Involvement of sialoadhesin in entry of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus into porcine alveolar macrophages
- PMID: 12857889
- PMCID: PMC165228
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.15.8207-8215.2003
Involvement of sialoadhesin in entry of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus into porcine alveolar macrophages
Abstract
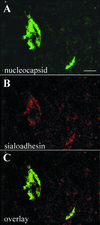
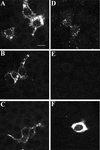
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) shows a very restricted tropism for cells of the monocyte/macrophage lineage. It enters cells via receptor-mediated endocytosis. A monoclonal antibody (MAb) that is able to block PRRSV infection of porcine alveolar macrophages (PAM) and that recognizes a 210-kDa protein (p210) was described previously (MAb41D3) (X. Duan, H. Nauwynck, H. Favoreel, and M. Pensaert, J. Virol. 72:4520-4523, 1998). In the present study, the p210 protein was purified from PAM by immunoaffinity using MAb41D3 and was subjected to internal peptide sequencing after tryptic digestion. Amino acid sequence identities ranging from 56 to 91% with mouse sialoadhesin, a macrophage-restricted receptor, were obtained with four p210 peptides. Using these peptide data, the full p210 cDNA sequence (5,193 bp) was subsequently determined. It shared 69 and 78% amino acid identity, respectively, with mouse and human sialoadhesins. Swine (PK-15) cells resistant to viral entry were transfected with the cloned p210 cDNA and inoculated with European or American PRRSV strains. Internalized virus particles were detected only in PK-15 cells expressing the recombinant sialoadhesin, demonstrating that this glycoprotein mediated uptake of both types of strains. However, nucleocapsid disintegration, like that observed in infected Marc-145 cells as a result of virus uncoating after fusion of the virus with the endocytic vesicle membrane, was not observed, suggesting a block in the fusion process. The ability of porcine sialoadhesin to mediate endocytosis was demonstrated by specific internalization of MAb41D3 into PAM. Altogether, these results show that sialoadhesin is involved in the entry process of PRRSV in PAM.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Sialoadhesin and CD163 join forces during entry of the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus.J Gen Virol. 2008 Dec;89(Pt 12):2943-2953. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.2008/005009-0. J Gen Virol. 2008. PMID: 19008379
-
The M/GP(5) glycoprotein complex of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus binds the sialoadhesin receptor in a sialic acid-dependent manner.PLoS Pathog. 2010 Jan 15;6(1):e1000730. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000730. PLoS Pathog. 2010. PMID: 20084110 Free PMC article.
-
IFN-alpha treatment enhances porcine Arterivirus infection of monocytes via upregulation of the porcine Arterivirus receptor sialoadhesin.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2007 Sep;27(9):757-66. doi: 10.1089/jir.2007.0001. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2007. PMID: 17892397
-
PRRSV receptors and their roles in virus infection.Arch Microbiol. 2015 May;197(4):503-12. doi: 10.1007/s00203-015-1088-1. Epub 2015 Feb 11. Arch Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25666932 Review.
-
PRRS virus receptors and their role for pathogenesis.Vet Microbiol. 2015 Jun 12;177(3-4):229-41. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2015.04.002. Epub 2015 Apr 13. Vet Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25912022 Review.
Cited by
-
Coinfections and their molecular consequences in the porcine respiratory tract.Vet Res. 2020 Jun 16;51(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s13567-020-00807-8. Vet Res. 2020. PMID: 32546263 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Porcine sialoadhesin: a newly identified xenogeneic innate immune receptor.Am J Transplant. 2012 Dec;12(12):3272-82. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2012.04247.x. Epub 2012 Sep 7. Am J Transplant. 2012. PMID: 22958948 Free PMC article.
-
Developing a Triple Transgenic Cell Line for High-Efficiency Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Infection.PLoS One. 2016 May 16;11(5):e0154238. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0154238. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27182980 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon-inducible mechanism of dendritic cell-mediated HIV-1 dissemination is dependent on Siglec-1/CD169.PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(4):e1003291. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003291. Epub 2013 Apr 11. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 23593001 Free PMC article.
-
Role of CD151, A tetraspanin, in porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus infection.Virol J. 2007 Jun 16;4:62. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-4-62. Virol J. 2007. PMID: 17572908 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allende, R., T. L. Lewis, Z. Lu, D. L. Rock, G. F. Kutish, A. Ali, A. R. Doster, and F. A. Osorio. 1999. North American and European porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome viruses differ in non-structural protein coding regions. J. Gen. Virol. 80:307-315. - PubMed
-
- Anderson, G. W., R. R. Rowland, G. A. Palmer, C. Even, and P. G. Plagemann. 1995. Lactate dehydrogenase-elevating virus replication persists in liver, spleen, lymph node, and testis tissues and results in accumulation of viral RNA in germinal centers, concomitant with polyclonal activation of B cells. J. Virol. 69:5177-5185. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

