Akt regulates basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor-coactivator complex formation and activity during neuronal differentiation
- PMID: 12808085
- PMCID: PMC164860
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.13.4417-4427.2003
Akt regulates basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor-coactivator complex formation and activity during neuronal differentiation
Abstract
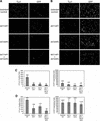
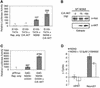
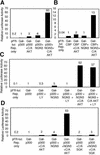
Neural basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factors regulate neurogenesis in vertebrates. Signaling by peptide growth factors also plays critical roles in regulating neuronal differentiation and survival. Many peptide growth factors activate phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) and subsequently the Akt kinases, raising the possibility that Akt may impact bHLH protein function during neurogenesis. Here we demonstrate that reducing expression of endogenous Akt1 and Akt2 by RNA interference (RNAi) reduces neuron generation in P19 cells transfected with a neural bHLH expression vector. The reduction in neuron generation from decreased Akt expression is not solely due to decreased cell survival, since addition of the caspase inhibitor z-VAD-FMK rescues cell death associated with loss of Akt function but does not restore neuron formation. This result indicates that Akt1 and Akt2 have additional functions during neuronal differentiation that are separable from neuronal survival. We show that activated Akt1 enhances complex formation between bHLH proteins and the transcriptional coactivator p300. Activated Akt1 also significantly augments the transcriptional activity of the bHLH protein neurogenin 3 in complex with the coactivators p300 or CBP. In addition, inhibition of endogenous Akt activity by the PI3K/Akt inhibitor LY294002 abolishes transcriptional cooperativity between the bHLH proteins and p300. We propose that Akt regulates the assembly and activity of bHLH-coactivator complexes to promote neuronal differentiation.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Protein kinase B/Akt regulates coxsackievirus B3 replication through a mechanism which is not caspase dependent.J Virol. 2004 Apr;78(8):4289-98. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.8.4289-4298.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15047842 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Akt/protein kinase B in the activity of transcriptional coactivator p300.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2004 Jul;61(13):1675-83. doi: 10.1007/s00018-004-4103-9. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2004. PMID: 15224190 Free PMC article.
-
Akt stimulates the transactivation potential of the RelA/p65 Subunit of NF-kappa B through utilization of the Ikappa B kinase and activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase p38.J Biol Chem. 2001 Jun 1;276(22):18934-40. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M101103200. Epub 2001 Mar 20. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11259436
-
NEUROD1: transcriptional and epigenetic regulator of human and mouse neuronal and endocrine cell lineage programs.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Jul 22;12:1435546. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1435546. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39105169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroprotection signaling of nuclear akt in neuronal cells.Exp Neurobiol. 2014 Sep;23(3):200-6. doi: 10.5607/en.2014.23.3.200. Epub 2014 Sep 18. Exp Neurobiol. 2014. PMID: 25258566 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in Neuroregeneration and Neuroprotection: A Review.Cureus. 2024 Jun 10;16(6):e62067. doi: 10.7759/cureus.62067. eCollection 2024 Jun. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38989389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurogenin 3 recruits CBP co-activator to facilitate histone H3/H4 acetylation in the target gene INSM1.FEBS Lett. 2007 Mar 6;581(5):949-54. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2007.01.087. Epub 2007 Feb 7. FEBS Lett. 2007. PMID: 17300785 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebrolysin enhances neurogenesis in the ischemic brain and improves functional outcome after stroke.J Neurosci Res. 2010 Nov 15;88(15):3275-81. doi: 10.1002/jnr.22495. J Neurosci Res. 2010. PMID: 20857512 Free PMC article.
-
Use of a multi-virus array for the study of human viral and retroviral pathogens: gene expression studies and ChIP-chip analysis.Retrovirology. 2004 May 25;1:10. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-1-10. Retrovirology. 2004. PMID: 15169557 Free PMC article.
-
New Insights Into the Intricacies of Proneural Gene Regulation in the Embryonic and Adult Cerebral Cortex.Front Mol Neurosci. 2021 Feb 15;14:642016. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2021.642016. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33658912 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anderson, M. F., M. A. Aberg, M. Nilsson, and P. S. Eriksson. 2002. Insulin-like growth factor-I and neurogenesis in the adult mammalian brain. Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res. 134:115-122. - PubMed
-
- Bailey, P., M. Downes, P. Lau, J. Harris, S. L. Chen, Y. Hamamori, V. Sartorelli, and G. E. Muscat. 1999. The nuclear receptor corepressor N-CoR regulates differentiation: N-CoR directly interacts with MyoD. Mol. Endocrinol. 13:1155-1168. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Arie, N., H. J. Bellen, D. L. Armstrong, A. E. McCall, P. R. Gordadze, Q. Guo, M. M. Matzuk, and H. Y. Zoghbi. 1997. Math1 is essential for genesis of cerebellar granule neurons. Nature 390:169-172. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
