Association of chromatin proteins high mobility group box (HMGB) 1 and HMGB2 with mitotic chromosomes
- PMID: 12925773
- PMCID: PMC181577
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e02-09-0581
Association of chromatin proteins high mobility group box (HMGB) 1 and HMGB2 with mitotic chromosomes
Abstract
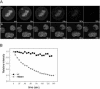
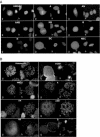
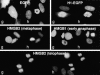
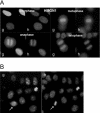
High mobility group box (HMGB) 1 and 2 are two abundant nonhistone nuclear proteins that have been found in association with chromatin. Previous studies based on immunofluorescence analysis indicated that HMGB1 dissociates from chromosomes during mitosis. In the present work, HMGB1 and 2 subcellular localization was reinvestigated in living cells by using enhanced green fluorescent protein- and Discosome sp. red fluorescent protein-tagged proteins. Contrary to previous reports, HMGB1 and 2 were shown to be present under two forms in mitotic cells, i.e., free and associated with the condensed chromatin, which rapidly exchange. A detailed analysis of HMGB2 interaction with mitotic chromosomes indicated that two sites encompassing HMG-box A and B are responsible for binding. Importantly, this interaction was rapidly inactivated when cells were permeabilized or exposed to chemical fixatives that are widely used in immunodetection techniques. A comparable behavior was also observed for two proteins of the HMG-nucleosome binding (HMGN) group, namely, HMGN1 and HMGN2.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Arabidopsis chromatin-associated HMGA and HMGB use different nuclear targeting signals and display highly dynamic localization within the nucleus.Plant Cell. 2006 Nov;18(11):2904-18. doi: 10.1105/tpc.106.047274. Epub 2006 Nov 17. Plant Cell. 2006. PMID: 17114349 Free PMC article.
-
High mobility group B2 is secreted by myeloid cells and has mitogenic and chemoattractant activities similar to high mobility group B1.Autoimmunity. 2009 May;42(4):308-10. doi: 10.1080/08916930902831845. Autoimmunity. 2009. PMID: 19811285
-
HMGB proteins and arthritis.Hum Cell. 2018 Jan;31(1):1-9. doi: 10.1007/s13577-017-0182-x. Epub 2017 Sep 15. Hum Cell. 2018. PMID: 28916968 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphorylation of maize and Arabidopsis HMGB proteins by protein kinase CK2alpha.Biochemistry. 2003 Apr 1;42(12):3503-8. doi: 10.1021/bi027350d. Biochemistry. 2003. PMID: 12653554
-
Structure and Functions of HMGB2 Protein.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 5;24(9):8334. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098334. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37176041 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Arabidopsis chromatin-associated HMGA and HMGB use different nuclear targeting signals and display highly dynamic localization within the nucleus.Plant Cell. 2006 Nov;18(11):2904-18. doi: 10.1105/tpc.106.047274. Epub 2006 Nov 17. Plant Cell. 2006. PMID: 17114349 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factor activity and nucleosome organization in mitosis.Genome Res. 2019 Feb;29(2):250-260. doi: 10.1101/gr.243048.118. Epub 2019 Jan 17. Genome Res. 2019. PMID: 30655337 Free PMC article.
-
Mitotic H3K9ac is controlled by phase-specific activity of HDAC2, HDAC3, and SIRT1.Life Sci Alliance. 2022 Aug 18;5(10):e202201433. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202201433. Print 2022 Oct. Life Sci Alliance. 2022. PMID: 35981887 Free PMC article.
-
The combination of a nuclear HMGB1-positive and HMGB2-negative expression is potentially associated with a shortened survival in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Tumour Biol. 2014 Oct;35(10):10555-69. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2328-8. Epub 2014 Jul 26. Tumour Biol. 2014. PMID: 25060178
-
Histone H1 Differentially Inhibits DNA Bending by Reduced and Oxidized HMGB1 Protein.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 25;10(9):e0138774. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138774. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26406975 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aidinis, V., Bonaldi, T., Beltrame, M., Santagata, S., Bianchi, M.E., and Spanopoulou, E. (1999). The RAG1 homeodomain recruits HMG1 and HMG2 to facilitate recombination signal sequence binding and to enhance the intrinsic DNA-bending activity of RAG1-RAG2. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19, 6532–6542. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bianchi, M.E. (1995). The HMG-box domain. In: DNA-Protein: Structural Interactions, ed. D. Lilley, Oxford: Oxford University Press, 177–200.
-
- Boonyaratanakornkit, V., Melvin, V., Prendergast, P., Altmann, M., Ronfani, L., Bianchi, M.E., Taraseviciene, L., Nordeen, S.K., Allegretto, E.A., and Edwards, D.P. (1998). High-mobility group chromatin proteins 1 and 2 functionally interact with steroid hormone receptors to enhance their DNA binding in vitro and transcriptional activity in mammalian cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 18, 4471–4487. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

