Regulation of phospholipase D1 subcellular cycling through coordination of multiple membrane association motifs
- PMID: 12876278
- PMCID: PMC2172799
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200302033
Regulation of phospholipase D1 subcellular cycling through coordination of multiple membrane association motifs
Abstract
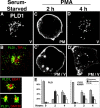
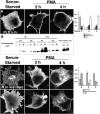
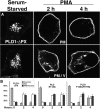
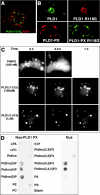
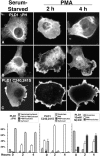
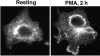
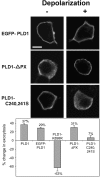
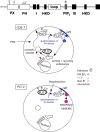
The signaling enzyme phospholipase D1 (PLD1) facilitates membrane vesicle trafficking. Here, we explore how PLD1 subcellular localization is regulated via Phox homology (PX) and pleckstrin homology (PH) domains and a PI4,5P2-binding site critical for its activation. PLD1 localized to perinuclear endosomes and Golgi in COS-7 cells, but on cellular stimulation, translocated to the plasma membrane in an activity-facilitated manner and then returned to the endosomes. The PI4,5P2-interacting site sufficed to mediate outward translocation and association with the plasma membrane. However, in the absence of PX and PH domains, PLD1 was unable to return efficiently to the endosomes. The PX and PH domains appear to facilitate internalization at different steps. The PH domain drives PLD1 entry into lipid rafts, which we show to be a step critical for internalization. In contrast, the PX domain appears to mediate binding to PI5P, a lipid newly recognized to accumulate in endocytosing vesicles. Finally, we show that the PH domain-dependent translocation step, but not the PX domain, is required for PLD1 to function in regulated exocytosis in PC12 cells. We propose that PLD1 localization and function involves regulated and continual cycling through a succession of subcellular sites, mediated by successive combinations of membrane association interactions.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mechanism of membrane binding of the phospholipase D1 PX domain.J Biol Chem. 2004 Dec 24;279(52):54918-26. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M407798200. Epub 2004 Oct 8. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15475361
-
Phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate specifically interacts with the phox homology domain of phospholipase D1 and stimulates its activity.J Cell Sci. 2005 Oct 1;118(Pt 19):4405-13. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02564. J Cell Sci. 2005. PMID: 16179605
-
Hierarchy of membrane-targeting signals of phospholipase D1 involving lipid modification of a pleckstrin homology domain.J Biol Chem. 2002 Aug 9;277(32):29152-61. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112169200. Epub 2002 May 20. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12021265
-
Regulation of phospholipase D activity, membrane targeting and intracellular trafficking by phosphoinositides.Biochem Soc Symp. 2007;(74):247-57. doi: 10.1042/BSS0740247. Biochem Soc Symp. 2007. PMID: 17233594 Review.
-
HS1BP3 inhibits autophagy by regulation of PLD1.Autophagy. 2017 May 4;13(5):985-986. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2017.1291483. Epub 2017 Feb 25. Autophagy. 2017. PMID: 28318354 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Phospholipase D in the Golgi apparatus.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 Sep;1791(9):876-80. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2009.04.003. Epub 2009 Apr 17. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. PMID: 19376267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RalA and PLD1 promote lipid droplet growth in response to nutrient withdrawal.Cell Rep. 2021 Jul 27;36(4):109451. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109451. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 34320341 Free PMC article.
-
Phospholipase C and D regulation of Src, calcium release and membrane fusion during Xenopus laevis development.Dev Biol. 2015 May 15;401(2):188-205. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2015.02.020. Epub 2015 Mar 5. Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 25748412 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Click chemistry and optogenetic approaches to visualize and manipulate phosphatidic acid signaling.J Biol Chem. 2022 Apr;298(4):101810. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101810. Epub 2022 Mar 8. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35276134 Free PMC article.
-
Phospholipase D activity regulates integrin-mediated cell spreading and migration by inducing GTP-Rac translocation to the plasma membrane.Mol Biol Cell. 2008 Jul;19(7):3111-23. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e07-04-0337. Epub 2008 May 14. Mol Biol Cell. 2008. PMID: 18480413 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brown, F.D., N. Thompson, K.M. Saqib, J.M. Clark, D. Powner, N.T. Thompson, R. Solari, and M.J. Wakelam. 1998. Phospholipase D1 localises to secretory granules and lysosomes and is plasma-membrane translocated on cellular stimulation. Curr. Biol. 8:835–838. - PubMed
-
- Choi, W.S., Y.M. Kim, C. Combs, M.A. Frohman, and M.A. Beaven. 2002. Phospholipase D1 and 2 regulate different phases of exocytosis in mast cells. J. Immunol. 168:5682–5689. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

