Irod/Ian5: an inhibitor of gamma-radiation- and okadaic acid-induced apoptosis
- PMID: 12925764
- PMCID: PMC181568
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e02-10-0700
Irod/Ian5: an inhibitor of gamma-radiation- and okadaic acid-induced apoptosis
Abstract
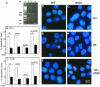
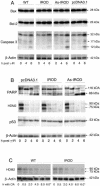
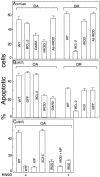
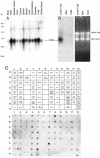
Protein phosphatase-directed toxins such as okadaic acid (OA) are general apoptosis inducers. We show that a protein (inhibitor of radiation- and OA-induced apoptosis, Irod/Ian5), belonging to the family of immune-associated nucleotide binding proteins, protected Jurkat T-cells against OA- and gamma-radiation-induced apoptosis. Unlike previously described antiapoptotic proteins Irod/Ian5 did not protect against anti-Fas, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, staurosporine, UV-light, or a number of chemotherapeutic drugs. Irod antagonized a calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II-dependent step upstream of activation of caspase 3. Irod has predicted GTP-binding, coiled-coil, and membrane binding domains. Irod localized to the centrosomal/Golgi/endoplasmic reticulum compartment. Deletion of either the C-terminal membrane binding domain or the N-terminal GTP-binding domain did not affect the antiapoptotic function of Irod, nor the centrosomal localization. The middle part of Irod, containing the coiled-coil domain, was therefore responsible for centrosomal anchoring and resistance toward death. Being widely expressed and able to protect also nonimmune cells, the function of Irod may not be limited to the immune system. The function and localization of Irod indicate that the centrosome and calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II may have important roles in apoptosis signaling.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Establishment of okadaic acid resistant cell clones using a cDNA expression library.Cell Death Differ. 2001 Jul;8(7):754-66. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4400873. Cell Death Differ. 2001. PMID: 11464220
-
Impaired autophagy and APP processing in Alzheimer's disease: The potential role of Beclin 1 interactome.Prog Neurobiol. 2013 Jul-Aug;106-107:33-54. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.06.002. Epub 2013 Jul 1. Prog Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23827971 Review.
-
IL-13 suppresses TNF-induced activation of nuclear factor-kappa B, activation protein-1, and apoptosis.J Immunol. 1998 Sep 15;161(6):2863-72. J Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9743347
-
Ceramide accumulation precedes caspase-dependent apoptosis in CHP-100 neuroepithelioma cells exposed to the protein phosphatase inhibitor okadaic acid.Cell Death Differ. 1999 Jul;6(7):618-23. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4400533. Cell Death Differ. 1999. PMID: 10453072
-
Apoptosis induced by protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) inhibition in T leukemia cells is negatively regulated by PP2A-associated p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase.Cell Signal. 2007 Jan;19(1):139-51. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2006.05.030. Epub 2006 Jun 7. Cell Signal. 2007. PMID: 16844342
Cited by
-
The apoptosis-inducing activity towards leukemia and lymphoma cells in a cyanobacterial culture collection is not associated with mouse bioassay toxicity.J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011 Apr;38(4):489-501. doi: 10.1007/s10295-010-0791-9. Epub 2010 Aug 6. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 20689978 Free PMC article.
-
New autoimmune genes and the pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes.Curr Diab Rep. 2004 Apr;4(2):135-42. doi: 10.1007/s11892-004-0069-6. Curr Diab Rep. 2004. PMID: 15035974
-
Integrated weighted gene coexpression network analysis identifies Frizzled 2 (FZD2) as a key gene in invasive malignant pleomorphic adenoma.J Transl Med. 2022 Jan 5;20(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s12967-021-03204-7. J Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 34986855 Free PMC article.
-
Cell Death Inducing Microbial Protein Phosphatase Inhibitors--Mechanisms of Action.Mar Drugs. 2015 Oct 22;13(10):6505-20. doi: 10.3390/md13106505. Mar Drugs. 2015. PMID: 26506362 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alternative Polyadenylation in Human Diseases.Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2017 Dec;32(4):413-421. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2017.32.4.413. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2017. PMID: 29271615 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Benitez-Bribiesca, L., and Sanchez-Suarez, P. (1999). Oxidative damage, bleomycin, and gamma radiation induce different types of DNA strand breaks in normal lymphocytes and thymocytes. A comet assay study. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 887, 133–149. - PubMed
-
- Beham, A., Marin, M.C., Fernandez, A., Herrmann, J., Brisbay, S., Tari, A.M., Lopez-Berestein, G., Lozano, G., Sarkiss, M., and McDonnell, T.J. (1997). Bcl-2 inhibits p53 nuclear import following DNA damage. Oncogene 15, 2767–2772. - PubMed
-
- Boe, R., Gjertsen, B.T., Vintermyr, O.K., Houge, G., Lanotte, M., and Doskeland, S.O. (1991). The protein phosphatase inhibitor okadaic acid induces morphological changes typical of apoptosis in mammalian cells. Exp. Cell Res. 195, 237–246. - PubMed
-
- Boesen-de Cock, J.G., Tepper, A.D., de Vries, E., van Blitterswijk, W.J., and Borst, J. (1999). Common regulation of apoptosis signaling induced by CD95 and the DNA-damaging stimuli etoposide and gamma-radiation downstream from caspase-8 activation. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 14255–14261. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

