- Lindsley, D. B. (1960) in Handbook of Physiology: Neurophysiology III, ed. Field, J. (Am. Physiol. Soc., Washington, DC), pp. 1553–1593.
-
- Steriade, M. (1996) Science 272, 225–231. - PubMed
-
- Robbins, T. & Everitt, B. (1996) in Handbook of Cognitive Neuroscience, ed. Gazzaniga, M. (MIT Press, Cambridge, MA), pp. 703–720.
-
- Press, W. H. (1988) Numerical Recipes in C: The Art of Scientific Computing (Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, U.K.).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

