Regulation of delta-opioid receptor trafficking via mu-opioid receptor stimulation: evidence from mu-opioid receptor knock-out mice
- PMID: 12832511
- PMCID: PMC6741164
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-12-04888.2003
Regulation of delta-opioid receptor trafficking via mu-opioid receptor stimulation: evidence from mu-opioid receptor knock-out mice
Abstract
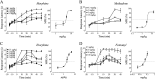
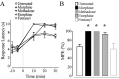
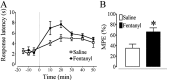
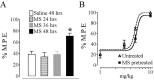
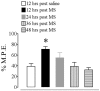
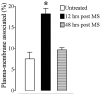
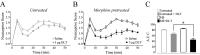
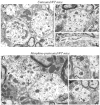
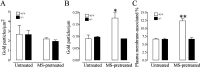
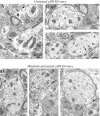
We recently demonstrated that prolonged treatment with morphine increases the antinociceptive potency of the delta-opioid receptor (deltaOR) agonist deltorphin and promotes cell surface targeting of deltaORs in neurons of the dorsal horn of the rat spinal cord (Cahill et al., 2001b). In the present study we examined whether these effects were mediated selectively via muOR. Using the same intermittent treatment regimen as for morphine, we found that methadone and etorphine, but not fentanyl, enhanced [D-Ala2]-deltorphin-mediated antinociception. However, continuous delivery of fentanyl for 48 hr resulted in augmented deltaOR-mediated antinociception when compared with saline-infused animals. Time course studies confirmed that a 48 hr treatment with morphine was necessary for the establishment of enhanced deltaOR-mediated antinociception. The observed increases in deltaOR agonist potency and deltaOR plasma membrane density were reversed fully 48 hr after discontinuation of morphine injections. Wild-type C57BL/6 mice pretreated with morphine for 48 hr similarly displayed enhanced deltaOR-mediated antinociception in a tonic pain paradigm. Accordingly, the percentage of plasma membrane-associated deltaOR in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord, as assessed by immunogold electron microscopy, increased from 6.6% in naive to 12.4% in morphine-treated mice. In contrast, morphine treatment of muOR gene knock-out (KO) mice did not produce any change in deltaOR plasma membrane density. These results demonstrate that selective activation of muOR is critical for morphine-induced targeting of deltaOR to neuronal membranes, but not for basal targeting of this receptor to the cell surface.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prolonged morphine treatment targets delta opioid receptors to neuronal plasma membranes and enhances delta-mediated antinociception.J Neurosci. 2001 Oct 1;21(19):7598-607. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-19-07598.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11567050 Free PMC article.
-
Mu-opioid receptor knockout prevents changes in delta-opioid receptor trafficking induced by chronic inflammatory pain.Pain. 2004 Jun;109(3):266-273. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2004.01.011. Pain. 2004. PMID: 15157687
-
Morphine-induced changes in delta opioid receptor trafficking are linked to somatosensory processing in the rat spinal cord.J Neurosci. 2004 Jun 16;24(24):5549-59. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2719-03.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15201327 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor expression and signaling properties in the brain, and structural ligand motifs that contribute to delta opioid receptor agonist-induced seizures.Neuropharmacology. 2023 Jul 1;232:109526. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2023.109526. Epub 2023 Mar 31. Neuropharmacology. 2023. PMID: 37004753 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances on the δ opioid receptor: from trafficking to function.Br J Pharmacol. 2015 Jan;172(2):403-19. doi: 10.1111/bph.12706. Epub 2014 Jul 1. Br J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 24665909 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The role of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 in neuropathic pain.Pain. 2020 Dec;161(12):2674-2689. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000002027. Pain. 2020. PMID: 32773603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Essential role of mu opioid receptor in the regulation of delta opioid receptor-mediated antihyperalgesia.Neuroscience. 2007 Dec 19;150(4):807-17. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.09.060. Epub 2007 Oct 5. Neuroscience. 2007. PMID: 17997230 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing analgesia and mu-opioid receptor internalization produced by intrathecal enkephalin: requirement for peptidase inhibition.Neuropharmacology. 2007 Oct;53(5):664-76. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2007.07.010. Epub 2007 Aug 2. Neuropharmacology. 2007. PMID: 17845806 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo opioid receptor heteromerization: where do we stand?Br J Pharmacol. 2015 Jan;172(2):420-34. doi: 10.1111/bph.12702. Epub 2014 Jul 1. Br J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 24666391 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Delta-Opioid Receptor; a Target for the Treatment of Pain.Front Mol Neurosci. 2020 May 5;13:52. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2020.00052. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32431594 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abdelhamid EE, Takemori AE ( 1991) Characteristics of μ and δ opioid binding sites in striatal slices of morphine-tolerant and -dependent mice. Eur J Pharmacol 198: 157–163. - PubMed
-
- Abdelhamid EE, Sultana M, Portoghese PS, Takemori AE ( 1991) Selective blockage of δ-opioid receptors prevents the development of morphine tolerance and dependence in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 258: 299–303. - PubMed
-
- Ango F, Robbe D, Tu JC, Xiao B, Worley PF, Pin JP, Bockaert J, Fagni L ( 2002) Homer-dependent cell surface expression of metabotropic glutamate receptor type 5 in neurons. Mol Cell Neurosci 20: 323–329. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
