App gene dosage modulates endosomal abnormalities of Alzheimer's disease in a segmental trisomy 16 mouse model of down syndrome
- PMID: 12890772
- PMCID: PMC6740714
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-17-06788.2003
App gene dosage modulates endosomal abnormalities of Alzheimer's disease in a segmental trisomy 16 mouse model of down syndrome
Abstract
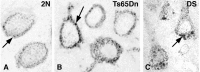
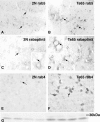
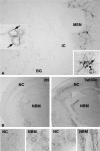
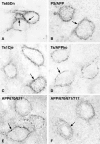
Altered neuronal endocytosis is the earliest known pathology in sporadic Alzheimer's disease (AD) and Down syndrome (DS) brain and has been linked to increased Abeta production. Here, we show that a genetic model of DS (trisomy 21), the segmental trisomy 16 mouse Ts65Dn, develops enlarged neuronal early endosomes, increased immunoreactivity for markers of endosome fusion (rab5, early endosomal antigen 1, and rabaptin5), and endosome recycling (rab4) similar to those in AD and DS individuals. These abnormalities are most prominent in neurons of the basal forebrain, which later develop aging-related atrophy and degenerative changes, as in AD and DS. We also show that App, one of the triplicated genes in Ts65Dn mice and human DS, is critical to the development of these endocytic abnormalities. Selectively deleting one copy of App or a small portion of the chromosome 16 segment containing App from Ts65Dn mice eliminated the endosomal phenotype. Overexpressing App at high levels in mice did not alter early endosomes, implying that one or more additional genes on the triplicated segment of chromosome 16 are also required for the Ts65Dn endosomal phenotype. These results identify an essential role for App gene triplication in causing AD-related endosomal abnormalities and further establish the pathogenic significance of endosomal dysfunction in AD.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endocytic pathway abnormalities precede amyloid beta deposition in sporadic Alzheimer's disease and Down syndrome: differential effects of APOE genotype and presenilin mutations.Am J Pathol. 2000 Jul;157(1):277-86. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)64538-5. Am J Pathol. 2000. PMID: 10880397 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting increased levels of APP in Down syndrome: Posiphen-mediated reductions in APP and its products reverse endosomal phenotypes in the Ts65Dn mouse model.Alzheimers Dement. 2021 Feb;17(2):271-292. doi: 10.1002/alz.12185. Epub 2020 Sep 25. Alzheimers Dement. 2021. PMID: 32975365 Free PMC article.
-
Endosomal abnormalities related to amyloid precursor protein in cholesterol treated cerebral cortex neuronal cells derived from trisomy 16 mice, an animal model of Down syndrome.Neurosci Lett. 2007 Aug 16;423(2):172-7. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2007.06.054. Epub 2007 Aug 3. Neurosci Lett. 2007. PMID: 17706358
-
Dysfunction of autophagy and endosomal-lysosomal pathways: Roles in pathogenesis of Down syndrome and Alzheimer's Disease.Free Radic Biol Med. 2018 Jan;114:40-51. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.10.001. Epub 2017 Oct 6. Free Radic Biol Med. 2018. PMID: 28988799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amyloid precursor protein and endosomal-lysosomal dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease: inseparable partners in a multifactorial disease.FASEB J. 2017 Jul;31(7):2729-2743. doi: 10.1096/fj.201700359. FASEB J. 2017. PMID: 28663518 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Altered voltage dependent calcium currents in a neuronal cell line derived from the cerebral cortex of a trisomy 16 fetal mouse, an animal model of Down syndrome.Neurotox Res. 2012 Jul;22(1):59-68. doi: 10.1007/s12640-011-9304-5. Epub 2011 Dec 28. Neurotox Res. 2012. PMID: 22203612
-
Amyloid-β-independent regulators of tau pathology in Alzheimer disease.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2020 Jan;21(1):21-35. doi: 10.1038/s41583-019-0240-3. Epub 2019 Nov 28. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 31780819 Review.
-
Alzheimer disease models and human neuropathology: similarities and differences.Acta Neuropathol. 2008 Jan;115(1):5-38. doi: 10.1007/s00401-007-0312-8. Epub 2007 Nov 16. Acta Neuropathol. 2008. PMID: 18038275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alpha- and beta-secretase activity as a function of age and beta-amyloid in Down syndrome and normal brain.Neurobiol Aging. 2007 Oct;28(10):1493-506. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2006.06.023. Epub 2006 Aug 9. Neurobiol Aging. 2007. PMID: 16904243 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of three Drosophila homologs of human chromosome 21 genes alters synaptic function: implications for Down syndrome.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Oct 6;106(40):17117-22. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0904397106. Epub 2009 Sep 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19805187 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allore R, O'Hanlon D, Price R, Neilson K, Willard HF, Cox DR, Marks A, Dunn RJ ( 1988) Gene encoding the beta subunit of S100 protein is on chromosome 21: implications for Down syndrome. Science 239: 1311-1313. - PubMed
-
- Bucci C, Parton RG, Mather IH, Stunnenberg H, Simons K, Hoflack B, Zerial M ( 1992) The small GTPase rab5 functions as a regulatory factor in the early endocytic pathway. Cell 70: 715-728. - PubMed
-
- Busciglio J, Yankner BA ( 1995) Apoptosis and increased generation of reactive oxygen species in Down's syndrome neurons in vitro Nature 378: 776-779. - PubMed
-
- Cataldo AM, Peterhoff CM, Troncoso JC, Gomez-Isla T, Hyman BT, Nixon RA ( 2000a) Endocytic pathway abnormalities precede amyloid beta deposition in sporadic Alzheimer's disease and Down syndrome: differential effects of APOE genotype and presenilin mutations. Am J Pathol 157: 277-286. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

