BMPs signal alternately through a SMAD or FRAP-STAT pathway to regulate fate choice in CNS stem cells
- PMID: 12796477
- PMCID: PMC2172962
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200211021
BMPs signal alternately through a SMAD or FRAP-STAT pathway to regulate fate choice in CNS stem cells
Abstract
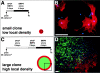
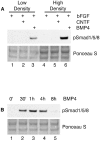
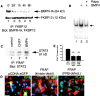
The ability of stem cells to generate distinct fates is critical for the generation of cellular diversity during development. Central nervous system (CNS) stem cells respond to bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) 4 by differentiating into a wide variety of dorsal CNS and neural crest cell types. We show that distinct mechanisms are responsible for the generation of two of these cell types, smooth muscle and glia. Smooth muscle differentiation requires BMP-mediated Smad1/5/8 activation and predominates where local cell density is low. In contrast, glial differentiation predominates at high local densities in response to BMP4 and is specifically blocked by a dominant-negative mutant Stat3. Upon BMP4 treatment, the serine-threonine kinase FKBP12/rapamycin-associated protein (FRAP), mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), associates with Stat3 and facilitates STAT activation. Inhibition of FRAP prevents STAT activation and glial differentiation. Thus, glial differentiation by BMP4 occurs by a novel pathway mediated by FRAP and STAT proteins. These results suggest that a single ligand can regulate cell fate by activating distinct cytoplasmic signals.
Figures

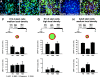
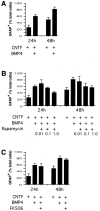

Similar articles
-
BMP signaling initiates a neural crest differentiation program in embryonic rat CNS stem cells.Exp Neurol. 2004 Aug;188(2):205-23. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2004.03.026. Exp Neurol. 2004. PMID: 15246821
-
Functional Notch signaling is required for BMP4-induced inhibition of myogenic differentiation.Development. 2003 Dec;130(24):6089-99. doi: 10.1242/dev.00834. Development. 2003. PMID: 14597575
-
Inhibition of glial maturation by bone morphogenetic protein 2 in a neural crest-derived cell line.Dev Neurosci. 2005 Jan-Feb;27(1):37-48. doi: 10.1159/000084531. Dev Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15886483
-
Neurotrophin-3 in the development of the enteric nervous system.Prog Brain Res. 2004;146:243-63. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(03)46016-0. Prog Brain Res. 2004. PMID: 14699968 Review.
-
BMP-Smad 1/5/8 signalling in the development of the nervous system.Prog Neurobiol. 2013 Oct;109:28-41. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.07.002. Epub 2013 Jul 24. Prog Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23891815 Review.
Cited by
-
Rapamycin inhibits both motility through down-regulation of p-STAT3 (S727) by disrupting the mTORC2 assembly and peritoneal dissemination in sarcomatoid cholangiocarcinoma.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2013 Feb;30(2):177-87. doi: 10.1007/s10585-012-9526-9. Epub 2012 Aug 9. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2013. PMID: 22875246
-
Specific Preferences in Lineage Choice and Phenotypic Plasticity of Glioma Stem Cells Under BMP4 and Noggin Influence.Brain Pathol. 2016 Jan;26(1):43-61. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12263. Epub 2015 May 19. Brain Pathol. 2016. PMID: 25808628 Free PMC article.
-
Bone morphogenetic protein 7 (BMP7) reverses obesity and regulates appetite through a central mTOR pathway.FASEB J. 2012 May;26(5):2187-96. doi: 10.1096/fj.11-199067. Epub 2012 Feb 13. FASEB J. 2012. PMID: 22331196 Free PMC article.
-
STAT3 regulation of glioblastoma pathogenesis.Curr Mol Med. 2009 Jun;9(5):580-90. doi: 10.2174/156652409788488739. Curr Mol Med. 2009. PMID: 19601808 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A BMP7 Variant Inhibits Tumor Angiogenesis In Vitro and In Vivo through Direct Modulation of Endothelial Cell Biology.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 28;10(4):e0125697. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125697. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25919028 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abraham, R.T., and G.J. Wiederrecht. 1996. Immunopharmacology of rapamycin. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 14:483–510. - PubMed
-
- Bjornson, C.R., R.L. Rietze, B.A. Reynolds, M.C. Magli, and A.L. Vescovi. 1999. Turning brain into blood: a hematopoietic fate adopted by adult neural stem cells in vivo. Science. 283:534–537. - PubMed
-
- Boeuf, H., K. Merienne, S. Jacquot, D. Duval, M. Zeniou, C. Hauss, B. Reinhardt, Y. Huss-Garcia, A. Dierich, D.A. Frank, et al. 2001. The ribosomal S6 kinases, cAMP-responsive element-binding, and STAT3 proteins are regulated by different leukemia inhibitory factor signaling pathways in mouse embryonic stem cells. J. Biol. Chem. 276:46204–46211. - PubMed
-
- Bonni, A., Y. Sun, M. Nadal-Vicens, A. Bhatt, D.A. Frank, I. Rozovsky, N. Stahl, G.D. Yancopoulos, and M.E. Greenberg. 1997. Regulation of gliogenesis in the central nervous system by the JAK-STAT signaling pathway. Science. 278:477–483. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

