XBX-1 encodes a dynein light intermediate chain required for retrograde intraflagellar transport and cilia assembly in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 12802075
- PMCID: PMC165097
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e02-10-0677
XBX-1 encodes a dynein light intermediate chain required for retrograde intraflagellar transport and cilia assembly in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
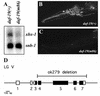
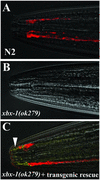
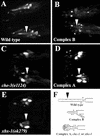
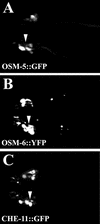
Intraflagellar transport (IFT) is a process required for flagella and cilia assembly that describes the dynein and kinesin mediated movement of particles along axonemes that consists of an A and a B complex, defects in which disrupt retrograde and anterograde transport, respectively. Herein, we describe a novel Caenorhabditis elegans gene, xbx-1, that is required for retrograde IFT and shares homology with a mammalian dynein light intermediate chain (D2LIC). xbx-1 expression in ciliated sensory neurons is regulated by the transcription factor DAF-19, as demonstrated previously for genes encoding IFT complex B proteins. XBX-1 localizes to the base of the cilia and undergoes anterograde and retrograde movement along the axoneme. Disruption of xbx-1 results in cilia defects and causes behavioral abnormalities observed in other cilia mutants. Analysis of cilia in xbx-1 mutants reveals that they are shortened and have a bulb like structure in which IFT proteins accumulate. The role of XBX-1 in IFT was further confirmed by analyzing the effect that other IFT mutations have on XBX-1 localization and movement. In contrast to other IFT proteins, retrograde XBX-1 movement was detected in complex A mutants. Our results suggest that the DLIC protein XBX-1 functions together with the CHE-3 dynein in retrograde IFT, downstream of the complex A proteins.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The retrograde IFT machinery of C. elegans cilia: two IFT dynein complexes?PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e20995. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020995. Epub 2011 Jun 10. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21695221 Free PMC article.
-
A novel dynein light intermediate chain colocalizes with the retrograde motor for intraflagellar transport at sites of axoneme assembly in chlamydomonas and Mammalian cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2003 May;14(5):2041-56. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e02-10-0682. Epub 2003 Jan 26. Mol Biol Cell. 2003. PMID: 12802074 Free PMC article.
-
Role of a class DHC1b dynein in retrograde transport of IFT motors and IFT raft particles along cilia, but not dendrites, in chemosensory neurons of living Caenorhabditis elegans.J Cell Biol. 1999 Nov 1;147(3):519-30. doi: 10.1083/jcb.147.3.519. J Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10545497 Free PMC article.
-
Intraflagellar transport: mechanisms of motor action, cooperation, and cargo delivery.FEBS J. 2017 Sep;284(18):2905-2931. doi: 10.1111/febs.14068. Epub 2017 Apr 18. FEBS J. 2017. PMID: 28342295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intraflagellar transport.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2003;19:423-43. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.19.111401.091318. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2003. PMID: 14570576 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of the dynein light intermediate chain in retrograde IFT and flagellar function in Chlamydomonas.Mol Biol Cell. 2016 Aug 1;27(15):2404-22. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E16-03-0191. Epub 2016 Jun 1. Mol Biol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27251063 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations in DYNC2LI1 disrupt cilia function and cause short rib polydactyly syndrome.Nat Commun. 2015 Jun 16;6:7092. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8092. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 26077881 Free PMC article.
-
Dynein modifiers in C. elegans: light chains suppress conditional heavy chain mutants.PLoS Genet. 2007 Aug;3(8):e128. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0030128. PLoS Genet. 2007. PMID: 17676955 Free PMC article.
-
Direct imaging of intraflagellar-transport turnarounds reveals that motors detach, diffuse, and reattach to opposite-direction trains.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Nov 9;118(45):e2115089118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2115089118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34732580 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-Organism Developmental Expression Profiling Identifies RAB-28 as a Novel Ciliary GTPase Associated with the BBSome and Intraflagellar Transport.PLoS Genet. 2016 Dec 8;12(12):e1006469. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006469. eCollection 2016 Dec. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 27930654 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson, P. (1995). Mutagenesis. Methods Cell Biol. 48, 31–58. - PubMed
-
- Cole, D.G., Diener, D.R., Himelblau, A.L., Beech, P.L., Fuster, J.C., and Rosenbaum, J.L. (1998). Chlamydomonas kinesin-II-dependent intraflagellar transport (IFT): IFT particles contain proteins required for ciliary assembly in Caenorhabditis elegans sensory neurons. J. Cell Biol. 141, 993–1008. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

